Implementation, Table 2: ieee 802.3af class vs. power levels – Allied Telesis AT-PC2002/POE User Manual
Page 25
AT-PC2002/POE Media Converter Installation Guide
25
Implementation
A standard Ethernet twisted pair cable contains four pairs of strands for a
total of eight strands. 10/100 Mbps network traffic requires only four
strands (1, 2, 3, and 6), leaving four strands in the cable unused (4, 5, 7,
and 8).
The PoE standard, IEEE 802.3af, describes two alternative ways for
delivering power to a powered device (PD) over twisted pair cabling.
Alternative A uses the same strands that carry the network traffic.
Alternative B uses the spare strands. The PoE implementation on the
AT-PC2002/POE Media Converter uses Alternative A, where power is
transmitted over strands 1, 2, 3, and 6.
Powered devices that comply with the IEEE 802.3af standard typically
support both power delivery methods. So long as a PD is compliant with
the standard, it should be able to receive its power from the media
converter while using either a straight or cross-over cable. The PoE
feature on the AT-PC2002/POE Media Converter should also work with
most legacy powered devices as long as the devices can be powered on
pins 1, 2, 3, and 6.
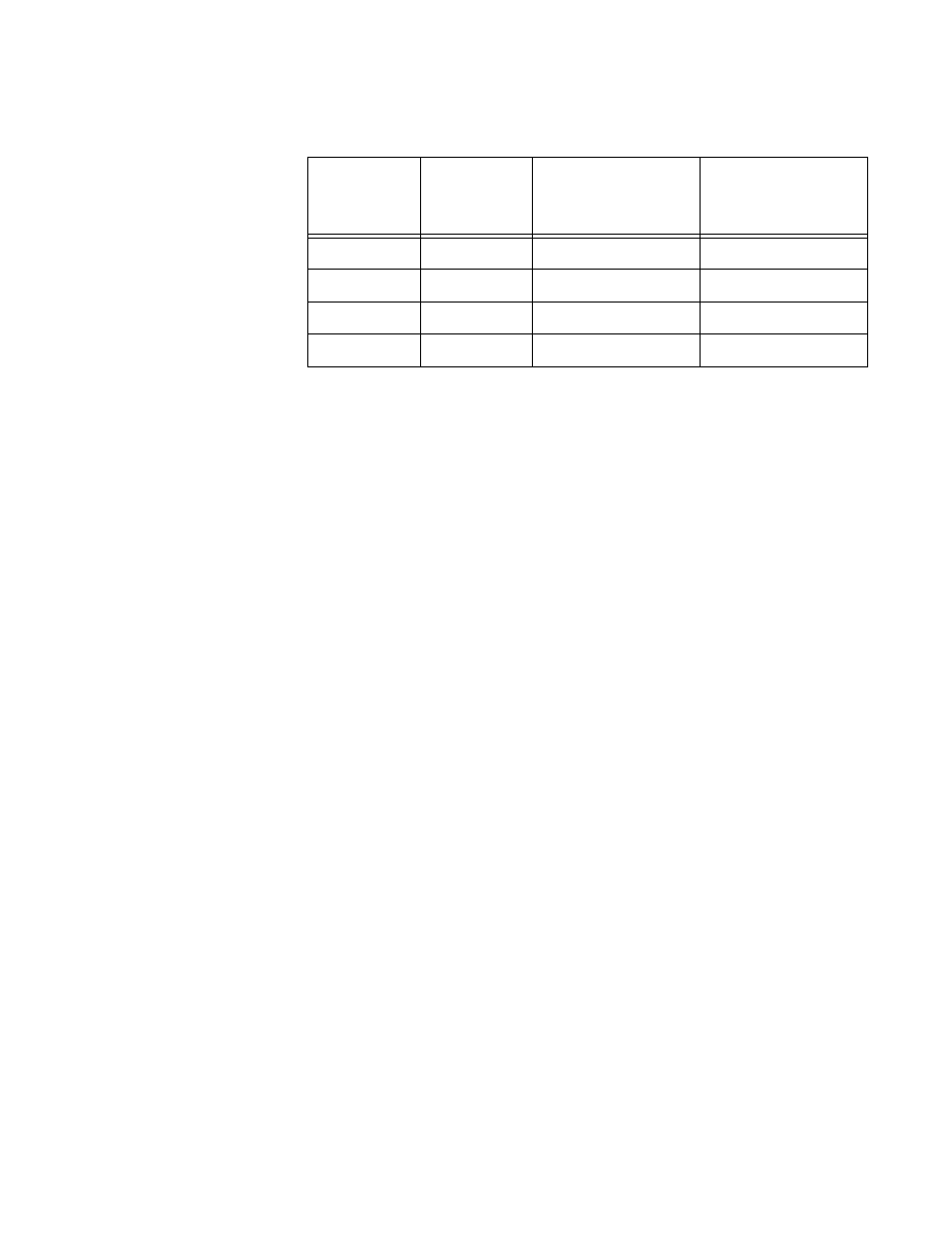
Table 2. IEEE 802.3af Class vs. Power Levels
Class
Usage
Minimum Power
Levels Output at
the PSE
Maximum Power
Levels Output at
the PD
0
Default
15.4W
0.44W to 12.95W
1
Optional
4.0W
0.44W to 3.84W
2
Optional
7.0W
3.84W to 6.49W
3
Optional
15.4W
6.49W to 12.95W
