Example of a clpr – HP 200 Storage Virtualization System User Manual
Page 12
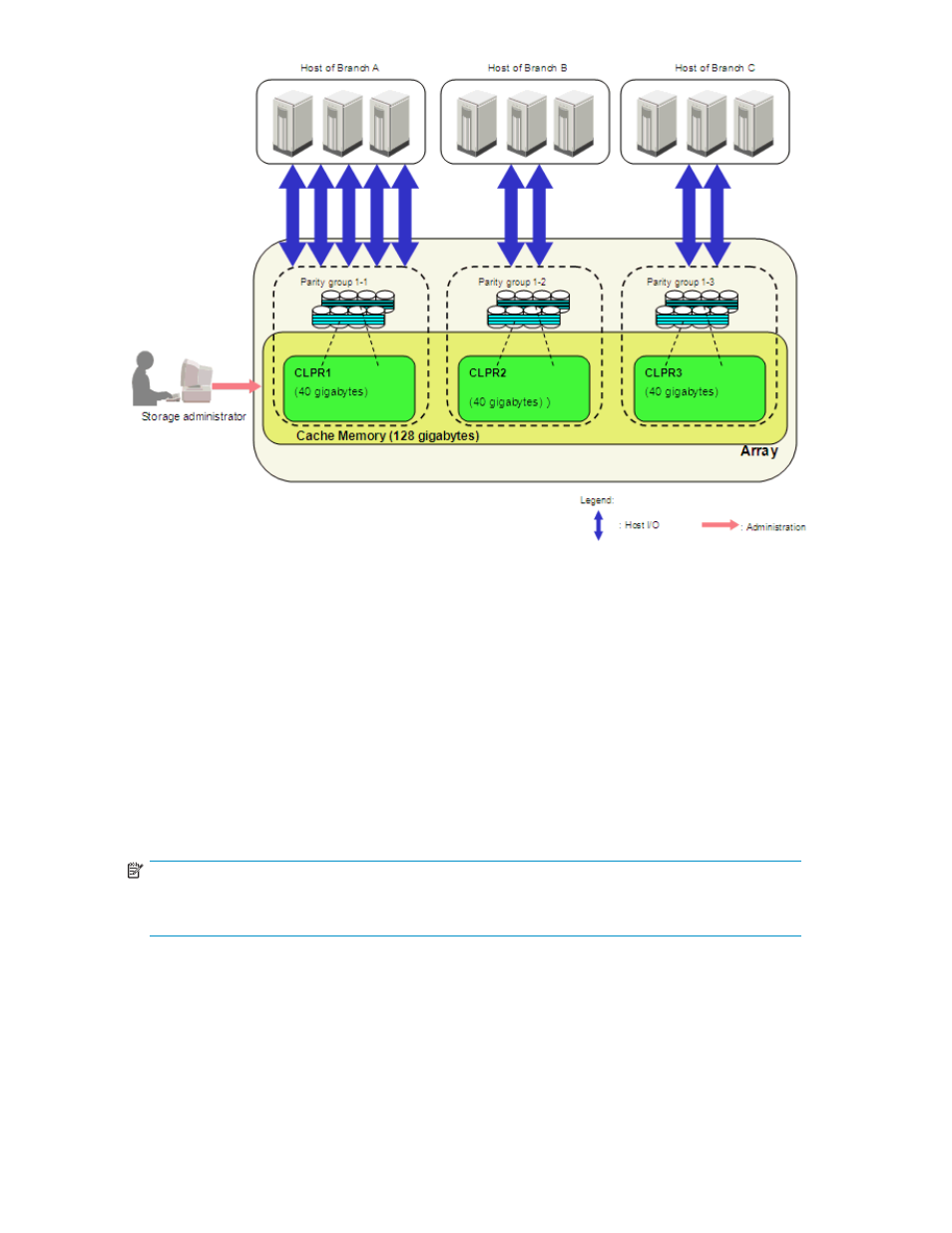
Figure 1 Example of a CLPR
To create a CLPR, allocate the parity groups to CLPR. For instructions on allocating parity groups, see
To create and manage a CLPR, you need user authority for the array. For more information about user
authority, see
Partition administration and administrator rights
and the HP StorageWorks XP Remote Web
Console user guide for XP12000/XP10000/SVS200.
To manage cache memory using the functions in XP Cache LUN or Partial Cache Residence (PCR), you
can set up the cache area for XP Cache LUN and PCR in each CLPR. For more information, see the HP
StorageWorks XP Cache LUN user guide for the XP12000/XP10000/SVS200.
•
Capacity criteria when creating a CLPR
If you create a CLPR, use the following formula to calculate the cache capacity allocated to the CLPR.
Cache capacity (GB) = Standard cache capacity (GB) + ↑ ((Cache Residency capacity (MB) +
PCR capacity MB))/2,048) ↑ x 2GB
NOTE:
The PCR capacity (MB) described in the formula is the Partial Cache Residence capacity (MB). For
more information about standard cache capacity, see
Overview of XP Disk/Cache Partition
12
