Not using a heat sink – Altera PowerPlay Early Power Estimator User Manual
Page 20
temperature is the estimated operating junction temperature based on your device and thermal
conditions.
You can consider the device as a heat source and the junction temperature is the temperature of the
device. While the temperature typically varies across the device, to simplify the analysis, you can assume
that the temperature of the device is constant regardless of where it is measured.
Power from the device can be dissipated through different paths. Different paths become significant
depending on the thermal properties of the system. The significance of power dissipation paths vary
depending on whether or not a heat sink is used for the device.
Not Using a Heat Sink
When you do not use a heat sink, the major paths of power dissipation are from the device to the air. You
can refer this as a junction-to-ambient thermal resistance. In this case, there are two significant junction-
to-ambient thermal resistance paths:
• From the device through the case to the air
• From the device through the board to the air
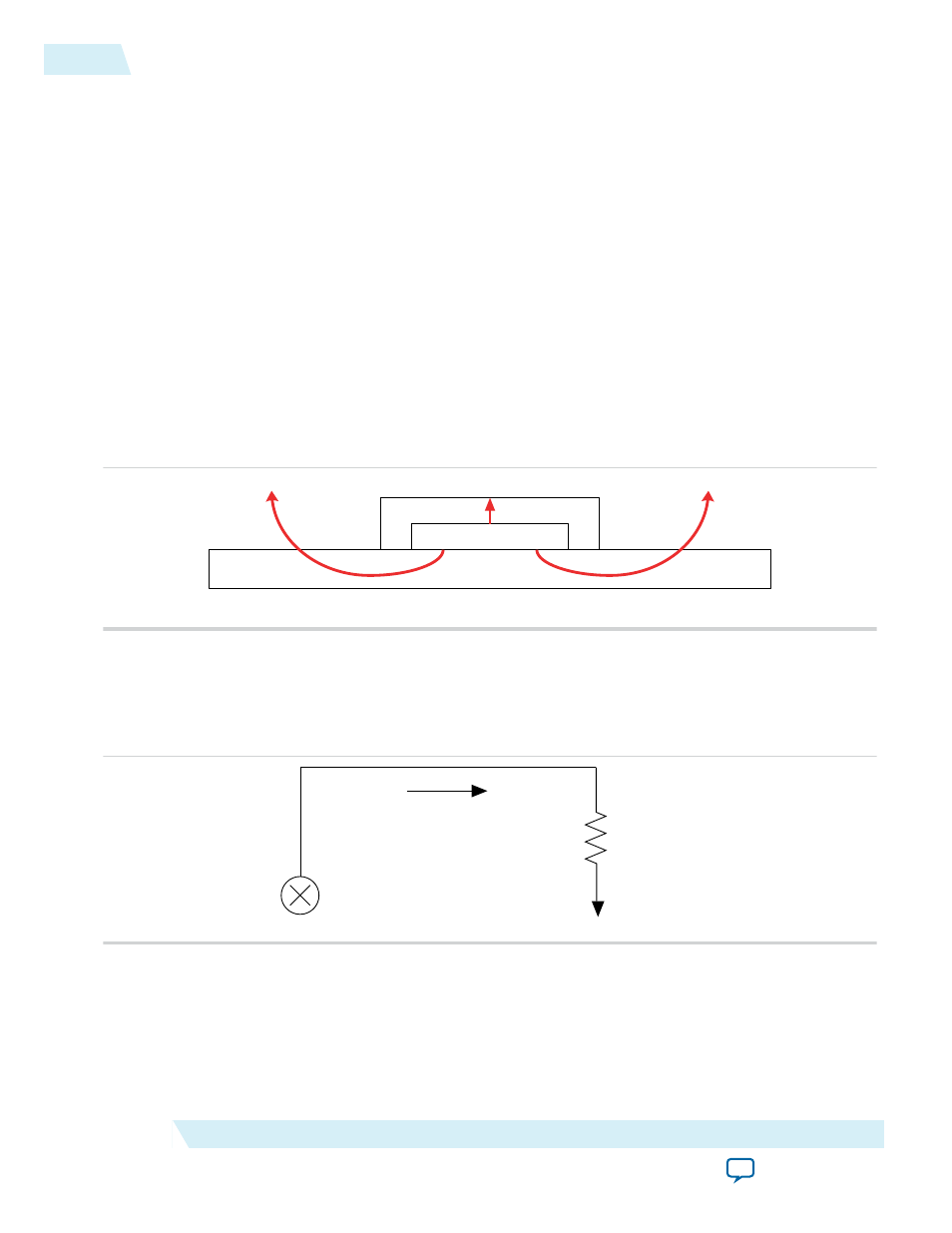
Figure 3-6: Thermal Representation without a Heat Sink
Case
Thermal Representation without Heat Sink
Board
Device
θJA
In the model used in the PowerPlay EPE spreadsheet, power is dissipated through the case and board. The
θ
JA
values are calculated for differing air flow options accounting for the paths through the case and
through the board.
Figure 3-7: Thermal Model in the PowerPlay EPE Spreadsheet without a Heat Sink
TJ
JA
TA
Power (P)
Heat
Source
θ
The ambient temperature does not change, but the junction temperature changes depending on the
thermal properties; therefore the junction temperature calculation is an iterative process.
The following equation shows the total power calculated based on the total θ
JA
value, ambient, and
junction temperatures.
3-10
Not Using a Heat Sink
UG-01070
2015.01.20
Altera Corporation
PowerPlay Early Power Estimator Worksheets
