Concentrations – PASCO PS-2108 Dissolved Oxygen Sensor User Manual
Page 24
PASPort Dissolved Oxygen Sensor
Model No. PS-2108
20
®
Experiment 3: Effect of Sodium Sulfite on Dissolved
O
2
Concentrations
Materials and Equipment Needed
• Dissolved Oxygen Sensor
• PASPort interface or logger
• 2 M sodium sulfite (25.2 g Na
2
SO
3
/100 ml)
• aquarium pump or large bottle
• PASPort USB Interface and DataStudio software
• 600 ml beaker
• 400 ml deionized water
• pipet
Optional Materials
• hot plate/stir plate and magnetic stir bar
CAUTION: Sodium sulfite is a potential skin irritant. Use safety glasses and avoid skin contact. Skin that
contacts the solution should be rinsed liberally with water.
Purpose
The purpose of the experiment is to explore the effect of the inorganic chemical, sodium
sulfite on dissolved O
2
concentrations. Sodium sulfite (Na
2
SO
3
) is a commonly used
chemical in photographic developers, paper making, dyeing, bleaching, and engraving.
Procedure
1. Set up and calibrate the Dissolved Oxygen Sensor.
2. Saturate the deionized water with air by vigorously shaking the
water in a bottle or by bubbling with the aquarium pump.
3. Monitor the dissolved O
2
concentrations of the deionized water
while stirring gently with the dissolved O
2
probe.
4. When the meter reading stabilizes, record for 30 seconds.
5. After 30 seconds, add 1 ml of the 2 M Na
2
SO
3
solution into the
water.
6. Continue stirring the solution and recording until the reaction stops.
7. Stop recording and save your data.
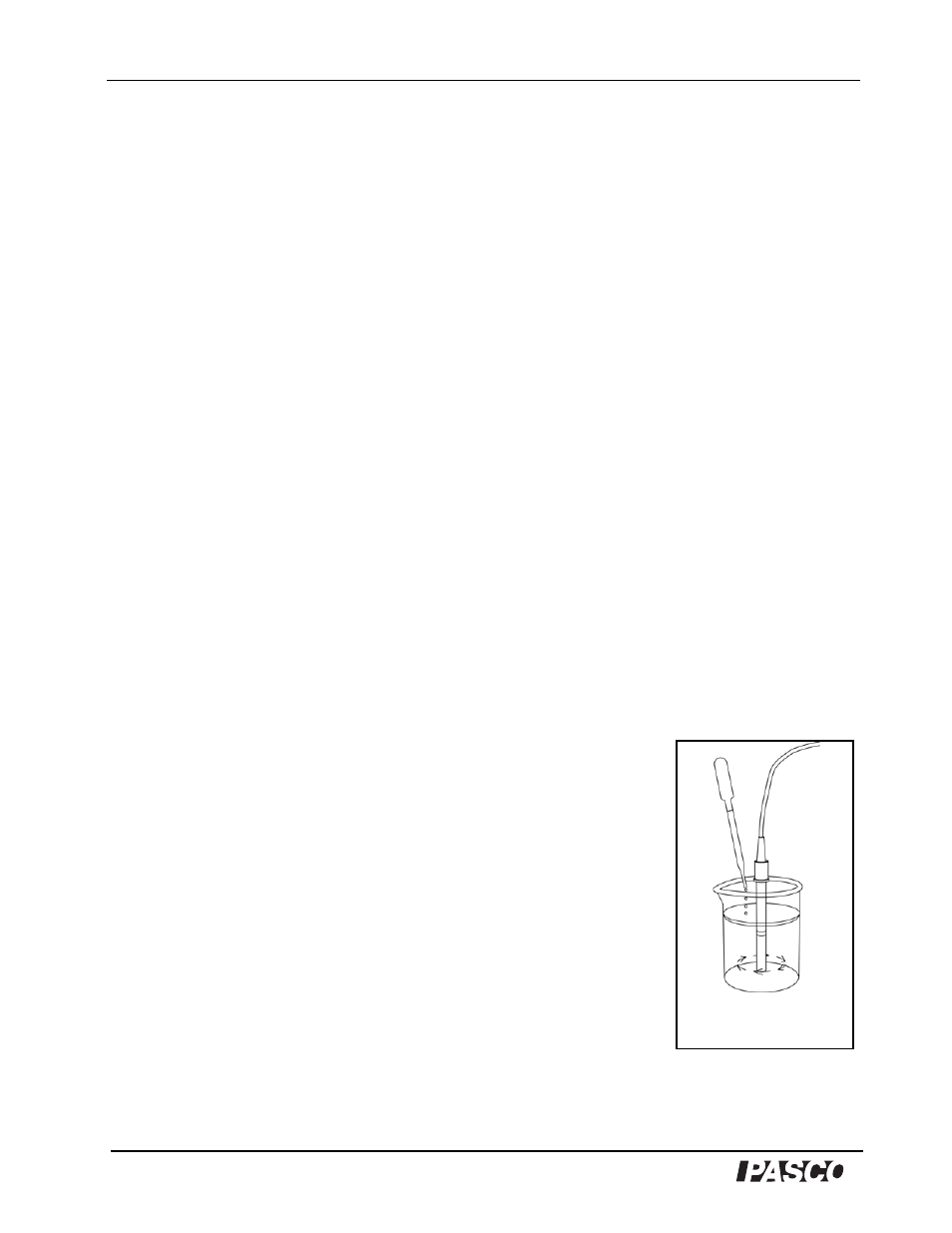
Figure 3
Stir test solution with probe
while adding sodium sulfite.
