2 comparison of industrial fieldbus systems, Preface, Comparison of industrial fieldbus systems – Lenze 931W User Manual
Page 7
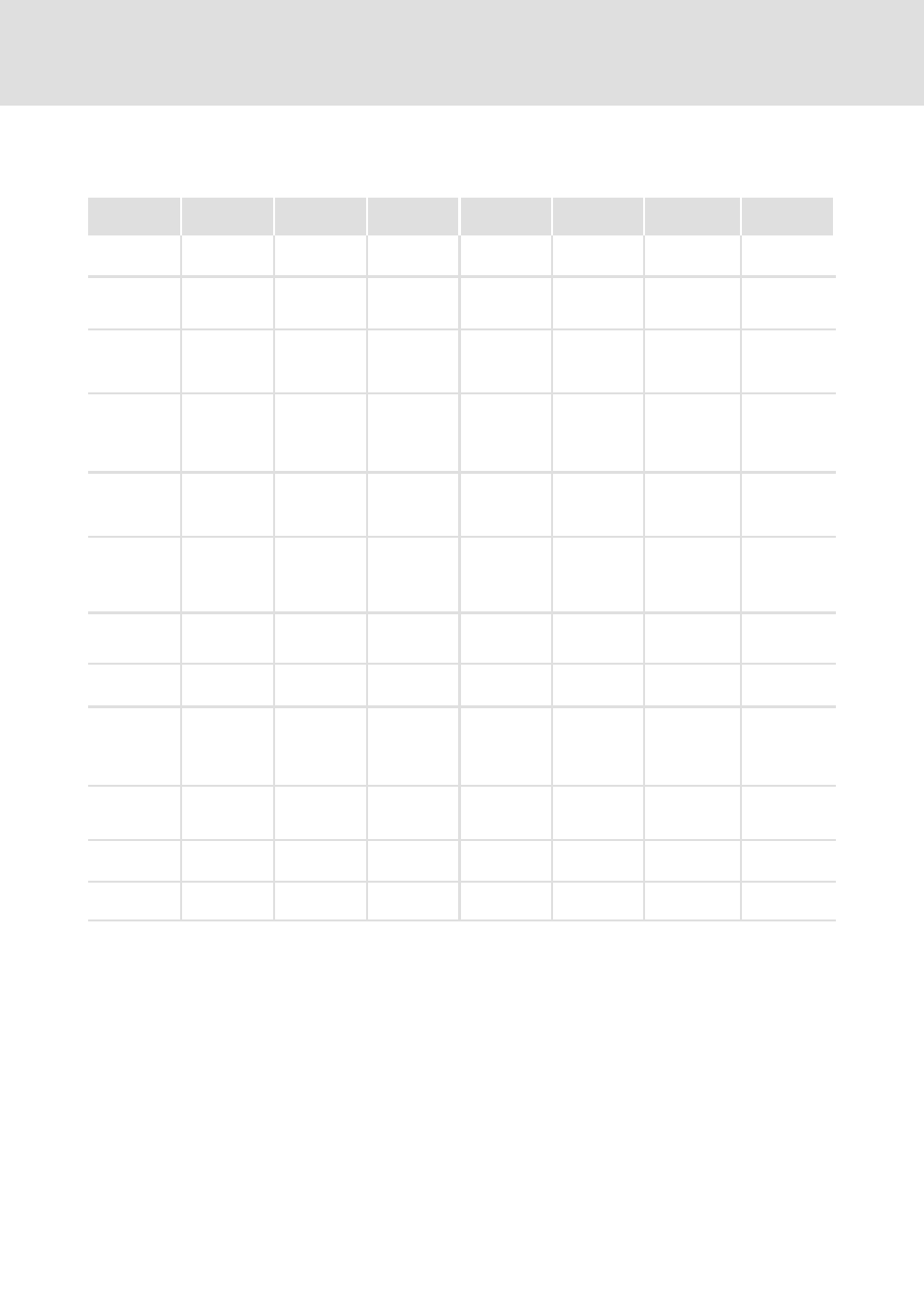
Preface
Comparison of industrial fieldbus systems
1
7
K-HB 13.0001-EN 2.1
1.2
Comparison of industrial fieldbus systems
CAN /
CANopen
DeviceNet
Profibus DP
AS-i
INTERBUS
INTERBUS-Loop LON
Topology
Line with
terminating
resistors
Line with
terminating
resistors
Line with
terminating
resistors
Line, tree, ring
(possible)
Ring
Ring
Line (2 wire) or any
other
Bus
management
Multi master
Single master
Single master
Single master
Single master
Only together with
INTERBUS-S; single
master (bus
terminal)
Multi master
Max. number
of nodes
(master and
slaves)
64
64
124 (4 segments, 3
repeaters),
max. 32 per
segment
124
sensors/actuators
1 master
512 slaves,
1 master
32 slaves
32385 stations
distributed to 255
subnetworks with
127 stations each
Max. distance
between
stations
without
repeater
Dependent on the
baud rate used
1 km (50 kbit/s)
25 m (1 Mbit/s)
100 m (500 kbit/s)
250 m (250 kbit/s)
500 m (125 kbit/s)
1.2 km (93.75
kbit/s)
100 m (12 Mbit/s)
100 m
1.5 m (local bus)
400 m (remote
bus)
2.5 km (optical
fibre)
10 m (max. 100 m
cable length
without repeater)
2 km at 78 kbit/s
(twisted pair),
6.1 km at 5.48
kbit/s (optical fibre
plastics)
Max. distance
between
stations with
repeater
General length
reduction,
dependent on the
repeater used
Not specified
10 km (93.75
kbit/s)
300 m (2
repeaters)
13 km (remote
bus),
100 km (optical
fibre)
No repeater
required
Almost any,
expandable by
subnetworks (no
repeater)
Transmission
medium
Shielded, twisted
pair cable
Shielded, twisted
pair cable
Shielded, twisted
pair cable
