4 code structure, Code structure, 4code structure – BECKHOFF ET9300 User Manual
Page 13
Application Note ET9300
11
4
Code Structure
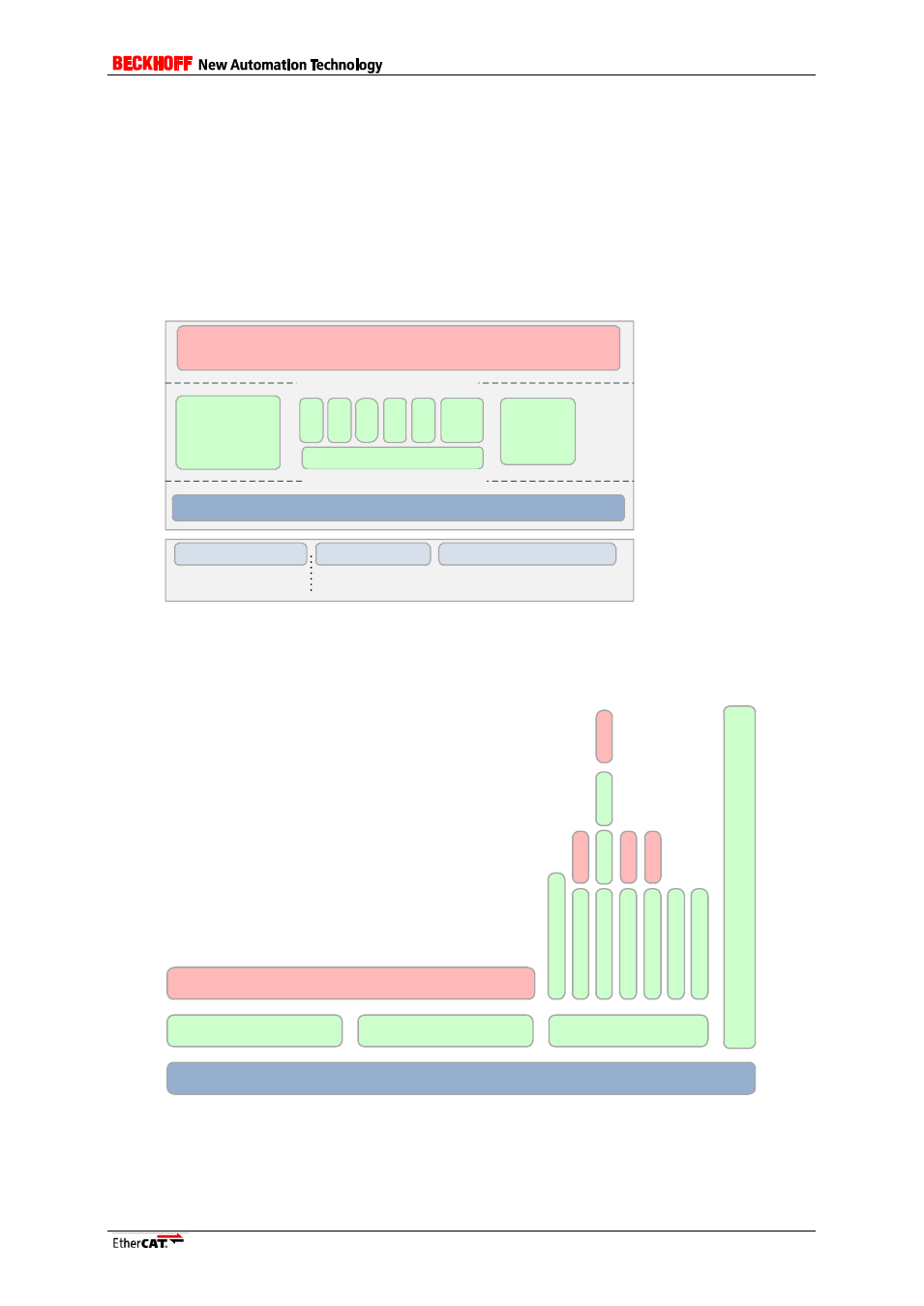
The EtherCAT slave stack as seen in Figure 1 consists of three parts:
- PDI/Hardware abstraction
- Generic EtherCAT stack
- User application
The functions and macros which shall be provided by the hardware access layer (Hardware function
set) are defined in chapter 5 Hardware Access. The behavior of the generic EtherCAT stack is
described in ETG.1000 Specification [2] . The functions which shall be provided by the application
(Application function set) are defined in chapter 6 Application.
PDI and hardware abstraction
EtherCAT
State
Machine
Mailbox
Process
data
A
o
E
C
o
E
F
o
E
S
o
E
V
o
E
E
o
E
Application
e.g. CiA402 Drive Profile
Mailbox
Process data
Register
ESC address space (DPRAM)
0x0000
0x1000
User
Application
Generic
EtherCAT stack
Hardware
access
EtherCAT Slave
Controller (extract)
Application function set
Hardware function set
Figure 1: EtherCAT Slave Stack Code
Figure 2 shows the association between the Slave Stack Code layers and the source files.
User application files (el9800appl.*,cia402appl.*,... )
PDI and hardware access functions (el9800hw.*; mcihw.*;fc1100hw.*)
Sate machine (ecatslv.*)
S
la
v
e
c
o
n
fi
g
u
ra
ti
o
n
h
e
a
d
e
r
(e
c
a
t_
d
e
f.
h
)
Mailbox handling (mailbox.*)
Process data handling (ecatappl.*)
E
m
e
rg
e
n
c
y
(
e
m
c
y
.*
)
A
o
E
(
e
c
a
ta
o
e
.*
)
C
o
E
(
e
c
a
tc
o
e
.*
)
F
o
E
(
e
c
a
tf
o
e
.*
)
S
o
E
(
e
c
a
ts
o
e
.*
)
V
o
E
s
d
o
s
e
rv
.*
o
b
jd
e
f.
*
a
o
e
a
p
p
l.
*
c
o
e
a
p
p
l.
*
fo
e
a
p
p
l.
*
E
o
E
(
e
c
a
te
o
e
.*
)
e
o
e
a
p
p
l.
*
Figure 2: File-Stack Association
The structure of the code can be adapted to the application specific requirements by using the Slave
Stack Code Tool (chapter 12).
