Clusters, Service nodes, Cluster controllers – Apple Qmaster 3 User Manual
Page 12
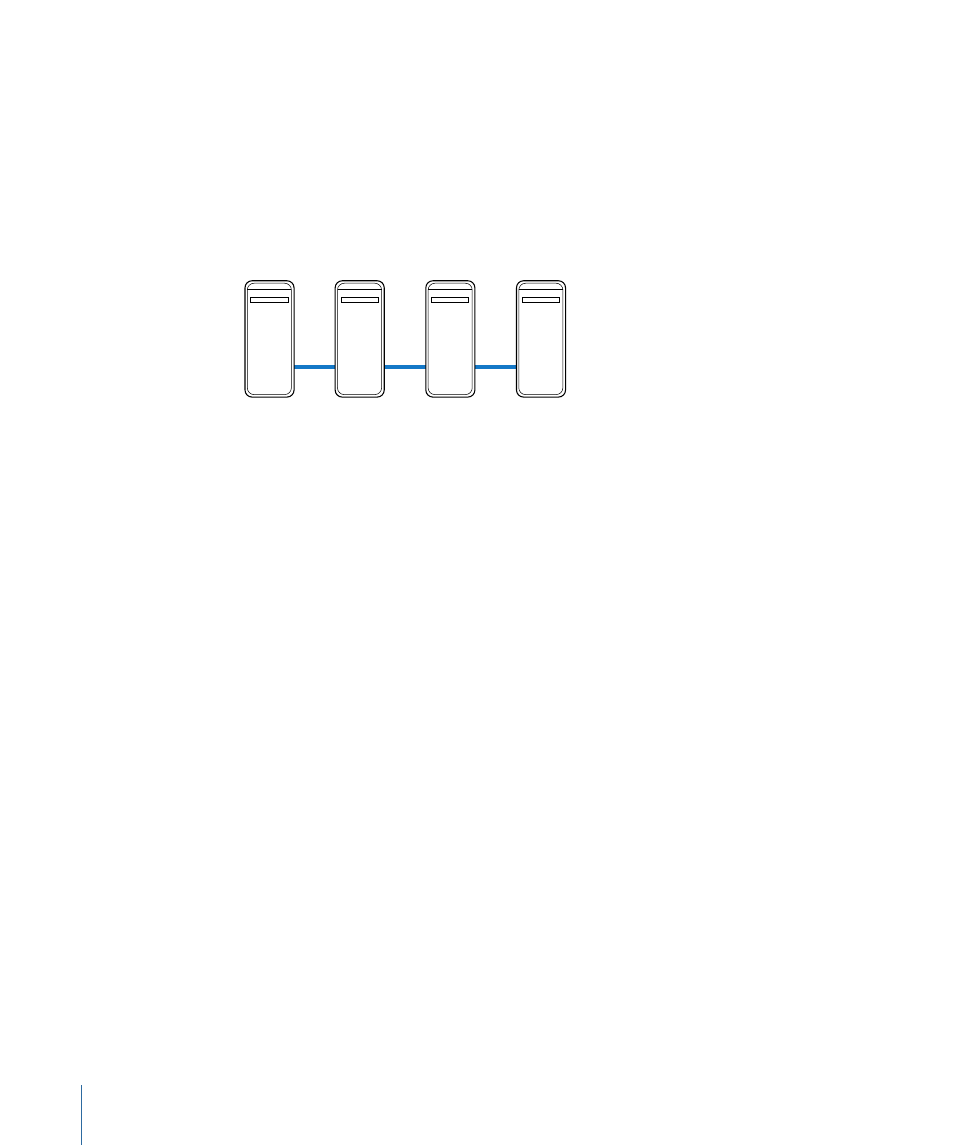
Clusters
When a client sends batches to the Apple Qmaster distributed processing system, all the
processing and subsequent moving of any output files is performed by a group of
Apple Qmaster–configured computers called a cluster. You can create one or more clusters
of service nodes, with one cluster controller included in each cluster. Each computer in
the cluster is connected to the other computers in the cluster through a network
connection.
Cluster
controller
Service
node
Service
node
Service
node
Example of a cluster
Note: This illustration provides only one simple example of a cluster. Other possibilities
are described in
Preparing a Network for Distributed Processing
.
Service Nodes
The service nodes are where the processing work is done. When you assign a group of
service nodes to a cluster, they function as one very powerful computer because all their
resources are shared. If one service node is overloaded or otherwise inaccessible, another
service node is used.
You make a computer available as a service node by configuring it in the Apple Qmaster
pane of System Preferences. The simple steps involved in using System Preferences to
configure a service node are described in
Note: The terms processing and rendering will come up frequently as you read this
document. The term processing is used here in a general way to cover both rendering
(for Shake and other frame-based rendering applications) and encoding (or transcoding
or compression) for Compressor. For more information, see the Shake User Manual and
the Compressor User Manual.
Cluster Controllers
The cluster controller software acts as the manager of a cluster. The cluster controller
directs the distribution of batches within the cluster. It has the ability to determine the
best use of the cluster resources based on work and availability variables. (See
Apple Qmaster System Distributes Batches
for more details.) The cluster controller is
responsible for accepting batch submissions, maintaining and managing the batch queue,
and doling out the work to the appropriate service node. It also tracks the status of all
outstanding batches.
12
Chapter 1
Distributed Processing Basics
