3 channel mux scan limits register, 4 4-bit digital i/o registers – Measurement Computing CIO-DAS16Jr/16 User Manual
Page 17
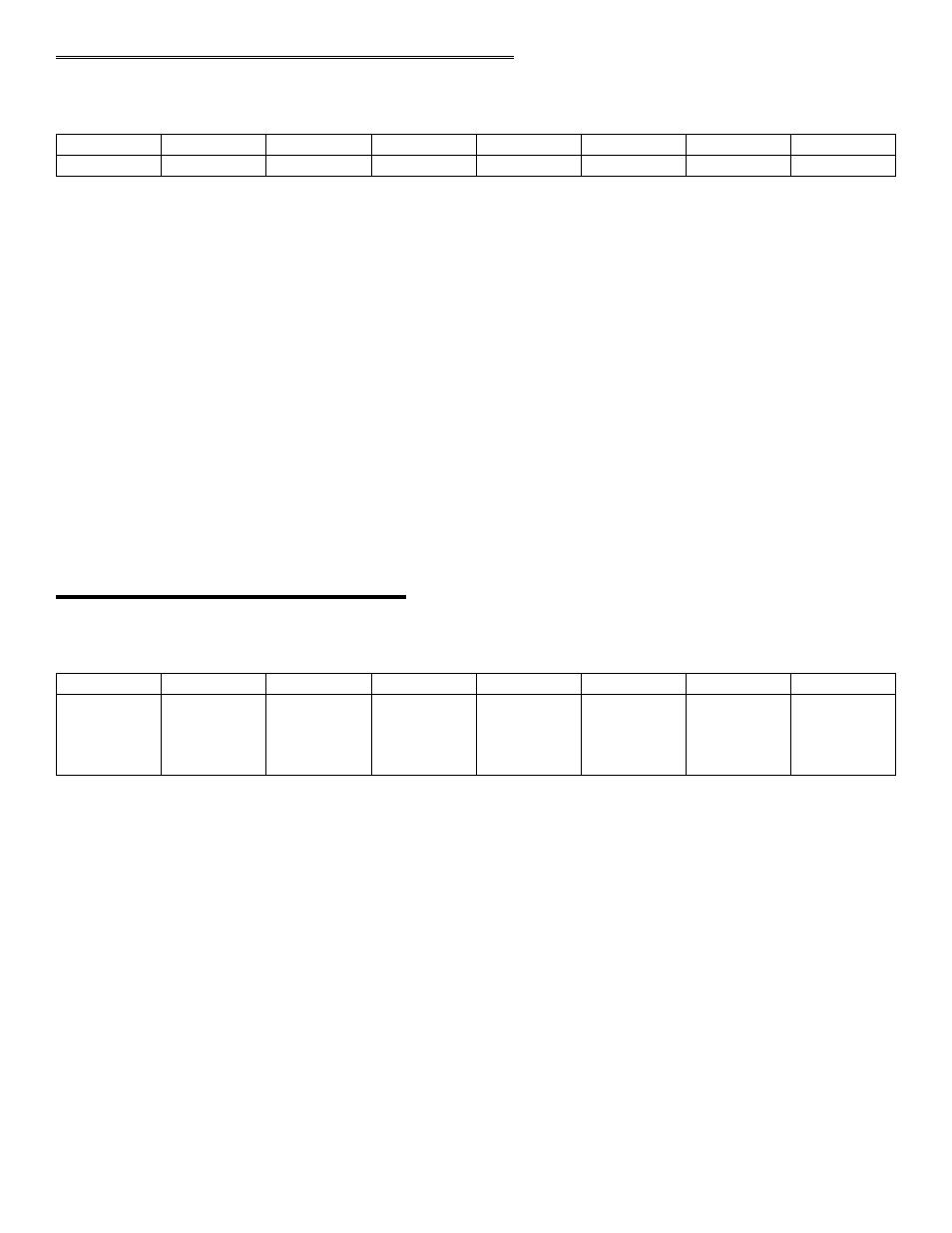
3.3 CHANNEL MUX SCAN LIMITS REGISTER
BASE ADDRESS + 2
CH L1
CH L2
CH L4
CH L8
CH H1
CH H2
CH H4
CH H8
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
A read and write register.
READ
The current channel scan limits are read as one byte. The high channel number scan limit is in the most significant 4
bits. The low channel scan limit is in the least significant 4 bits.
WRITE
The channel scan limits desired are written as one byte. The high channel number scan limit is in the most significant
4 bits. The low channel scan limit is in the least significant 4 bits.
Bits 3-0 contain the starting channel number and bits 7-4 contain the ending channel number. If you wanted to scan
channels 1, 2, 3 in that order, you could do so by placing the 3 in bits 7-4 and the 1 in bits 3-0.
NOTE
Every write to this register sets the current A/D channel MUX setting to the number in bits 3-0. See
BASE + 8.
3.4 4-BIT DIGITAL I/O REGISTERS
BASE ADDRESS + 3
DI0,
TRIG
DI1
DI2,
CTR0
GATE
DI3
0
0
0
0
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
When read...
READ
The signals present at the inputs are read as one byte, the most significant four bits of which are always zero. Note
that pins 25 (digital input 0) and 24 (digital input 2) have two functions each.
The TRIG function of digital input 0 may be used to hold of the first sample of an A/D set by holding it low (0V)
until you are ready to take samples, which are then paced by the 8254. It can also be used as the source of an external
start conversion pulse, synchronizing A/D conversions to some external event.
When written to..
WRITE
The upper four bits are ignored. The lower four bits are latched TTL outputs. Once written, the state of the inputs
cannot be read back because a read back would read the separate digital input lines (see above).
13
