Configuration considerations, Configuration procedure – H3C Technologies H3C SR8800 User Manual
Page 102
93
Table 10 Requirements for the user groups of each service
Requirements (right)
Number of groups
IP assignment
Service type (below)
VoIP service
2
10.1.1.X, 10.1.2.X
VoD service
3
20.1.1.X, 20.1.2.X, 20.1.3.X
VPN 5
30.1.1.X, 30.1.2.X, 30.1.3.X, 30.1.4.X,
30.1.5.X
Internet 5
40.1.1.X, 40.1.2.X, 40.1.3.X, 40.1.4.X,
40.1.5.X
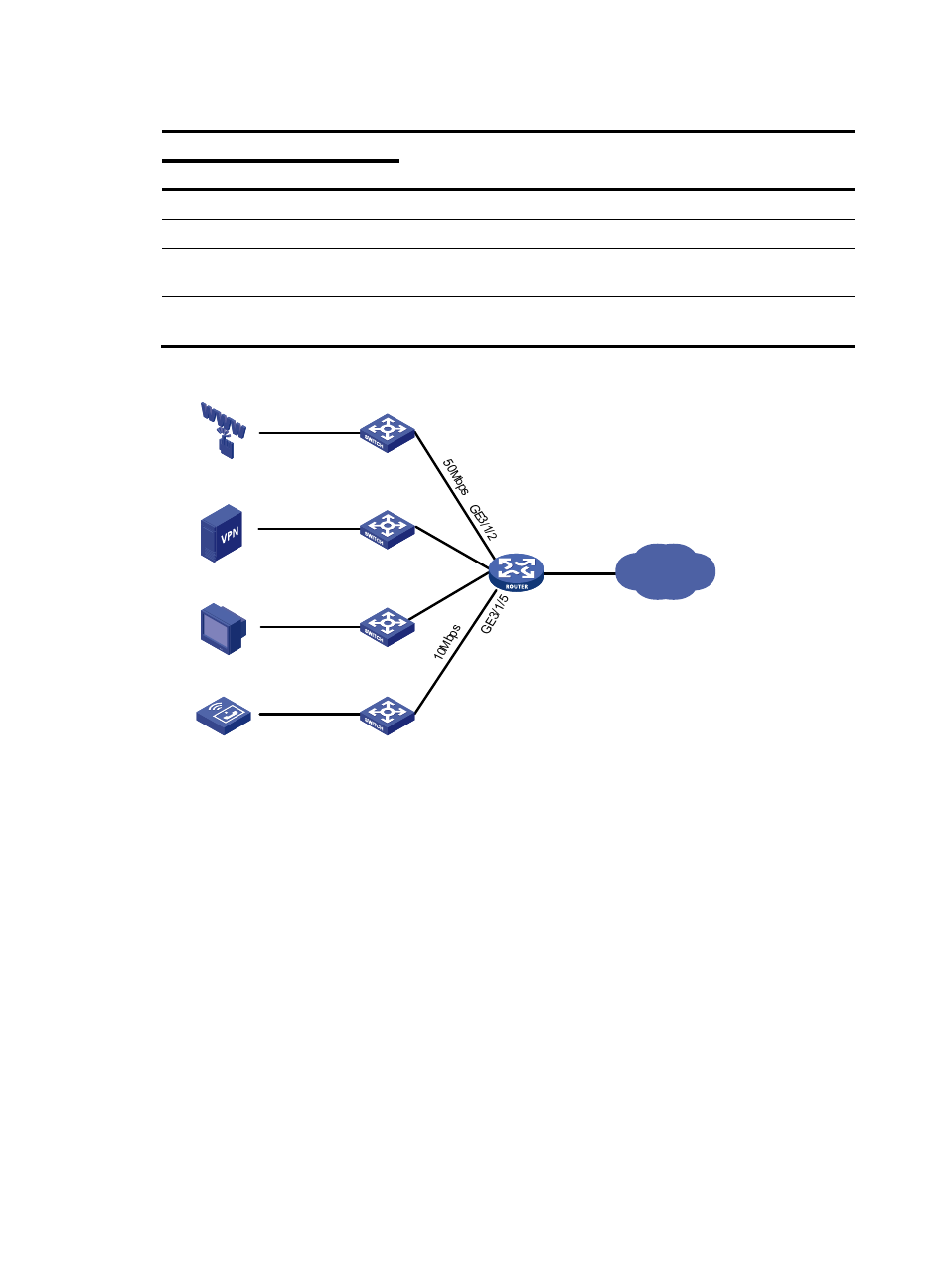
Figure 29 Network diagram
Configuration considerations
•
Map VoIP traffic with IP precedence 6 or 7 to the pre-defined forwarding class NC, VoD traffic with
IP precedence 4 or 5 to the pre-defined forwarding class EF, VPN traffic with IP precedence 2 or 3
to the pre-defined forwarding class AF, and Internet traffic with IP precedence 0 or 1 to the
pre-defined forwarding class BE.
•
Mark VoIP traffic, VoD traffic, VPN traffic, and Internet traffic with a QoS-local ID by source IP
address, and then map VoIP traffic, VoD traffic, VPN traffic, and Internet traffic each to a forwarding
group by QoS-local ID.
•
The user groups of the VoIP, VoD, VPN, and Internet services are each assigned to a distinct
forwarding group by instantiation.
Configuration procedure
1.
Map different classes of traffic to forwarding classes.
As all traffic is differentiated by IP precedence, you can use the default UP-to-forwarding class
mapping table for mapping different classes of traffic to the pre-defined forwarding classes. To this
end, you must use the qos trust auto command on the incoming ports to specify the trusted priority
type.
WAN
Internet
VPN
VoD
VoIP
Router
Switch
Switch
Switch
Switch
16Mbps
30 Mbps
qos-local-id
301 to 305
qos-local-id
201 to 205
qos- local-id
101 to 103
qos- local-id
1 to 2
20 Mbps
GE
3/1/
3
GE
3/1
/4
Mp-group 2/1/1
