9 control port interface, 1 rise time for control port clock, Figure 6. i2c buffer example – Cirrus Logic CS4341A User Manual
Page 11: 2 map auto increment, Cs4341a
CS4341A
DS582F2
11
3.9
Control Port Interface
The control port is used to load all the internal register settings (see section 5). The operation of the control
port may be completely asynchronous with the audio sample rate. However, to avoid potential interference
problems, the control port pins should remain static if no operation is required.
The control port operates in one of two modes: I
2
C or SPI.
Notes: MCLK must be applied during all I
2
C communication.
3.9.1
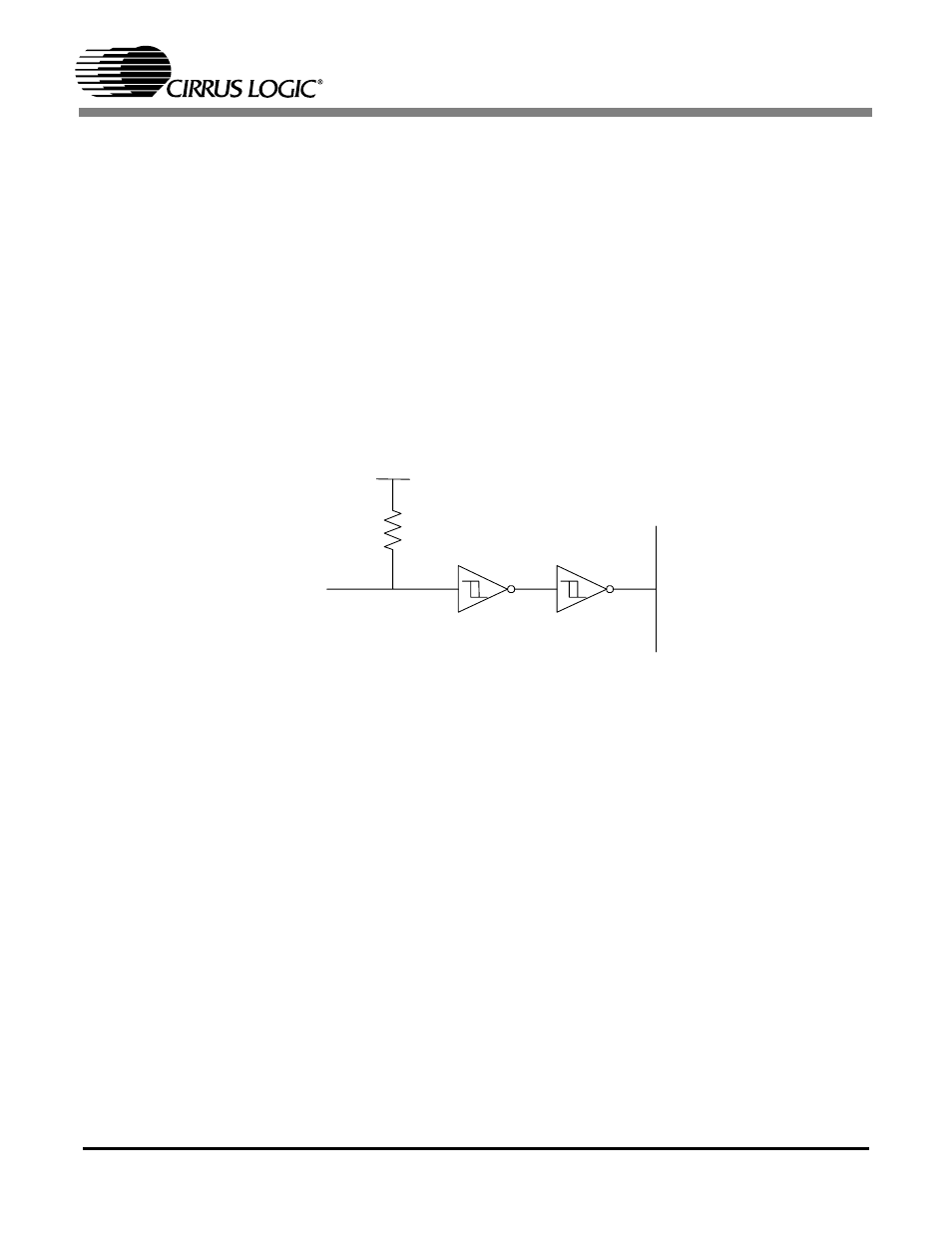
Rise Time for Control Port Clock
When excess capacitive loading is present on the I
2
C clock line, pin 6 (SCL/CCLK) may not have
sufficient hysteresis to meet the standard I
2
C rise time specification. This prevents the use of com-
mon I
2
C configurations with a resistor pull-up. A workaround is achieved by placing a Schmitt
Trigger buffer, a 74HC14 for example, on the SCL line just prior to the CS4341A. This will not
affect the operation of the I
2
C bus as pin 6 is an input only.
3.9.2
MAP Auto Increment
The device has MAP (memory address pointer) auto increment capability enabled by the INCR bit
(also the MSB) of the MAP. If INCR is set to 0, MAP will stay constant for successive I
2
C writes
or reads, and SPI writes. If INCR is set to 1, MAP will auto increment after each byte is written,
allowing block reads or writes of successive registers.
P in 6
V A
S C L
Figure 6. I
2
C Buffer Example
