Car2548fp series rectifier, Data sheet, Digital feature descriptions – GE Industrial Solutions CAR2548FP series User Manual
Page 8
GE
Data Sheet
CAR2548FP series rectifier
Input: 90Vac to 264Vac; Output: 48Vdc @ 2500W; 3.3Vdc or 5 Vdc @ 1A
March 28, 2013
©2013 General Electric Company. All rights reserved.
Page 8
resistor. The end user should add additional pull up resistance
as necessary to ensure that rise and fall time timing and the
maximum sink current is in compliance to the I²C
specifications.
Serial Data (SDA):
This line is a bi-directional data line. . This
signal is pulled up internally to 3.3V by a 10kΩ resistor. The
end user should add additional pull up resistance as
necessary to ensure that rise and fall time timing and the
maximum sink current is in compliance to the I²C
specifications.
Digital Feature Descriptions
PMBus™ compliance:
The power supply is fully compliant to
the Power Management Bus (PMBus™) rev1.2 requirements.
Manufacturer specific commands located between addresses
0xD0 to 0xEF provide instructions that either do not exist in
the general PMBus specification or make the communication
interface simpler and more efficient.
Master/Slave:
The ‘host controller’ is always the MASTER.
Power supplies are always SLAVES. SLAVES cannot initiate
communications or toggle the Clock. SLAVES also must
respond expeditiously at the command of the MASTER as
required by the clock pulses generated by the MASTER.
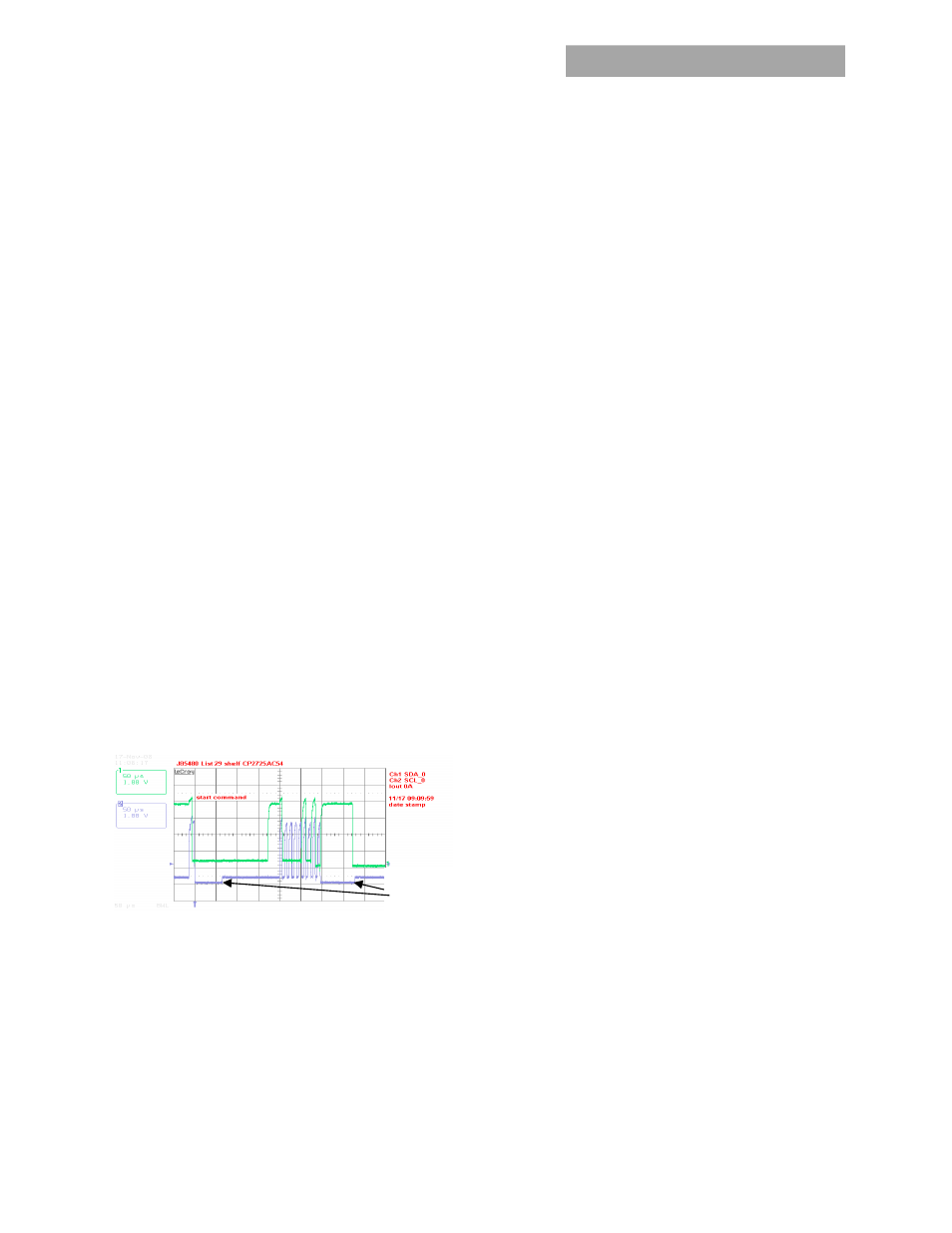
Clock stretching:
The ‘slave’ µController inside the power
supply may initiate clock stretching if it is busy and it desires
to delay the initiation of any further communications. During
the clock stretch the ‘slave’ may keep the clock LO until it is
ready to receive further instructions from the host controller.
