Introduction to the charger, Overview – Fire-Lite CHG-120F Battery Charger User Manual
Page 7
CHG-120F Instruction 03/21/01 PN 50888:B0
7
1. Introduction to the Charger
Overview
The CHG-120F battery charger is designed to charge lead-acid batteries that provide
emergency standby power for a Fire Alarm Control Panel (FACP). Two 12-volt batteries are
always used in series to supply 24 VDC nominal. The following list gives answers to some
common questions about the charger:
•
What types of FACPs can be used with the charger? Any 24 VDC FACP that uses
lead-acid 25 AH to 120 AH batteries and that has the feature to disable the FACP
battery charger.
•
Where does the charger mount? You can mount the charger in a CAB-A3F or
CAB-B3F Cabinet or in a BB-55F Battery Box.
•
How many outputs does the charger provide? The charger provides two output
circuits for connection to multiple loads (such as a power supply, amplifier, auxiliary
amplifier, and so forth).
•
What options are available with the charger? You can configure the charger to
disable the charger’s ground fault detection, to delay AC loss reporting (8 or 16 hours),
and to operate with 120 VAC or 240 VAC.
•
How long does it take the charger to charge batteries? Typically, it takes 9 hours to
charge 25 AH batteries, 20 hours to charge 55 AH batteries, and 38 hours to charge
120 AH batteries. Refer to “Specifications” on page 8 for details.
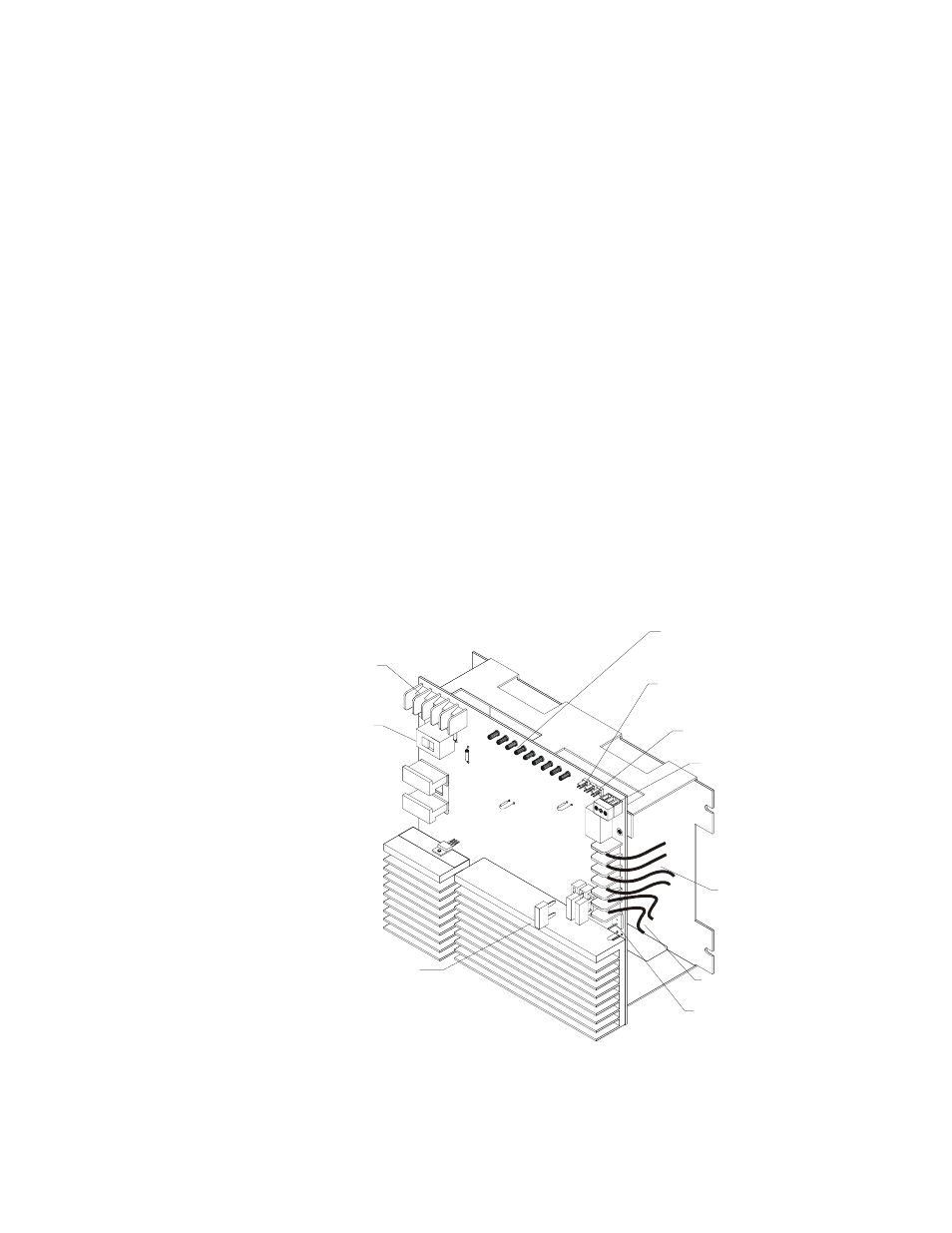
Figure 1 identifies features of the charger:
Figure 1 Charger Features
Note:
Throughout this
manual, the term “charger”
refers to a CHG-120F.
Note: For detailed descriptions of charger connections, jumpers, and
switches, see “Charger Connections, Jumpers, and Switches” on page 10.
Voltage Selection
Switch for 120 VAC or
240 VAC operation
15 A replaceable fuses provide
short circuit and overload
protection
Optional Ammeter
connection
Nine LED status
indicators
Open collector trouble daisy
chain connections
External trouble
input
25 AH – 120 AH
battery connections
Form-C trouble relay to
other devices
Heavy duty primary
AC power
connections
Two output circuits to
load (power supply,
auxiliary power supply,
amplifiers, etc.)
