Technical data – KROHNE OPTISYS CL 1100 EN User Manual
Page 39
TECHNICAL DATA
7
39
OPTISYS CL 1100
www.krohne.com
01/2013 - 4002492301 - MA OPTISYS CL 1100 R02 en
Chlorine dioxide measurement
Chlorine dioxide (ClO
2
) is an instable, non-storable, toxic gas with a characteristic scent. The
molecule consists of one chlorine atom and two oxygen atoms – represented in the chemical
formula ClO
2
. It is very reactive. To avoid the risk of spontaneous explosions of gaseous chlorine
dioxide or concentrated solutions, it is generally handled in dilution with low concentrations.
ClO
2
is soluble in water, but tends to evaporate quickly. Typically it is prepared on site, for
example from hydrochloric acid and sodium chlorite. The procedure provides solutions with
approx. 2 g/l ClO
2
that can be safely handled and stored for several days.
The disinfection effect of ClO
2
is due to the transfer of oxygen instead of chlorine, so that no
chlorinated byproducts are formed. ClO
2
is used as disinfectant against biofilm, bacteria, spores,
and viruses. Today it is believed that the molecule´s unpaired electron is transferred to the DNA
of the microorganism which cracks and causes cell necrosis. ClO
2
has a long-term effect of
several days. In contrast to chlorine, the disinfection strength of ClO
2
does not depend on pH,
and neither does the measurement show a pH influence in the range of pH 6 to pH 9.
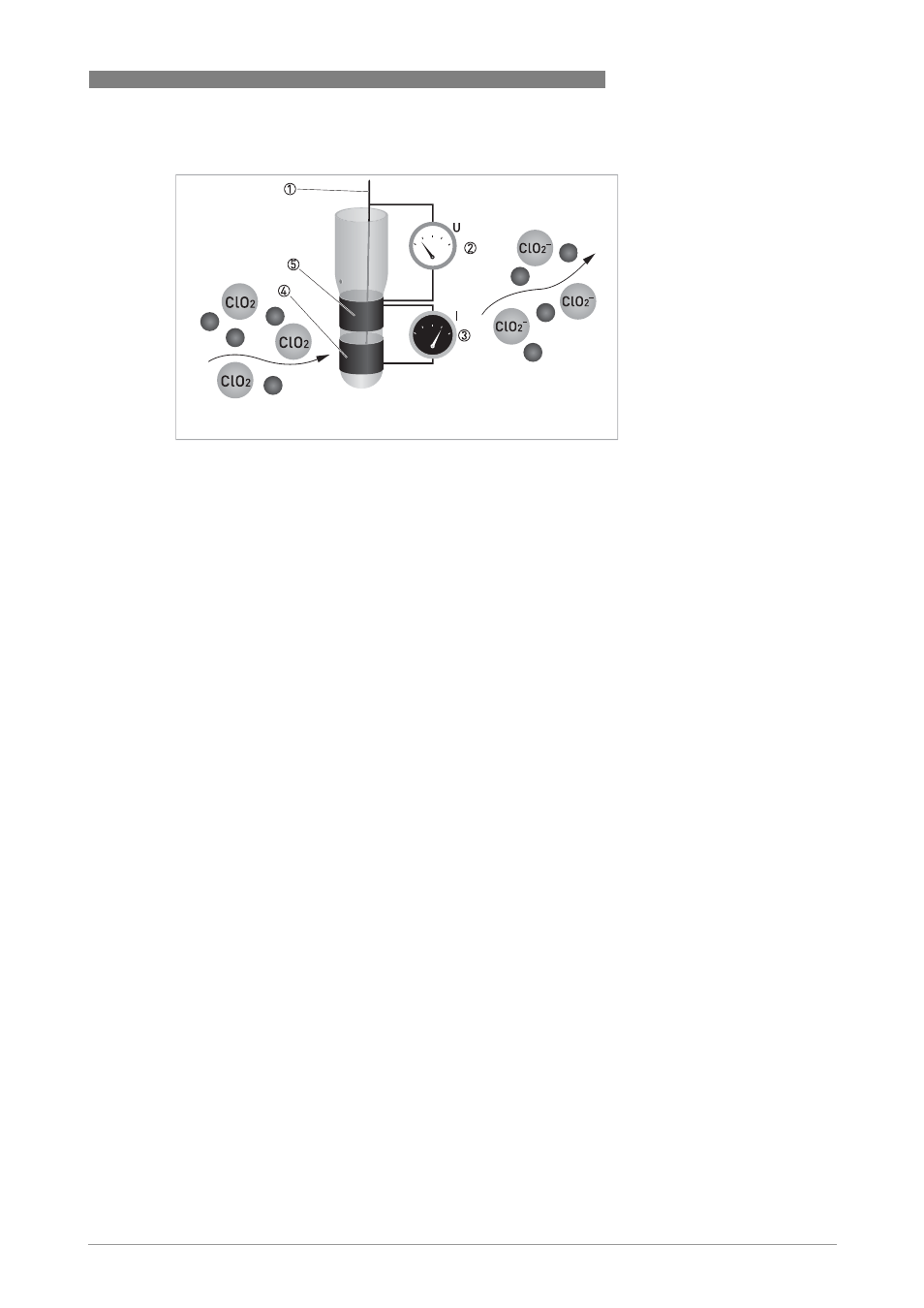
ClO
2
is measured potentiostatic with measuring and counter electrodes of pure gold and an
Ag/AgCl reference. The measurement shows good selectivity towards ClO
2
. A precise potential is
applied to the measuring electrode, leading to an accumulation of negative charges on the metal
surface. ClO
2
molecules that hit the surface take a defined portion of the charge with them. The
controller measures the potential between measuring and reference electrode and readjusts
the charge on the electrode surface. The current necessary to maintain a constant charge is a
direct measure for the concentration of chlorine dioxide.
Chlorine dioxide measurement
Figure 7-3: Chlorine dioxide measurement
1 Reference electrode
2 Voltage measurement
3 Current needed to maintain the constant potential
4 Counter electrode
5 Measuring electrode
