Relation between wred and the queuing mechanism, Introduction to wred configuration, Configuration methods – H3C Technologies H3C SR8800 User Manual
Page 65: Introduction to wred parameters
56
formula: average queue size=previous average queue size×(1-2
-n
)+Current queue size ×2
-n
, where n can
be configured with the qos wred weighting-constant command.
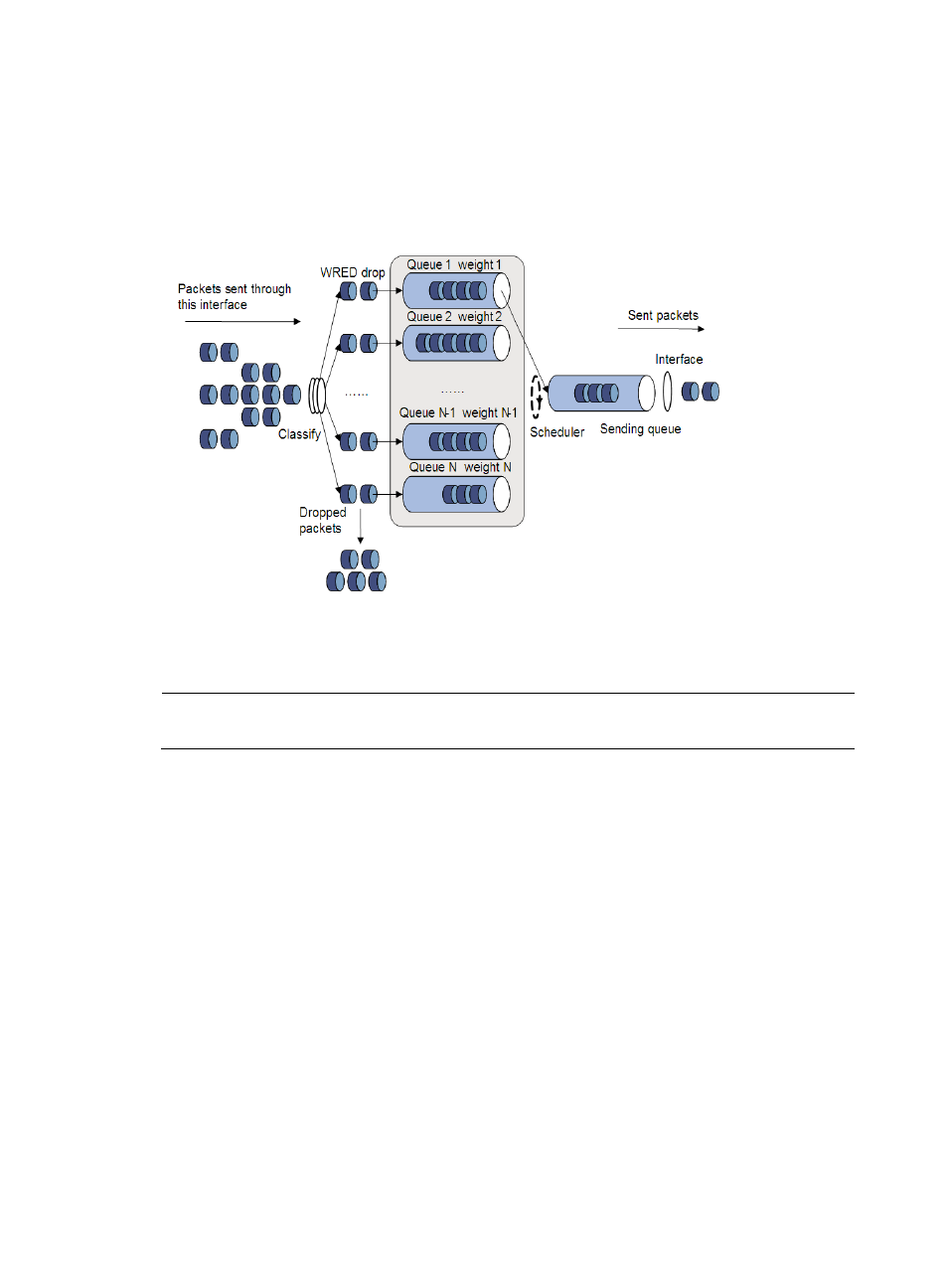
Relation between WRED and the queuing mechanism
The relation between WRED and the queuing mechanism is shown in
:
Figure 20 Relationship between WRED and queuing mechanism
Introduction to WRED configuration
NOTE:
WRED is applicable to only SPE cards.
Configuration methods
You can configure WRED by configuring a WRED table in system view and then apply the WRED table
to an interface.
Introduction to wred parameters
Determine the following parameters before configuring WRED:
•
Upper threshold and lower threshold—When the average queue size is smaller than the lower
threshold, no packet is dropped. When the average queue size is between the lower threshold and
the upper threshold, the packets are dropped at random. The longer the queue is, the higher the
drop probability is. When the average queue size exceeds the upper threshold, subsequent packets
are dropped.
•
Drop precedence—A parameter used for packet drop. The value 0 corresponds to green packets,
the value 1 corresponds to yellow packets, and the value 2 corresponds to red packets. Red packets
are dropped preferentially.
•
Exponent used for average queue size calculation—The bigger the exponent is, the more
insensitive to real-time queue size changes the average queue size is.
