Two’s complement binary numbers, Positive decimal values, Appendix b – Rockwell Automation 1769-IT6 Compact I/O 1769-IT6 Thermocouple/mV Input Module User Manual
Page 111: Appendix
Rockwell Automation Publication 1769-UM004B-EN-P - March 2010
111
Appendix
B
Two’s Complement Binary Numbers
The processor memory stores 16-bit binary numbers. Two’s complement binary is
used when performing mathematical calculations internal to the processor.
Analog input values from the analog modules are returned to the processor in
16-bit two’s complement binary format. For positive numbers, the binary
notation and two’s complement binary notation are identical.
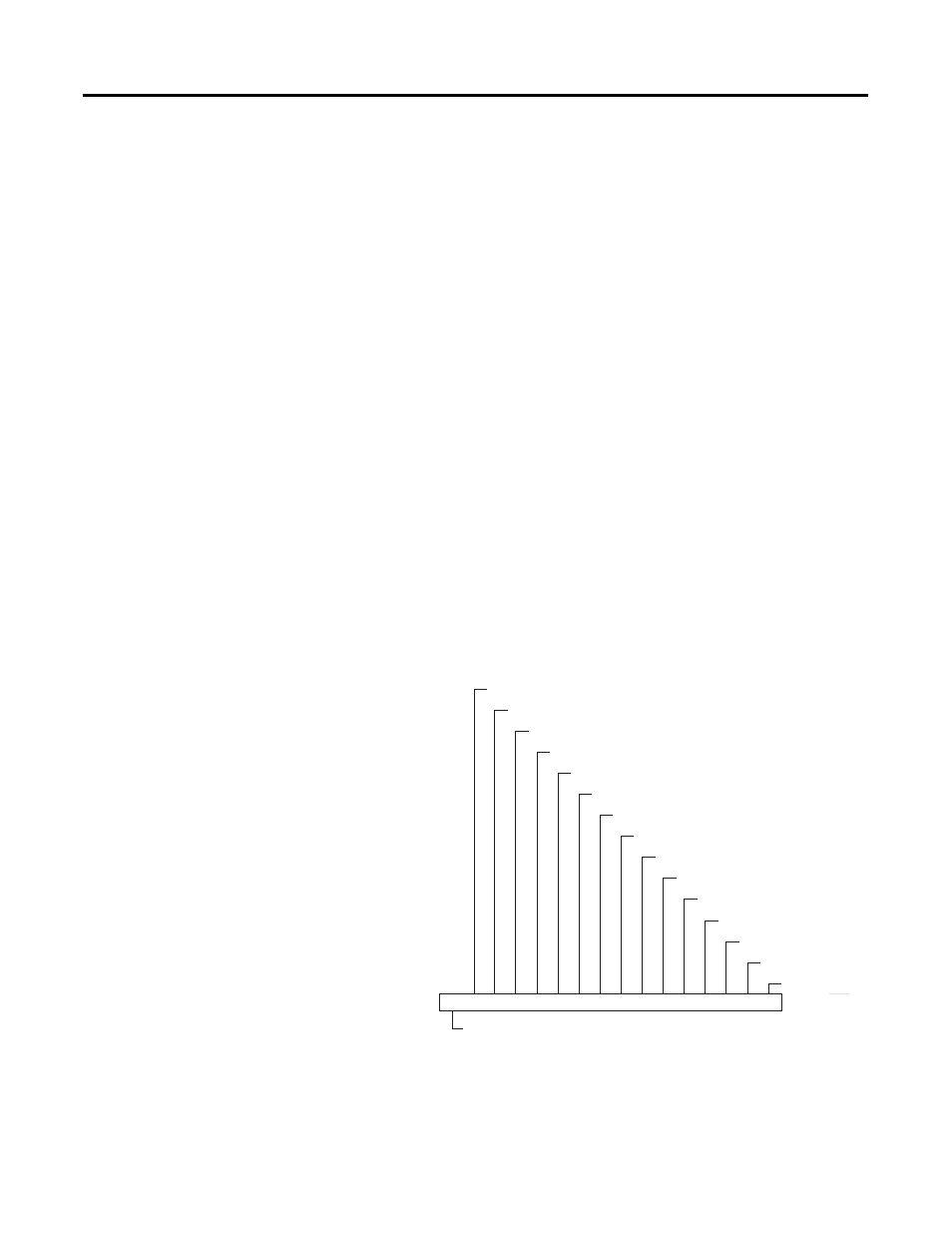
As indicated in the figure on the next page, each position in the number has a
decimal value, beginning at the right with 20 and ending at the left with 215.
Each position can be 0 or 1 in the processor memory. A 0 indicates a value of 0; a
1 indicates the decimal value of the position. The equivalent decimal value of the
binary number is the sum of the position values.
Positive Decimal Values
The leftmost position is always 0 for positive values. As indicated in the figure
below, this limits the maximum positive decimal value to 32,767 (all positions are
1 except the leftmost position). This is an example.
0000 1001 0000 1110 = 211+28+23+22+21 = 2048+256+8+4+2 = 2318
0010 0011 0010 1000 = 213+29+28+25+23 = 8192+512+256+32+8 = 9000
1 x 2 = 2
1 x 2 = 1
1 x 2 = 16384
1 x 2 = 8192
1 x 2 = 4096
1 x 2 = 2048
1 x 2 = 1024
1 x 2 = 128
1 x 2 = 512
1 x 2 = 256
1 x 2 = 64
1 x 2 = 32
1 x 2 = 16
1 x 2 = 8
1 x 2 = 4
0 x 2 = 0
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
15
0
16384
8192
4096
2048
1024
512
256
128
64
32
16
8
4
2
1
32767
This position is always 0 for positive numbers.