Unshielded,
untwisted flat pair
cable
Shielded, twisted
5-wire cable
Optical fibre,
infrared
Unshielded, twisted
pair cable
Unshielded,
untwisted pair
cable
Radio, optical fibre,
power supply
system (Powerline)
Auxiliary
energy supply
via bus cable
Possible via
additional wires in
the bus cable
Possible via
additional wires in
the bus cable
Possible via
additional wires in
the bus cable
Current supply via
data cable
(2 to 8 A)
Separate, Group
via bus terminal
(remote bus)
Current supply via
data cable
(ca. 1.5 A)
possible via
additional wires in
the bus cable
Baud rate
10 kbit/s - 1 Mbit/s 125 kbit/s,
250 kbit/s,
500 kbit/s
9.6 kbit/s - 12
Mbit/s
167 kbit/s
500 kbit/s or
2 Mbit/s
500 kbit/s
78 kbit/s - 1.25
Mbit/s
Typical update
time (e.g. 8
stations, 4
Bytes user
data)
Approx. 1.32 ms at
1 Mbit/s (high
priority)
Approx. 2.64 ms at
500 kbit/s (high
priority)
Approx. 2.5 ms at
500 kbit/s
Typically 5 ms
(4 bits each)
At least 2 ms
(process data)
At least 2 ms
(process data)
Approx. 70 ms
Telegram
length (user
data)
0 to 8 bytes
0 to 8 bytes
0 to 246 bytes
4 bits
1 to 64 bytes data,
up to 246 bytes
parameters
1 to 64 bytes data,
up to 246 bytes
parameters
1 to 228 bytes
data,
Typically approx.
11 bytes
Telegram
length (total)
106 bits at 8 bytes
user data
106 bits at 8 bytes
user data
User data +
6 to 11 bytes
21 bits, of which:
14 bits master, 7
bits slave
User data +
6 bytes
User data +
6 bytes
max. 255 bytes,
User data + 27
bytes
Bus access
methods
CSMA/CA
message-oriented
CSMA/CA
message-oriented
Cyclic polling
Cyclic polling
Time base /
distributed shift
register
Time base /
distributed shift
register
Modified
CSMA/CD
Tab. 1
Comparison of industrial fieldbus systems
