Serial x4 flash – Achronix Speedster22i Configuration User Manual
Page 11
UG033, December 18, 2013
11
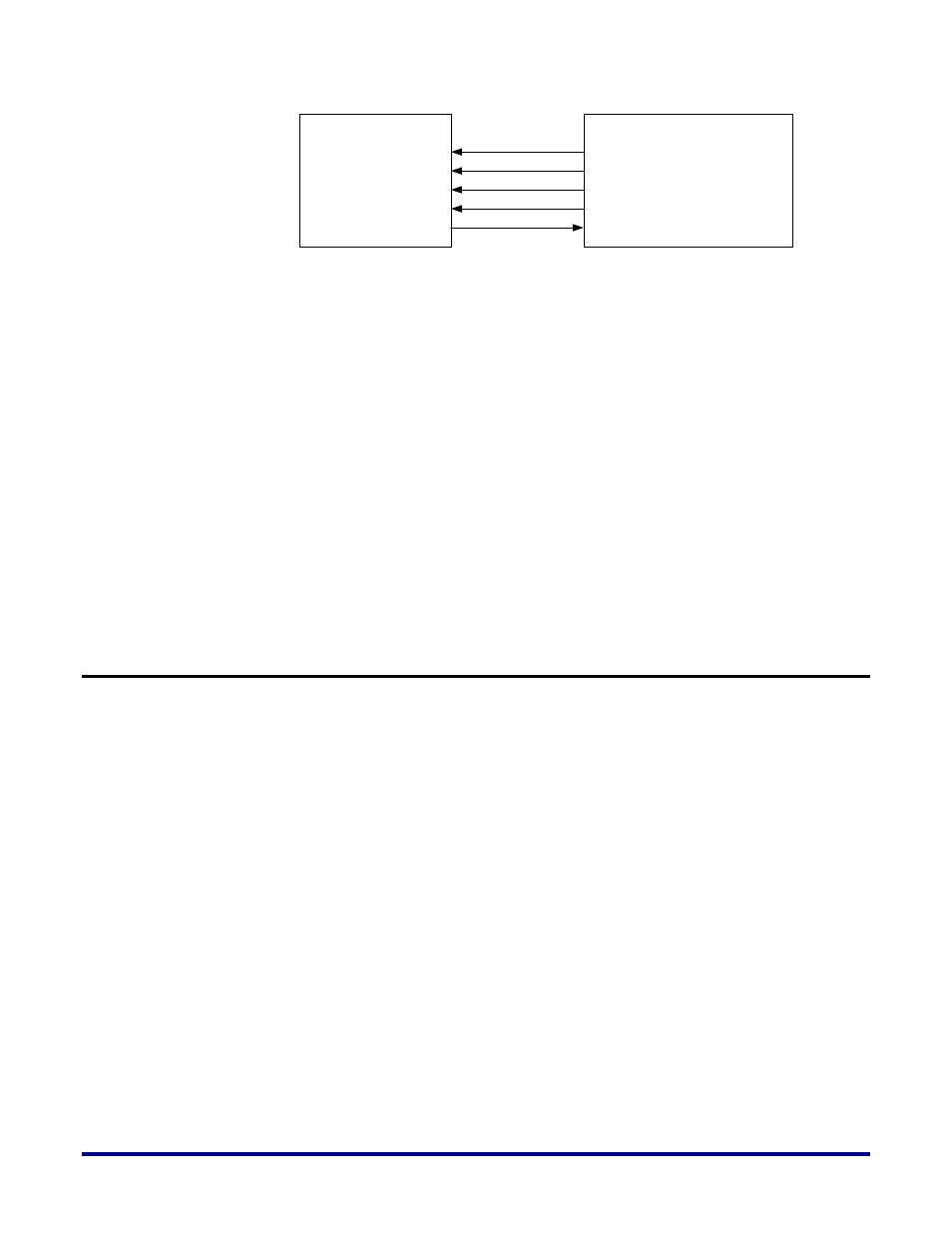
SPI Flash
Speedster22iHD FPGA
SCLK
HOLDN
DI
CSN
DO
SCK
HOLDN
SDI
CSN[0]
SDO[0]
Figure 6: Flash Connectivity to Speedster22iHD FPGA in x1 Mode
This interface contains a configuration mode fast read engine that reads the data from the
flash from address 0. The number of words read in the bitstream can be controlled by the
bitstream by programming one of the configuration registers. This block also contains a
master controller that interfaces to the JTAG unit for programming of the serial flash. The
flash programming instructions are sent via JTAG.
Configuration operation in serial flash x1 mode is very similar to CPU mode. The only
difference comes during the writing of the bitstream. SCK is used for clocking and the
bitstream is a single bit interface provided through the SDO[0] port. CSN[0] is pulled low
during the valid bitstream window and is then pulled high once the last bit is clocked in.
Transitioning from the end of the bitstream to user mode is done exactly as in CPU mode,
with SCK providing the clock to the FPGA.
Serial x4 Flash
Serial x4 Flash programming mode is essentially an enhanced and higher bandwidth
implementation of the Serial x1 Flash mode. The FPGA is again the master, and interfaces
with not 1 but 4 Flash memory modules to increase the data bandwidth from x1 to x4.
Figure 7 below provides a block diagram of how 4 Serial Flash memories can be connected to
a Speedster22iHD FPGA in Flash x4 mode.
