Overview, Testing the sensors, Materials required – Franklin Fueling Systems TSP-DDS User Manual
Page 2: Installation sequence
Overview
The TSP-DDS sensor is an intelligent BriteSensor ® that
is used to monitor for the presence of liquid hydrocarbons
(product) in Dispenser Sumps. The longer TSP-DTS
sensor is also an intelligent BriteSensor ® that is used in
Turbine Sump applications. The sensors use intrinsically
safe (I.S) leak detection circuits and are approved for
use in these Class 1, Division 1, Group D Hazardous
Areas. The sensors have an upper and lower float and a
conductive polymer strip that reacts specifically with liquid
hydrocarbons (the electrical resistance increases).
Like other BriteSensors, these sensors have a
microprocessor that analyze the environmental conditions
at the sensor and transmits data to the Automatic Tank
Gauge console. The TSP-DDS and TSP-DTS sensors
detect and communicate: WATER present (lower float),
PRODUCT present (polymer strip), SUMP FULL (top
float), a NORMAL no-alarm state, plus transmits a specific
sensor ID code.
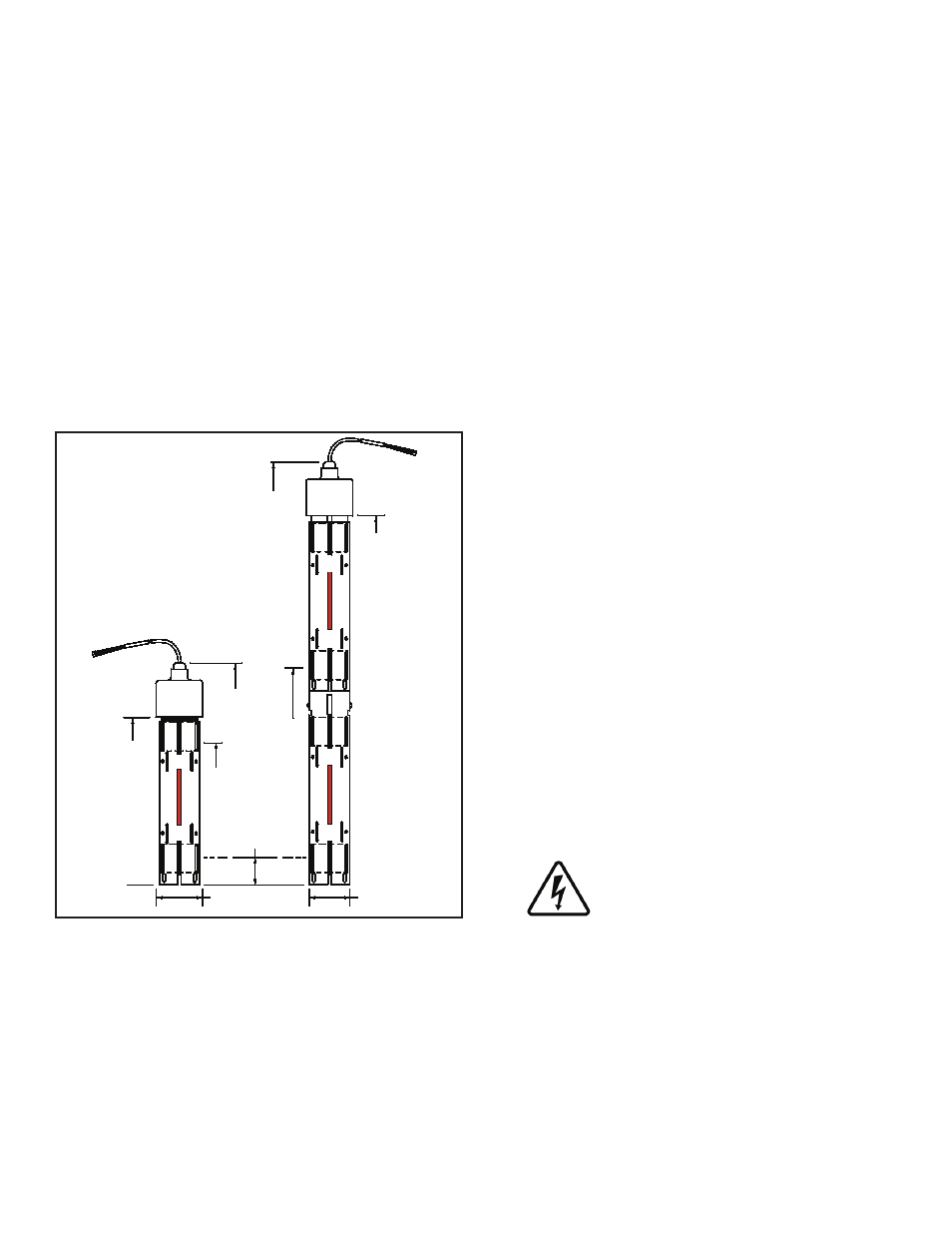
21.7 Inch
(551.2 mm)
2.5 inch (63.5 mm)
Max. dia. [ typ ]
TSP-DDS
Discriminating
Dispenser sump
Sensor
(Britesensor
®
)
Datum
8.86 inch (225 mm)
Length of detection
7.5 inch
(190.5 mm)
High level
1.0 inch
(25.4 mm)
Low level
11.8 inch
(299 mm)
2.38 inch (60.5 mm)
Dia. [ Typ ]
11.0 inch
(279.4 mm)
High level
18.76 inch (476.5 mm)
Length of detection
TSP-DTS
Discriminating
Turbine sump
Sensor
(Britesensor
®
)
Figure 1: TSP-DDS and DTS dimensions
No-strip electrical wire connectors, 25 feet of cable
attached to the sensor, a Model ID tag, and a cord-grip
fitting for connection to a weatherproof electrical junction
box are supplied with the sensors (see diagrams).
Testing the Sensors
Turn the sensor so the bottom faces up (both floats are
actuated) – the WATER and SUMP FULL alarms will
be generated. Although sensors may be washed and
recovered after exposure to liquid hydrocarbons, we
