Long-running transactions – HP Integrity NonStop J-Series User Manual
Page 209
Problem Resolution
HP NonStop AutoTMF Software User’s Guide—429952-016
C-3
Locking Problems
once locking is dictated by more stringent rules.
below compares non-
audited and audited locking rules:
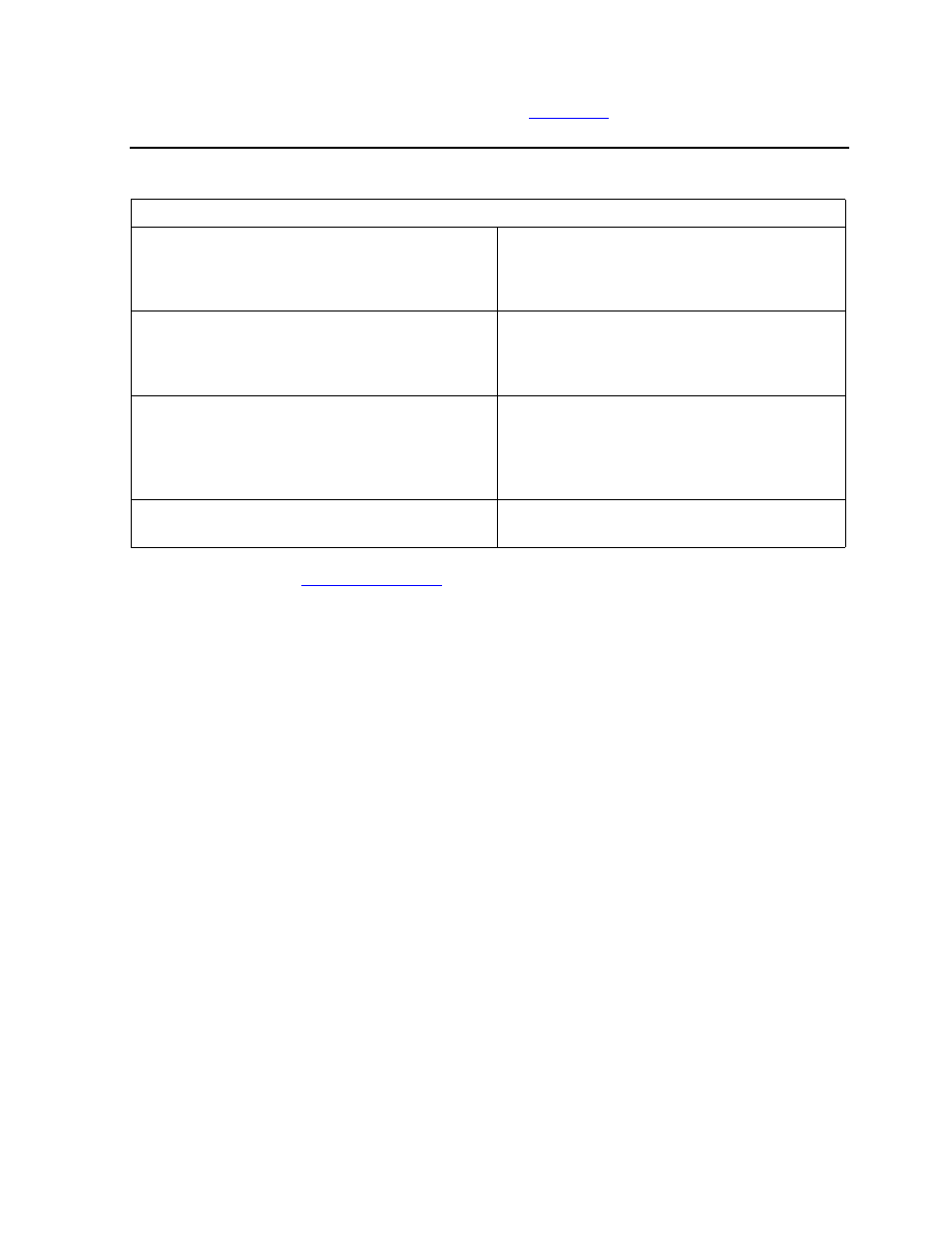
Table C-1. Non-Audited and Audited Locking Rules:
AutoTMF supplies a
command with options to assist in identifying the
processes and transactions that are holding locks. Particularly useful are the following:
The TXSTATUS option displays a summary of all transactions or processes that
are holding locks.
The DEADLOCK option display sets of granted and waiting lock requests that form
a deadlock. If the RESOLVE option is specified with DEADLOCK, the command
presents the user with a list of transactions and processes that are participants in
the deadlock and prompts the user to select either a process to abend or a
transaction to abort to resolve the deadlock. Note that deadlocks can resolve
themselves if the waiting operations use timed I/O.
Lock collisions, delays and deadlocks typically can be solved by a change in
configuration, such as configuring a file as SEPARATETX, changing MAXUPDATE
values, setting ISOLATION to NORMAL or STRONG, and so on.
Once the programs in contention are identified, tracing the programs is the surest way
to identify the configuration change that will correct the situation.
Long-Running Transactions
Long-running transactions can lead to unilateral aborts if the TMF AutoAbort time limit
is reached. Unilateral aborts can have a severe impact on an application because all
non-committed updates from a process are rolled back.
Non Audited
Audited
Locks are never required by the file system
Not required for updates or deletes
Inserts do not create locks
Locks are required for certain operations
Update or delete require an explicit
lock operation
All locking operations are explicit
Locking operations are explicit and implicit
Implicit for inserted records
Explicit otherwise
All unlock operations are explicit
Unlock operations are explicit and implicit
Explicit for unmodified records
Implicit for modified records when the
transaction is committed
Locks are held by a file open and cannot be
shared
Locks are held by a transaction and can be
shared