The maximum clock stretch interval is 25ms.
The host controller needs to recognize this clock stretching,
and refrain from issuing the next clock signal, until the clock
line is released, or it needs to delay the next clock pulse
beyond the clock stretch interval of the power supply.
Note that clock stretching can only be performed after
completion of transmission of the 9
th
ACK bit, the exception
being the START command.
Figure 1. Example waveforms showing clock stretching.
I
²C Bus Lock-Up detection:
The device will abort any
transaction and drop off the bus if it detects the bus being
held low for more than 35ms.
Communications speed:
Both 100kHz and 400kHz clock
rates are supported. The power supplies default to the
100kHz clock rate. The minimum clock speed specified by
SMBus is 10 kHz.
Packet Error Checking (PEC):
Although the power supply will
respond to commands with or without the trailing PEC, it is
highly recommended that PEC be used in all communications.
The integrity of communications is compromised if packet
error correction is not employed. There are many functional
features, including turning OFF the main output, that should
require validation to ensure that the correct command is
executed.
PEC is a CRC-8 error-checking byte, based on the polynomial
C(x) = x
8
+ x
2
+ x + 1, in compliance with PMBus™
requirements. The calculation is based in all message bytes,
including the originating write address and command bytes
preceding read instructions. The PEC is appended to the
message by the device that supplied the last byte.
SMBAlert#
:
The µC driven SMBAlert# signal informs the
‘master/host’ controller that either a STATE or ALARM change
has occurred. Normally this signal is HI. The signal will change
to its LO level if the power supply has changed states and the
signal will be latched LO until the power supply either receives
a ‘clear’ instruction as outlined below or executes a READ
STATUS_WORD. If the alarm state is still present after the
STATUS registers were reset, then the signal will revert back
into its LO state again and will latch until a subsequent reset
signal is received from the host controller.
The signal will be triggered for any state change, including
the following conditions;
VIN under or over voltage
Vout under or over voltage
IOUT over current
Over Temperature warning or fault
Fan Failure
Communication error
PEC error
Invalid command
Detected internal faults
The power supply will clear the SMBusAlert# signal (release
the signal to its HI state) upon the following events:
Receiving a CLEAR_FAULTS command
The main output recycled (turned OFF and then ON) via
the ENABLE signal pin
The main output recycled (turned OFF and then ON) by
the OPERATION command
Execution of a READ of the STATUS_WORD register
Global broadcast:
This is a powerful command because it
can instruct all power supplies to respond simultaneously in
one command. But it does have a serious disadvantage. Only
a single power supply needs to pull down the ninth
acknowledge bit. To be certain that each power supply
responded to the global instruction, a READ instruction should
be executed to each power supply to verify that the
command properly executed. The GLOBAL BROADCAST
command should only be executed for write instructions to
slave devices.
Read back delay:
The power supply issues the SMBAlert #
notification as soon as the first state change occurred.
During
an event a number of different states can be transitioned to
before the final event occurs. If a read back is implemented
rapidly by the host a successive SMBAlert# could be triggered
by the transitioning state of the power supply. In order to
avoid successive SMBAlert# s and read back and also to
avoid reading a transitioning state, it is prudent to wait more
than 2 seconds after the receipt of an SMBAlert# before
Clock
Stretch
