Understanding snmp basics, Table 1 – Dell POWEREDGE M1000E User Manual
Page 20
2
Fabric OS MIB Reference
53-1001768-01
Understanding SNMP basics
1
Understanding SNMP basics
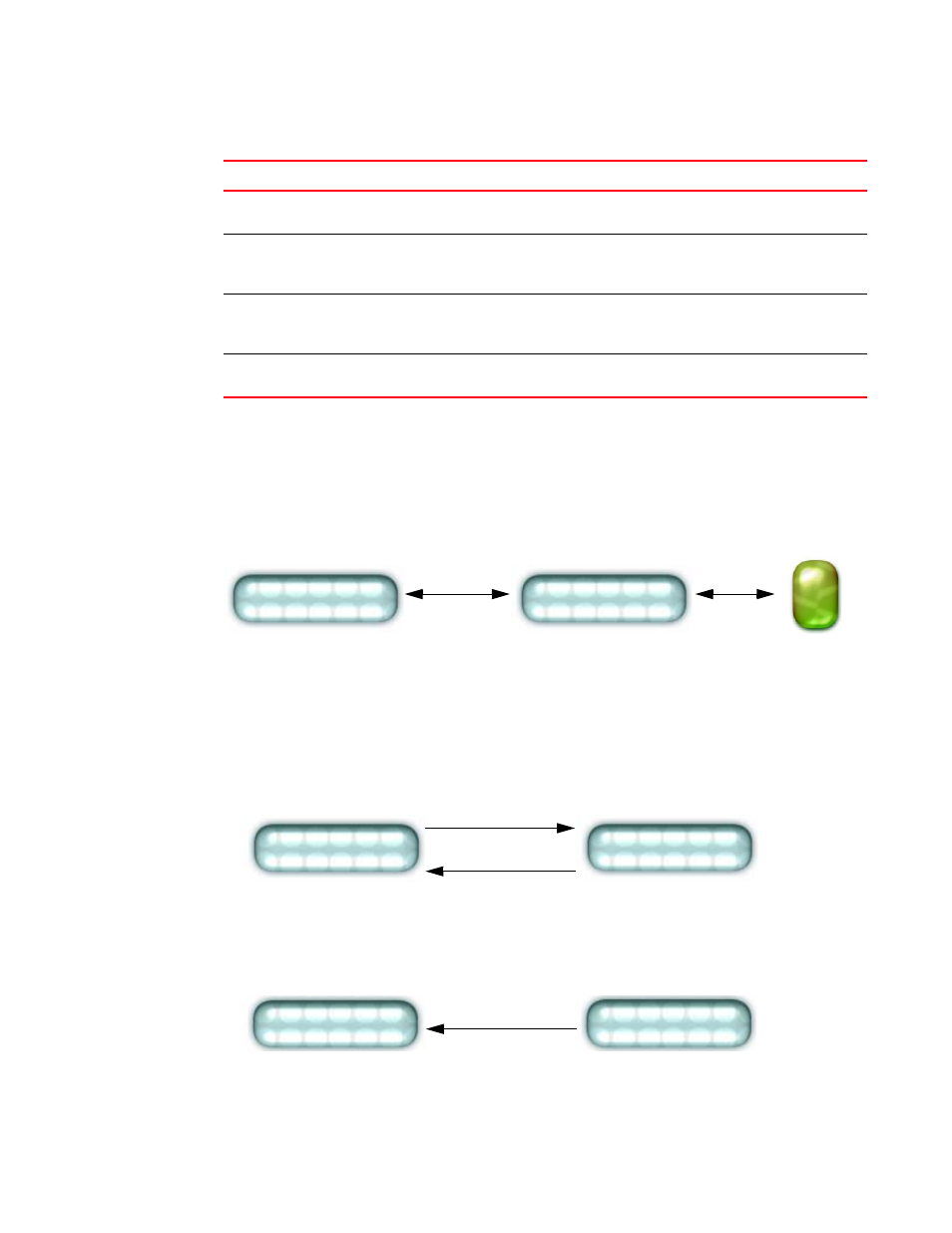
Every Brocade switch carries an agent and management information base (MIB), as shown in
. The agent accesses information about a device and makes it available to an SNMP
network management station.
FIGURE 1
SNMP structure
When active, the management station can get information or set information when it queries an
agent. SNMP commands, such as get, set, getnext, setnext, and getresponse, are sent from the
management station, and the agent replies once the value is obtained or modified (
Agents use variables to report such data as the number of bytes and packets in and out of the
device, or the number of broadcast messages sent and received. These variables are also known
as managed objects. All managed objects are contained in the MIB.
FIGURE 2
SNMP query
The management station can also receive traps, unsolicited messages from the switch agent if an
unusual event occurs (
). Refer to
on page 4 for more
information.
FIGURE 3
SNMP trap
TABLE 1
Security level options
Security level
Protocol
Query behavior
Traps
No security [0]
(noAuthnoPriv)
SNMPv1
SNMPv3
Allowed.
Allowed.
Sent.
Sent.
Authentication only [1]
(authNoPriv)
SNMPv1
SNMPv3
Allowed.
All SNMPv3 users allowed except
noAuthNoPriv users.
Sent.
Sent for all SNMPv3 users
except noAuthNoPriv users.
Authentication and
Privacy [2]
(authPriv)
SNMPv1
SNMPv3
Not allowed.
Only SNMPv3 users with authPriv
privilege are allowed.
Not Sent.
Sent only for authPriv users.
No Access [3]
SNMPv1
SNMPv3
Not allowed.
Not Sent.
Agent
Management Station
SNMP
MIB
Management Station
Agent
get, getnext, set
reply
TRAP
Management Station
Agent