recommend not testing for product alarms because of the
long after-test recovery period involved.
Test sensors on a yearly basis, or more frequently if
required by local code.
Materials Required
Optional – TSP-DB1 epoxy seal kit for no-strip electrical
•
connectors – recommended for sites: within flood zones,
high groundwater tables, with poor drainage, or when
junction boxes are not used.
Optional – Model TSP-KS a unistrut-mounting-kit is
•
recommended for mounting the sensors (See Figures 2
and 3).
• ½ or ¾ inch NPT (National Pipe Thread, tapered), Rigid
Metal Conduit (RMC) or nonmetallic (PVC) if allowed by
local code.
EYS Seal fittings and Epoxy to fill the fitting after
•
operational testing is completed.
Weatherproof junction box, gasket, and cover, plus a
•
¾ to ½
inch NPT reducing bushing if ½ inch RMC is
used – see the ATG Installation Guide for recommended
electrical junction boxes
Wire: THHN, TFFN or THWN, 18 AWG: Red, White, &
•
Black, or Alpha Cable # 58113, (3.3 mm) 0.131” O.D.
1,500 feet (457 meters) max. length. Alpha cable 58113
must be used if using nonmetallic (PVC) conduit.
Slip joint pliers to seat the no-strip, self-sealing wire
•
connectors – connectors are supplied with the sensor
U.L. classified thread sealant or pipe dope.
•
Installation Sequence
1. Install sensor in sump.
2. Install conduit, EYS fittings, and weatherproof
junction box.
3. Shut off power.
ELECTRICAL DANGER Avoid electrical
shock hazards: ensure all power
going to the ATG console is turned off,
tagged, and locked-out at the power
panel before doing any maintenance or
installation work at the ATG console
4. Install the sensor cable through the supplied
compression fitting.
5. Install the compression fitting at the waterproof
junction box and tighten the cord-grip fitting.
6. Trim wire/cables at the junction box to a 6 or 8 inch
length (15 or 20 cm) or service-loop, and splice the
sensor and console wires together per Figure 4.
7. Power up console for next step.
2
