4 3 )] ( [ mbar hg mm, Umrechungsfaktor [mbar] auf [mm(hg) – Heidolph VAC control automatic User Manual
Page 21
21
D
2. Durch ziehen einer Linie nach rechts wird der Schnittpunkt mit der Lösungsmittel-Geraden
ermittelt.
3. Von diesem Schnittpunkt senkrecht nach unten kann das notwendige Vakuum abgelesen
werden.
10.3. bei Lösungsmitteln die nicht aufgeführt sind
-
Für die Ermittlung des richtigen Vakuums können folgende Punkte eine Hilfestellung sein:
1. Die Steigung der Geraden wird durch die Verdampfungsenthalpie bestimmt. Sie ist für
chemisch verwandte Substanzen mit naheliegendem Siedepunkt ähnlich. Die eingezeichneten
Geraden können somit als Orientierung für Substanzen mit leicht abweichendem Siedepunkt
dienen.
2. Mit einer Wasserstrahl- oder Membranpumpe lässt sich eine Siedepunkterniedrigung von ca.
100 °C erreichen.
3. Faustregel: Die Reduzierung des Druckes um die Hälfte erniedrigt den Siedepunkt um etwa
15 °C.
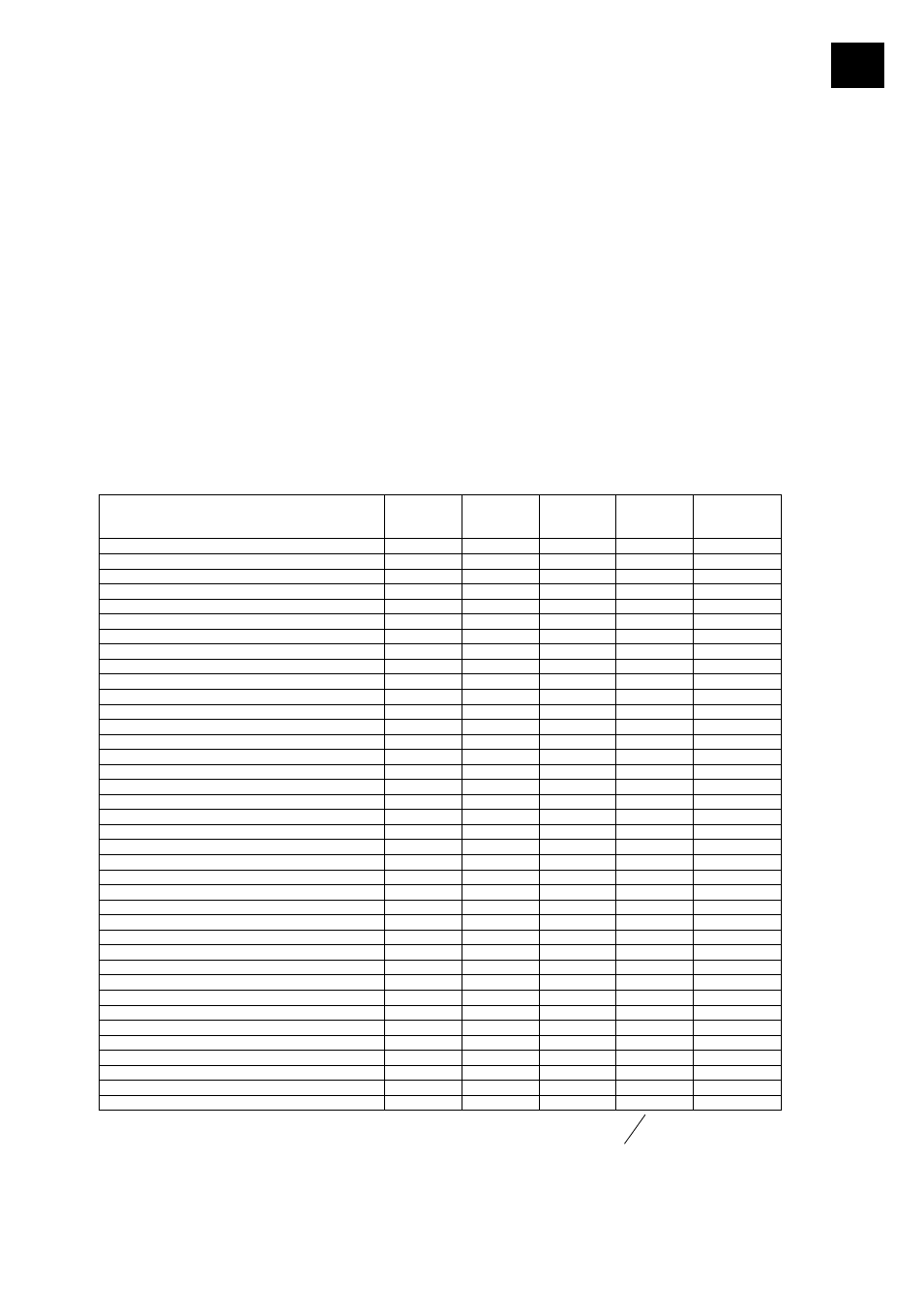
Lösungsmittel
Summen-
formel
MW
[g/mol]
Sdp.
