Goulds Pumps 3408A - IOM User Manual
Page 24
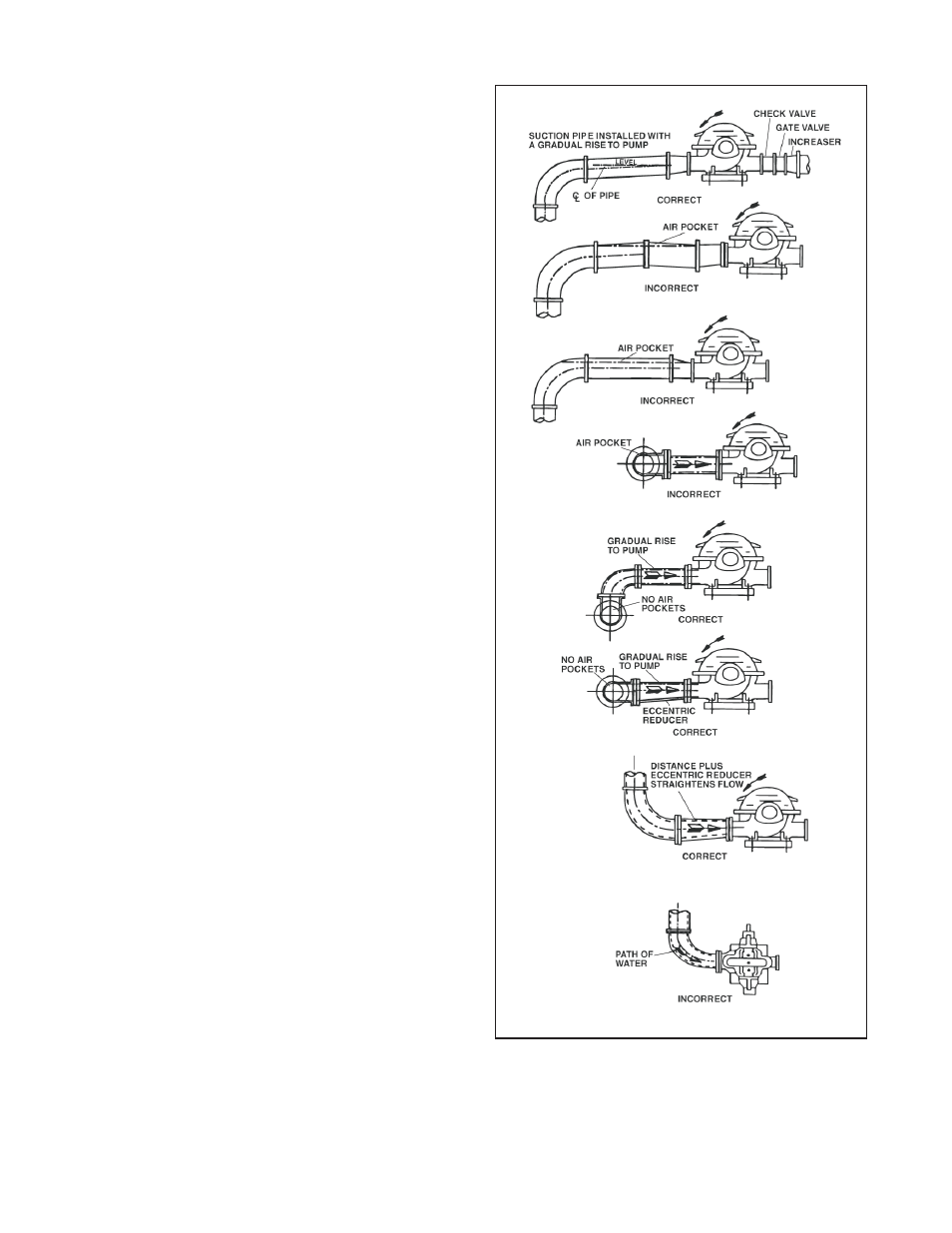
Suction Piping
When installing the suction piping, observe the
following precautions. See Figure 9.
The sizing and installation of the suction piping is
extremely important. It must be selected and
installed so that pressure losses are minimized and
sufficient liquid will flow into the pump when
started and operated. Many NPSH (Net Positive
Suction Head) problems can be attributed directly
to improper suction piping systems.
Friction losses caused by undersized suction piping can
increase the fluid’s velocity into the pump. As
recommended by the Hydraulic Institute, Standard
ANSI/HI 1.1-1.5-1994, suction pipe velocity should not
exceed the velocity in the pump suction nozzle. In some
situations pipe velocity may need to be further reduced to
satisfy pump NPSH requirements and to control suction
line losses. Pipe friction can be reduced by using pipes that
are one to two sizes larger than the pump suction nozzle in
order to maintain pipe velocities less than 5 feet/second.
Suction piping should be short in length, as direct as
possible, and never smaller in diameter than the pump
suction opening. If the suction pipe is short, the pipe
diameter can be the same size as the suction opening. If
longer suction pipe is required, pipes should be one or two
sizes larger than the opening, depending on piping length.
Suction piping for horizontal double suction pumps should
not be installed with an elbow close to the suction flange of
the pump, except when the suction elbow is in the vertical
plane. A suction pipe of the same size as the suction nozzle,
approaching at any angle other than straight up or straight
down, must have the elbow located 10 pipe diameters from
the suction flange of the pump. Vertical mounted pumps
and other space limitations require special piping.
There is always an uneven turbulent flow around an elbow.
When it is in a position other than the vertical it causes
more liquid to enter one side of the impeller than the other.
See Figure 10. This results in high unequalized thrust loads
that will overheat the bearings and cause rapid wear, in
addition to affecting hydraulic performance.
Figure 9: Suction Pipe Installations
(Piping supports not shown)
16
3408A IOM 6/08
