Thermal considerations – GE Industrial Solutions Austin Minilynx SIP User Manual
Page 14
Data Sheet
October 2, 2009
Austin MiniLynx
TM
SIP Non-isolated Power Modules:
2.4 – 5.5Vdc input; 0.75Vdc to 3.63Vdc Output; 3A output current
LINEAGE
POWER
14
Thermal Considerations
Power modules operate in a variety of thermal
environments; however, sufficient cooling should always
be provided to help ensure reliable operation.
Considerations include ambient temperature, airflow,
module power dissipation, and the need for increased
reliability. A reduction in the operating temperature of
the module will result in an increase in reliability. The
thermal data presented here is based on physical
measurements taken in a wind tunnel. The test set-up
is shown in Figure 35. Note that the airflow is parallel to
the long axis of the module as shown in figure 34. The
derating data applies to airflow in either direction of the
module’s long axis.
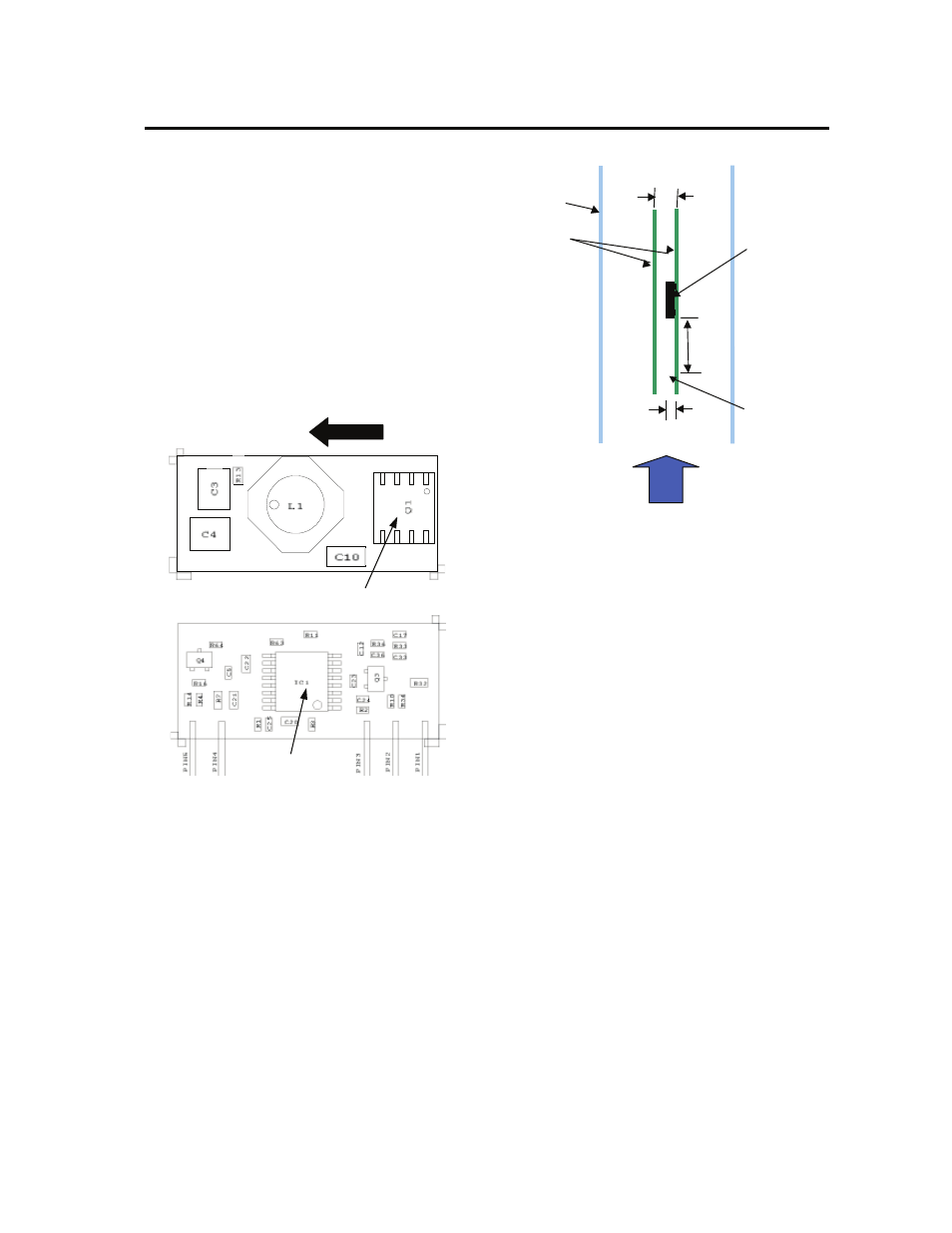
Tref2
Tref1
Airflow
Figure 34. Tref Temperature measurement location.
The thermal reference point, T
ref
used in the
specifications is shown in Figure 34. For reliable
operation this temperature should not exceed 115
o
C.
The output power of the module should not exceed the
rated power of the module (Vo,set x Io,max).
Please refer to the Application Note “Thermal
Characterization Process For Open-Frame Board-
Mounted Power Modules” for a detailed discussion of
thermal aspects including maximum device
temperatures.
Figure 35. Thermal Test Set-up.
Air
flow
x
Power Module
Wind Tunnel
PWBs
5.97_
(0.235)
76.2_
(3.0)
Probe Location
for measuring
airflow and
ambient
temperature
25.4_
(1.0)
