Gearbox input chains, Chain maintenance, Chain slack – Great Plains ADC2350BE Operator Manual User Manual
Page 80: Gearbox input chains chain maintenance
76
ADC2350/E and ADC2350B/BE
Great Plains Manufacturing, Inc.
167-085M
2012-08-01
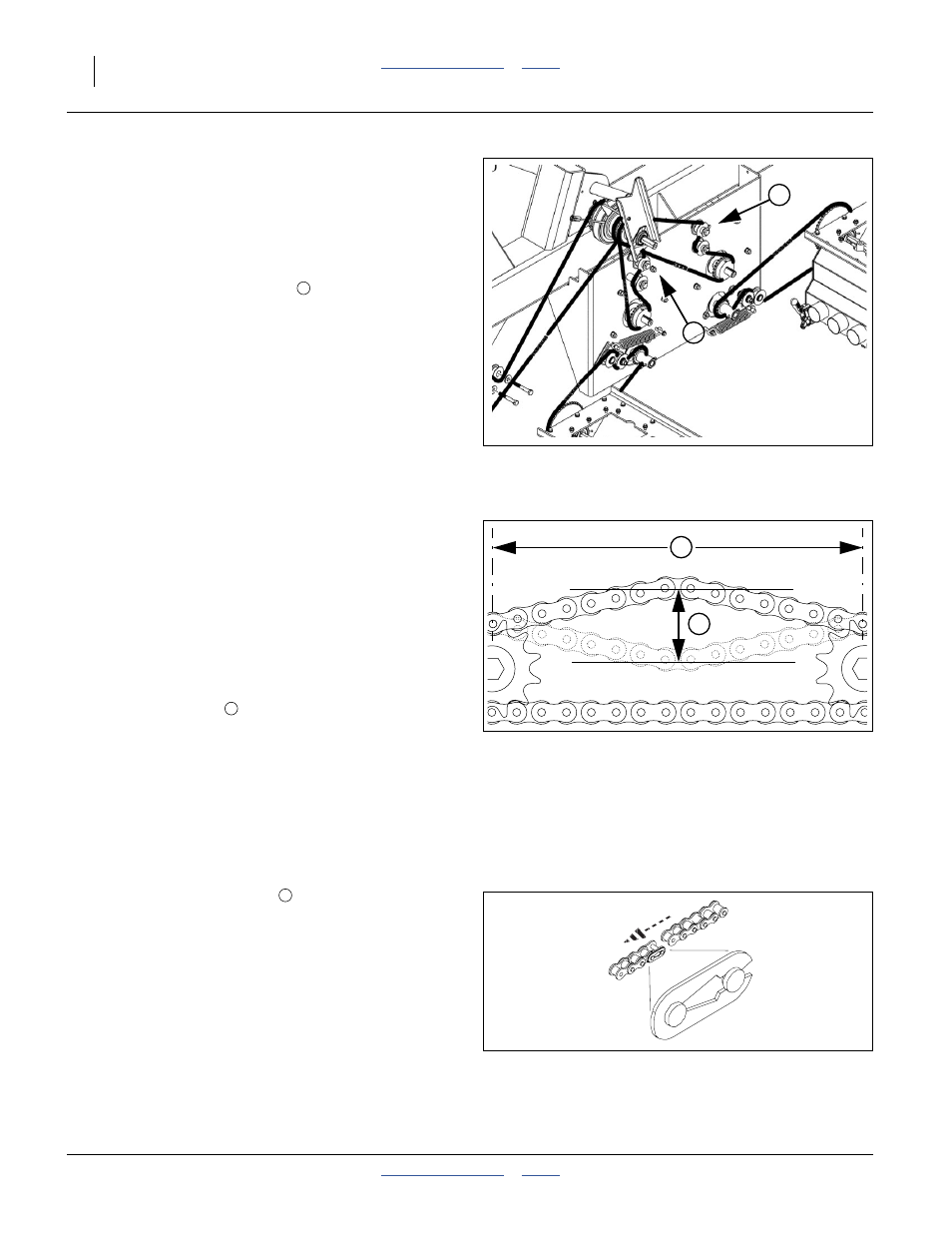
Gearbox Input Chains
Refer to Figure 85
These chains connect the clutch output to each of the
two gearboxes.
Check chain tension. The rear spans should have
1
⁄
2
inch (13 mm) slack at the midpoint. To adjust, loosen
the bolts holding the upper idlers
and move idler.
Retighten the bolts.
Note: The gearbox output chains are tensioned by spring
idlers and require no adjustment.
Chain Maintenance
Initially check the drive chains after the first 10 hours of
drill use. The slack of new chains tends to increase
during the first few hours of operation due to seating.
Thereafter, check the chains every 100 hours.
Lubricate chains any time there is a chance of moisture,
and when being stored at the end of the planting season.
Chain Slack
Refer to Figure 86, which, for clarity, greatly exaggerates
slack, and omits the idlers.
1.
Measure the span
for allowable slack:
Locate the longest span of each chain (usually the
span which does not run through the idlers).
2.
Determine the ideal slack:
Long chains (over 91 cm / 36 inches):
1
⁄
4
inch per foot (2.1 cm/m)
Vertical short chains:
1
⁄
4
inch per foot (2.1 cm/m)
Horizontal short chains:
1
⁄
2
inch per foot (4.2 cm/m).
3.
Measure the current slack
:
Acting at a right angle to the chain span at the centre
of the span, deflect the chain in both directions. The
slack is the distance of the movement.
4.
Adjust the idlers for ideal slack.
Whenever mounting a chain, make sure the clip at the
removable link is oriented to minimize snags.
Refer to Figure 87 (arrow shows chain direction)
Install clip with open end facing away from direction of
chain travel (shown by gray or striped arrows in chain
routing diagrams).
Figure 85
Gearbox Input Chains
26313
1
1
1
Figure 86
Measuring Chain Slack
27264
2
1
1
Figure 87
Chain Clip Orientation
26482
2
