Operational conditions, 1 load inertia – IAI America RS User Manual
Page 35
4. Operational Conditions
29
4. Operational Conditions
4.1 Load Inertia
Operate with the load inertia within the allowable range.
Load inertia
Type
Deceleration
ratio
kg•m
2
(kgf•cm•s
2
)
1/50
0.058 (0.59)
RS-30
1/100
0.23 (2.35)
1/50
0.11 (1.1)
RS-60
1/100
0.42 (4.3)
٧
Regarding the load inertia
The rotary actuator is an actuator that applies a rotational torque to the loaded work piece and
makes the work piece have a rotational motion.
The rotational torque applies the load inertia and angular acceleration that can be figured out with
the following formula.
T = J•Į
T : Torque
N•m (kgf•cm)
J : Load inertia
kg•m
2
(kgf•cm•s
2
)
Į : Angular acceleration rad/s
2
i.e. applying a torque to an object with load inertia generates an angular acceleration. Therefore, for
the rotary actuator, the loadable amount is expressed with the load inertia.
٧
Calculation of the Load Inertia
Load inertia is a specific value for an object determined by the weight and profile.
It is to be calculated as;
J = ³ r
2
dM
r : Distance from center
dM : Small mass
For example, if the loaded work piece is offset from the rotary shaft, the following formula can be
applied.
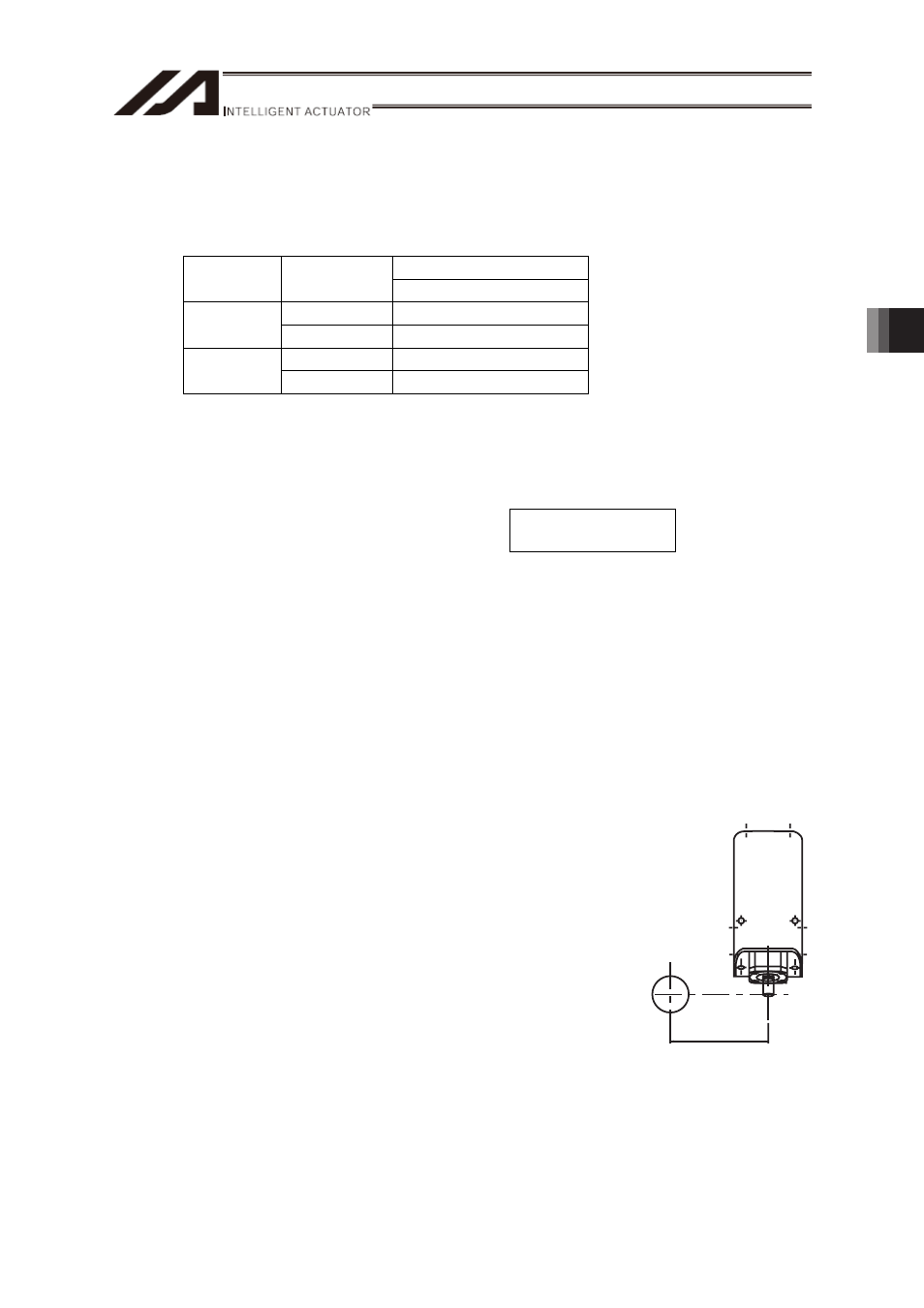
J = M•r
2
M : Mass of the loaded piece (kg)
r : Distance from the center (Offset distance) (m)
(Offset distance)
r
M
(Loaded
work piece)
typically Z is used for
angular velocity
