OSRAM OPTOTRONIC Constant current LED power supplies with 3DIM User Manual
Page 34
34
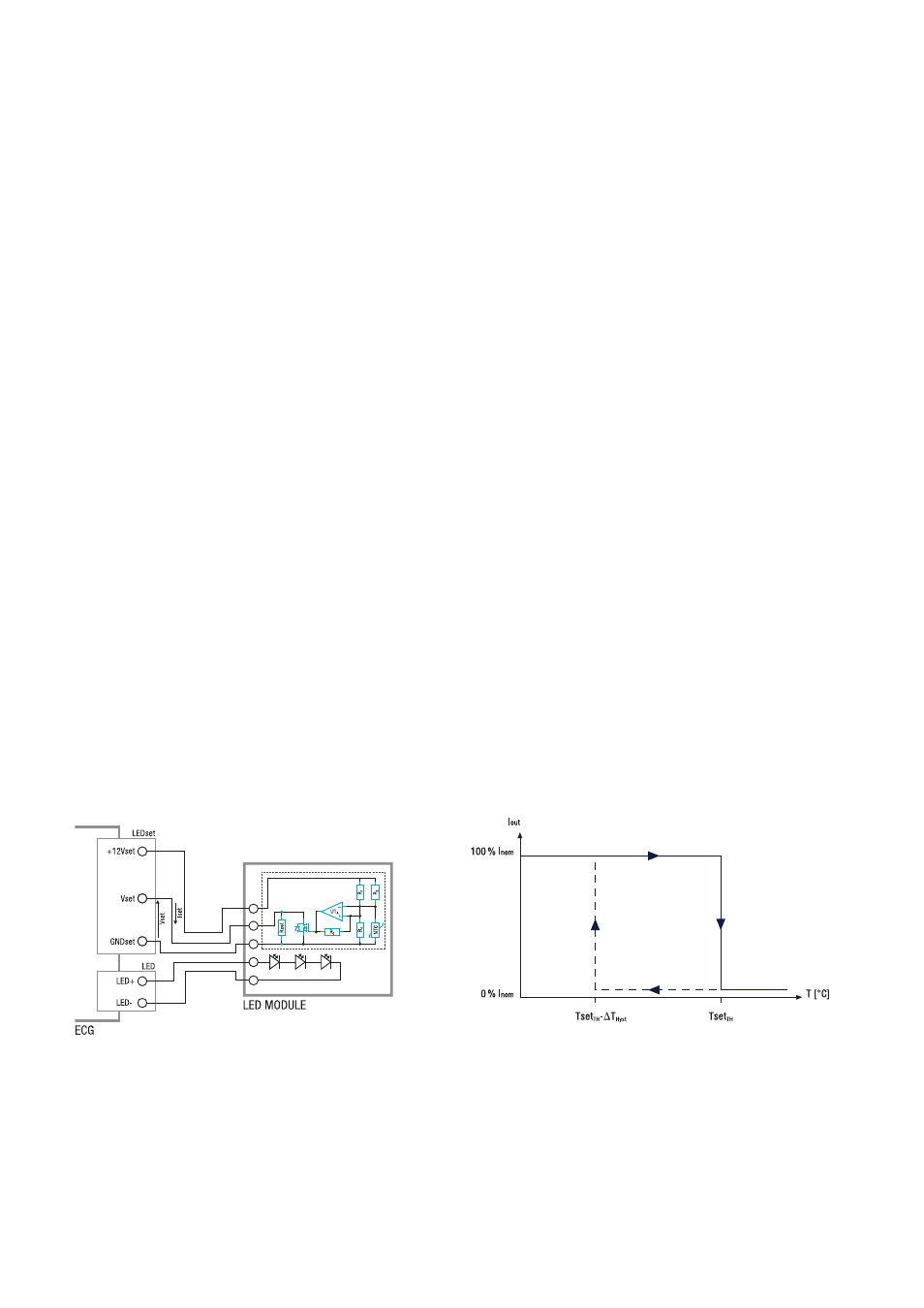
3.3.2. Overtemperature protection (discrete NTC)
3.3.2.1. Application solution 1 –
overtemperature protection by comparator
The application solutions analyzed in 3.3.1. show the imple-
mentation of the LED module’s overtemperature protection
by means of a dedicated IC chip that integrates the tempera-
ture sensing. Similar results can be achieved by implementing
electronic circuits based on a discrete NTC component and
an OPAMP (operation amplifi er) which acts like a comparator.
Benefi ts of this solution:
• The cost of the circuit components is lower.
• In some applications, the sensing component needs to be
placed very close to the LED or in other places where
space can be a problem. The use of a discrete NTC
(i.e. an SMD NTC) can solve this issue.
• It allows the implementation of continuous derating
functions (not only steps of Iout).
Drawbacks:
• The NTC resistance variation needs to be converted into a
useful signal according to the operating range of the Vset
characteristic. This implies the need for a higher number of
(low-cost) components.
• Depending on the complexity, the tuning of the circuit de-
sign needs more time, especially concerning the variation
of the Vset output with respect to the tolerance of the dis-
crete components used.
This chapter shows how an overtemperature protection
circuit can be implemented by using an OPAMP IC in posi-
tive feedback confi guration (acting like a comparator).
LEDset APPLICATIONS
Figure 27: Thermal derating – NTC + OPAMP solution.
Figure 28: NTC + OPAMP solution – output characteristic.
