PASCO ME-9833 Physical Pendulum Set User Manual
Page 28
®
Model No. ME-9833
Physical Pendulum Set
28
Sample Data for Experiment 3: Moment of Inertia Based on Period of Oscillation
Determine the calculated moment of inertia and the measured moment of inertia and record the
results in the Data Section.
Questions
1. How does your value for the calculated moment of inertia compare to the measured moment
of inertia?
The value for the calculated moment of inertia compares relatively well with the measured moment
of inertia.
2. Do your results support or disprove the idea that the moment of inertia of a physical
pendulum can be determined from its period of oscillation. Why or why not?
The results support the idea that the moment of inertia of a physical pendulum can be determined
from its period of oscillation. The calculated and measured values for the moment of inertia
compare relatively well.
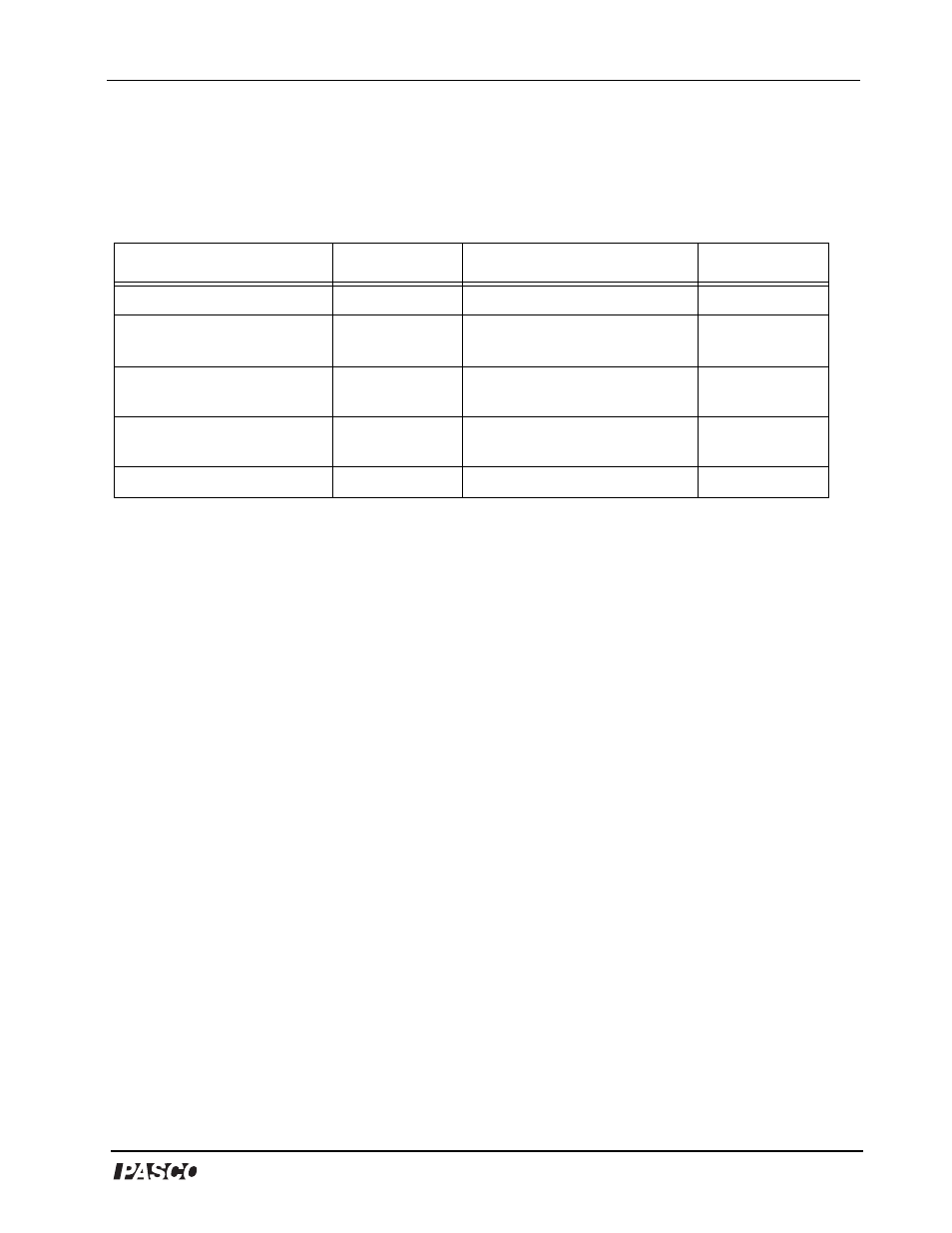
Table 3: Data Section
Item
Value
Item
Value
Mass of solid disk, M:
0.08818 kg
Mass of hanger, m:
0.00512 kg
Distance from pivot to center of
gravity, L
cg
:
0.40 m
Average angular acceleration,
α
cg
:
8.87 rad/s
2
Average measured period of
oscillation, T:
0.497 s
Torque,
τ:
0.000737 N m
Calculated value for moment of
inertia, I:
0.000075 kg m
2
Measured value for moment of
inertia, I:
0.000083 kg m
2
Radius of step pulley, r:
0.0149 m
Percent difference:
9.6%