[°C]
H
vap
[J/g]
Vacuum für
Sdp bei 40°C
[mbar]
Aceton
C
3
H
6
O
58,08
56,5
550
556
Acetonitril
C2H3N
41,05
81,8
833
230
Benzol
C
6
H
6
78,11
80,1
549
236
n-Butanol (Butylalkohol)
C
4
H
10
O
74,12
117,5
619
25
tert.-Butanol (tert.-Butylalkohol)
C
4
H
10
O
74,12
82,9
588
130
2-Butanon (Methylethylketon)
C
4
H
8
O
72,11
79,6
473
243
tert.-Butylmethylether
C
5
H
12
O
88,15
55,0
Chlorbenzol
C
6
H
5
CI
112,60
132,2
375
36
Cyclohexan
C
6
H
12
84,16
80,7
389
235
1,2-Dichlorethan
C
2
H
4
CI
2
98,96
82,4
336
210
1,2-Dichlorethylen (cis)
C
2
H
2
CI
2
96,94
59,0
320
479
1,2-Dichlorethylen (trans)
C
2
H
2
CI
2
96,94
47,8
313
751
Dichlormethan (Methylenchlorid)
CH
2
CI
2
84,93
40,7
373
atm.
Diethylether
C
4
H
10
O
74,12
34,6
392
atm.
Diisopropylether
C
6
H
14
O
102,20
67,5
318
375
Dimethylformamid
C
3
H
7
NO
73,09
153,0
11
1,4-Dioxan
C
4
H
8
O
2
88,11
101,1
406
107
Ethanol
C
2
H
6
O
46,07
78,4
879
175
Ethylacetat
C
4
H
8
O
2
88,11
77,1
394
240
Heptan
C
7
H
16
85,09
98,4
439
120
Hexan
C
6
H
14
86,18
68,7
370
335
Methanol
CH
4
O
32,04
64,7
1225
337
3-Methyl-1-Butanol (Isoamylalkohol)
C
5
H
12
O
88,15
130,6
593
14
Pentachlorethan
C
2
HCI
5
202,30
160,5
203
13
Pentan
C
5
H
12
72,15
36,1
382
atm.
n-Pentanol (Amylalkohol)
C
5
H
12
O
88,15
137,8
593
11
1-Propanol (n-Propylalkohol)
C
3
H
8
O
60,10
97,8
787
67
2-Propanol (Isopropylalkohol)
C
3
H
8
O
60,10
82,5
701
137
1,1,2,2-Tetrachlorethan
C
2
H
2
CI
4
167,90
145,9
247
35
Tetrachlorethylen
C
2
CI
4
165,80
120,8
233
53
Tetrachlormethan (Carbontetrachlorid)
CCI
4
153,80
76,7
225
271
Tetrahydrofuran
C
4
H
8
O
72,11
66,0
357
Toluol
C
7
H
8
92,14
110,6
425
77
1,1,1-Trichlorethan
C
2
H
3
CI
3
133,40
74,1
251
300
Trichlorethylen
C
2
HCI
3
131,40
86,7
265
183
Trichlormethan (Chloroform)
CHCI
3
119,40
61,3
263
474
Wasser
H
2
O
18,02
100,0
2259
72
Xylol (Isomeren-Gemisch)
C
8
H
10
106,20
137-143
390
25
Umrechungsfaktor [mbar] auf [mm(Hg)]:
]
[
4
3
)]
(
[
mbar
Hg
mm
