Physical storage elements, Storage management process example, Figure 4 storage management process example – HP ProLiant ML310 G3 Storage Server User Manual
Page 30
Single Server
Cluster Implementation
Physical Disks
Logical Drives
RAID Arrays
Selective Storage
Presentaion
Visible Disks
Partitioning
NTFS Volumes
Shadow Copies
(Snapshots)
Cluster Physical
Disk Resources
Fault-tolerant
CIFS/SMB and
NFS File Shares
Cluster Virtual
Server Groups
(Network Name)
(IP Address)
(Cluster Admin)
File Folders
Storage
Elements
Logical
Storage
Elements
File
System
Elements
Shadow Copy
Elements
Cluster
Elements
File
Sharing
Elements
CIFS and NFS
File Shares
\Engineering
\Marketing
\Users
\Sales
\Engineering
\Marketing
\Users
\Sales
\Customers
from 02/10/03 09:30 \snapshot.0
from 02/10/03 11:30 \snapshot.1
from 02/10/03 09:30 \snapshot.0
from 02/10/03 11:30 \snapshot.1
Q:
Q:
Q:
R:
R:
R:
R:
T:
S:
S:
U:
U:
\Users
\\VirtualServerA
IP Addresss 172.1.1.1.
\\VirtualServerA
IP Addresss 172.1.1.2.
\Sales
\Marketing
\Engineering
\Snapshot.0
\Snapshot.1
\Sales
\Users
\Customers
\Marketing
\Engineering
\Snapshot.0
\Snapshot.1
T:
gl0044
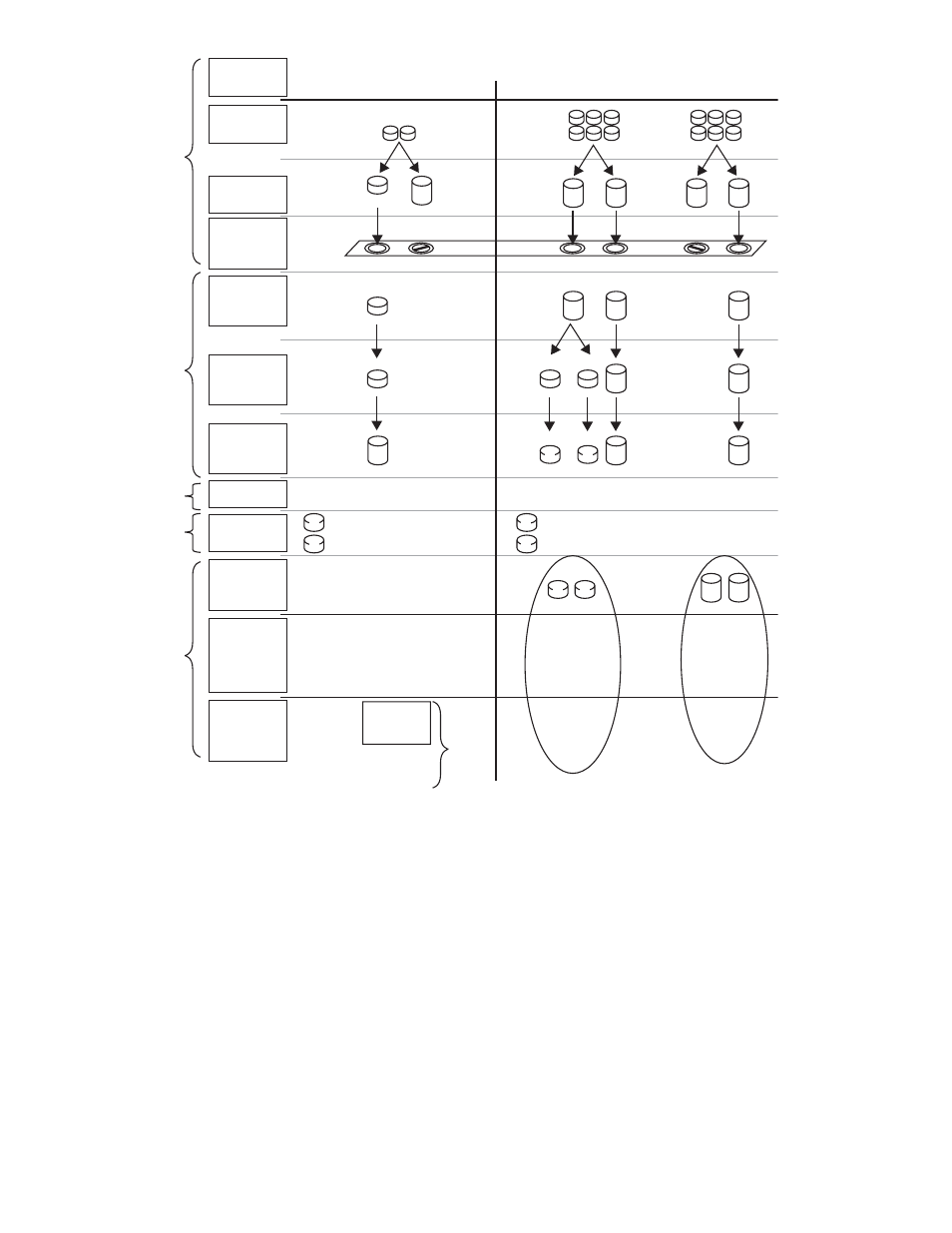
Figure 4 Storage management process example
Physical storage elements
The lowest level of storage management occurs at the physical drive level. Minimally, choosing the best
disk carving strategy includes the following policies:
•
Analyze current corporate and departmental structure.
•
Analyze the current file server structure and environment.
•
Plan properly to ensure the best configuration and use of storage.
• Determine the desired priority of fault tolerance, performance, and storage capacity.
• Use the determined priority of system characteristics to determine the optimal striping policy
and RAID level.
•
Include the appropriate number of physical drives in the arrays to create logical storage elements
of desired sizes.
30
Storage management overview
