Data format, Message protocol, Message format – Research Concepts RC2500 User Manual
Page 80: Message delimiters
RC2500 Antenna Controller
Appendix D
RCI RS-422 Specification
73
Research Concepts, Inc. • 5420 Martindale Road • Shawnee, Kansas 66218-9680 • USA
www.researchconcepts.com
Data Format
The data format supports the industry's standard asynchronous ASCII format with one start bit, eight data
bits (7-bit ASCII with the 8th bit sent as even parity), and one stop bit. The ASCII control character
subset 00-1F (hex) are reserved for message control. The printable ASCII characters 20-7F (hex) are
used for address, command and data characters. The standard bus data rate via direct connect (up to
1,500 ft.) is 9,600 BAUD; the data rate for devices connected to a master via modem is 1,200 BAUD,
typically.
Message Protocol
Message format and protocol over the bus is a derivative of IBM's binary synchronous communications
protocol (BISYNC). The master station sends a command over the bus to all remote stations. The
station whose address is contained in the second byte of the command message carries out the
requested commands, and then replies with a response message containing its own address and status
information relating to its present condition. A remote station only sends a response following a
command containing its unique address from the master. This prevents bus contention caused by more
than one remote device communicating over the bus at the same time.
A remote device ignores all commands that contain parity or checksum errors, protocol errors, a wrong
address, or message overrun errors. A remote device replies with a not-acknowledged (NAK) character,
15 hex, if it receives an invalid command or data.
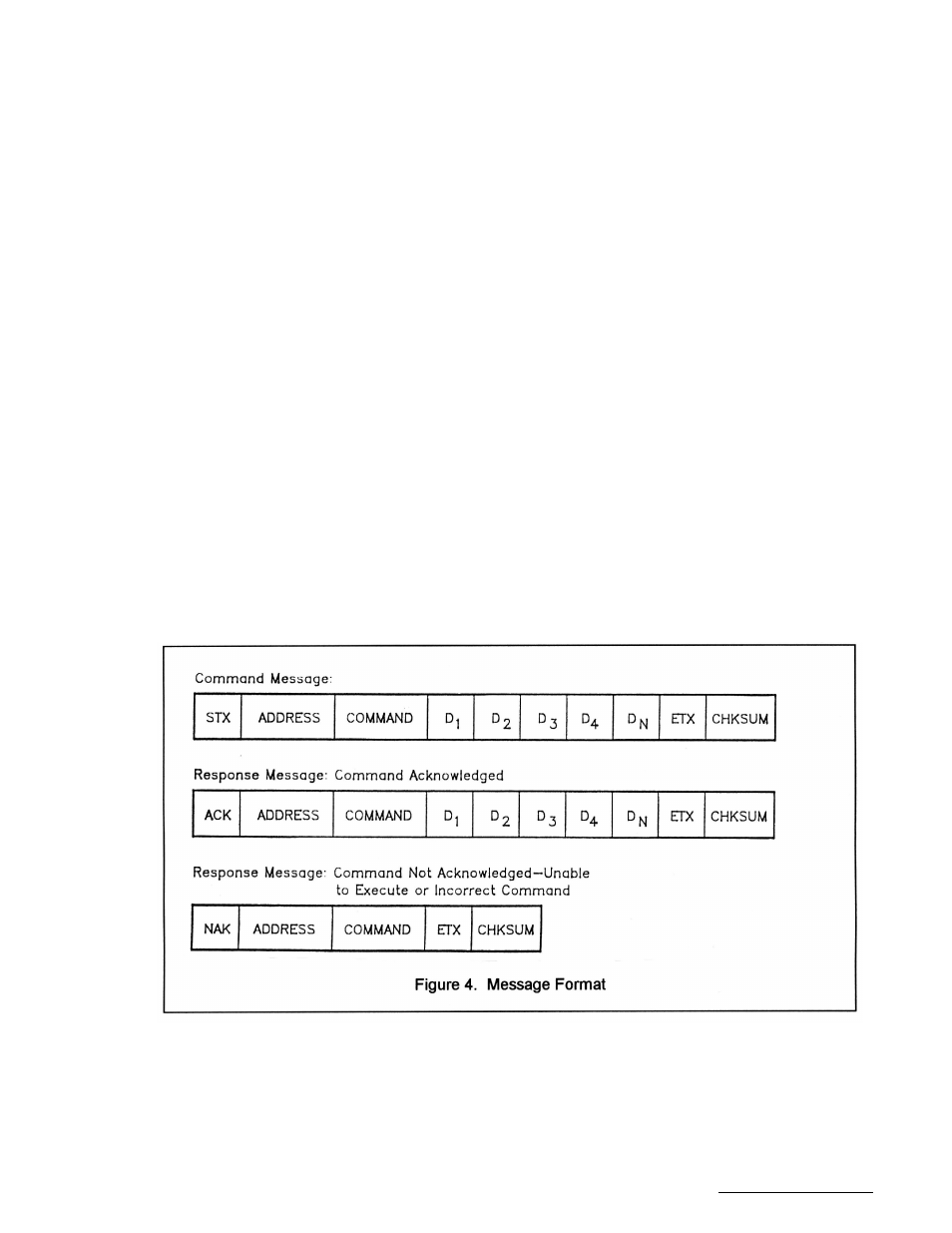
Message Format
Command messages (see Figure 4) begin with Start-of-text byte, STX, followed by a remote address, a
command byte and multiple data bytes. The End-of-text byte, ETX, is sent following the last data byte,
and the message is terminated by a checksum character. Response messages are identical to
command messages in format (but not content) with the exception of the ACK (Acknowledge) or NAK
(Not Acknowledge) character at the start of the message instead of STX. Figure 4 illustrates the format
of the command and response messages. A command or reply message may have a variable length.
Message Delimiters
A command message begins with STX (02 hex), the ASCII Start-of-text control character. A message-
acknowledged reply begins with ACK (06 hex), the ASCII Acknowledge control character, and a
message-not acknowledged reply begins with NAK (15 hex), the ASCII Not Acknowledge control
character. All messages end with the ETX (03 hex), the ASCII End-of-text control character, followed by
the checksum byte.
