Technical information, Technical information -1 – Yokogawa PH72 Personal pH/ORP Meter User Manual
Page 68
IM 12B03D02-01E
9-1
9. Technical Information
9. Technical Information
9.1 Measurement Principle of pH Meter (Glass Electrode
Method)
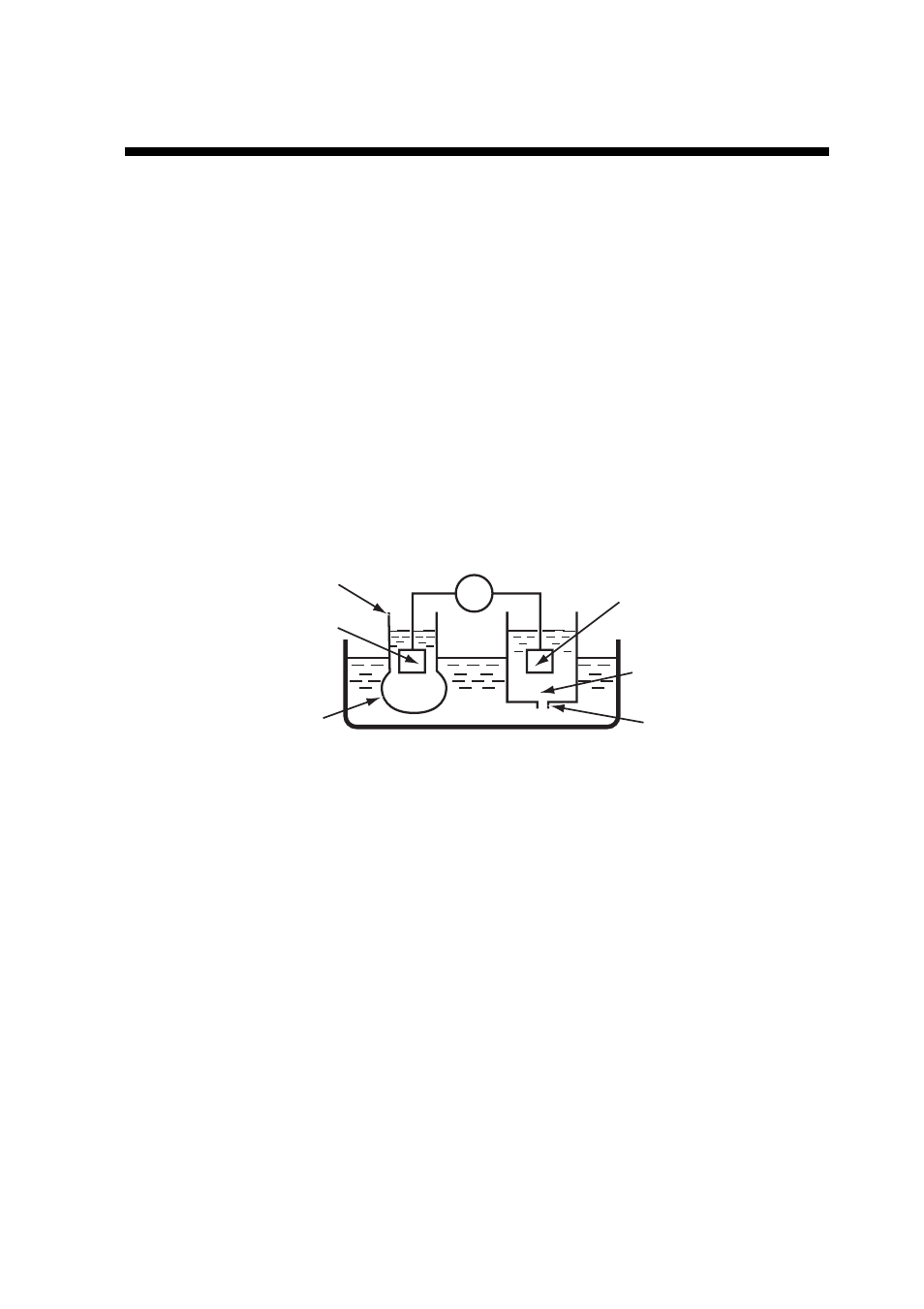
A pH meter makes use of the potential difference developed between the two sides of a
thin glass membrane that separates two solutions with different pH. Figure 9.1 shows the
schematic diagram of the measurement principle. A glass electrode is filled with a pH 7
solution and has an inner electrode that measures the potential difference corresponding
to the pH difference between the internal solution and the test solution. A reference
electrode has a constant potential irrespective of the pH of the test solution, which is
supported by potassium chloride (KCl) solution. It prevents the reference electrode from
making contact with the test solution but itself has electrical contact with the test solution
through the liquid junction. A voltmeter measures the potential difference between the
electrodes. As the membrane resistivity is high (several 10 to 100 M
Ω
), the voltmeter
with high input impedance is required. The external leak resistance should also be
sufficiently high (10
12
Ω
or greater).
F0901.EPS
V
pH7
KCl solution
Voltmeter
Test solution
Liquid junction
Reference electrode
pH electrode
Inner electrode
Glass membrane
Figure 9.1
Measurement Principle of pH Meter
