Data transmission formats used in binary mode – Toshiba TOSVERT VF-S11 User Manual
Page 13
E6581222
11
4.1.2. Data transmission formats used in binary mode
A communication number is used to specify a data item, data is written in hexadecimal form, and
data in transmission characters are represented by binary codes (HEX codes).
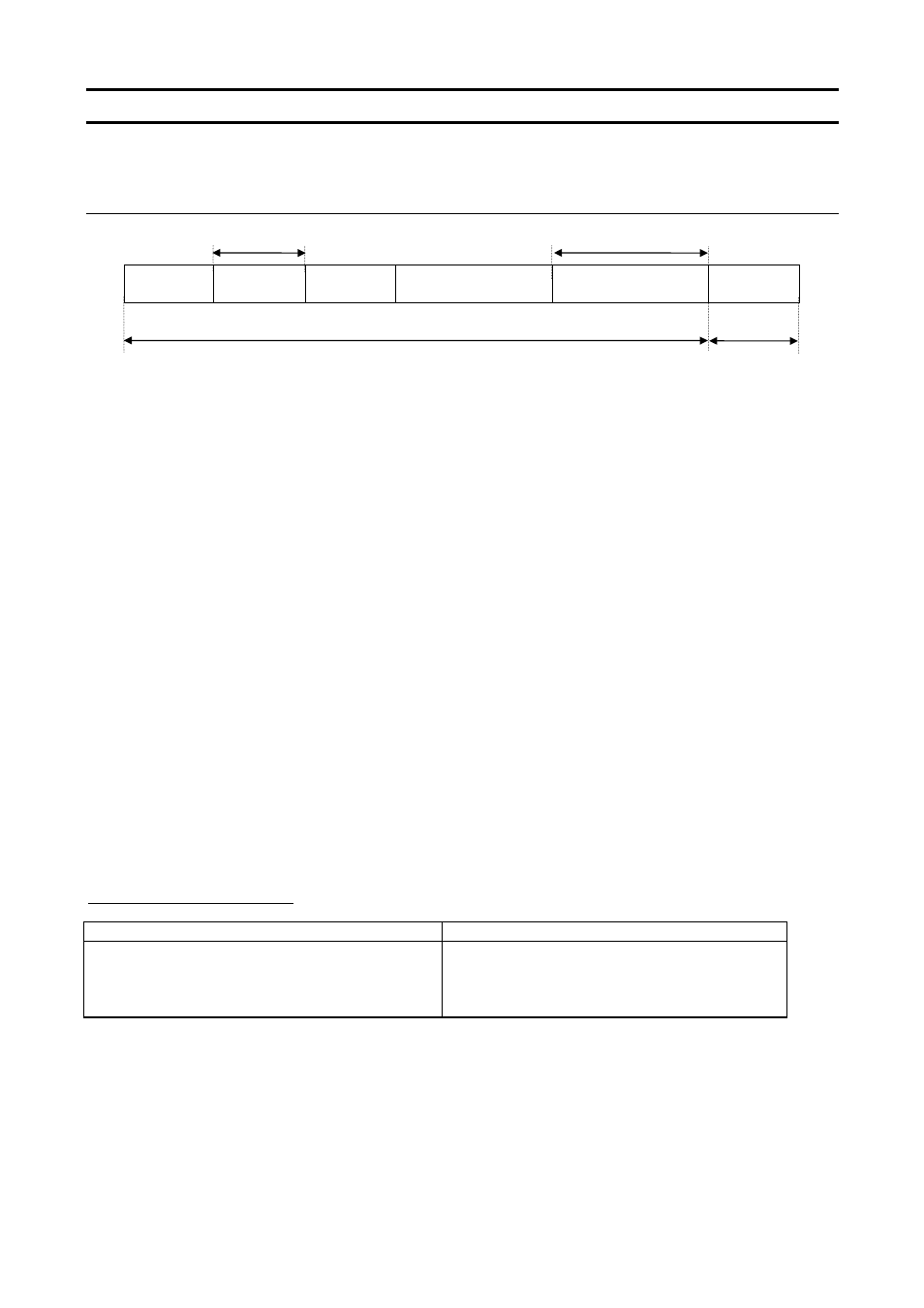
■ Computer
→ VF-S11 (binary mode)
Omissible in one-to-one communications
No data for the 52H (R) command
“/”
(2FH)
INV-NO
1 byte
CMD
1 byte
Communication No.
2 bytes
DATA
2 bytes
SUM
1 byte
Checksum area
Not omissible
1. 2FH (“/”) (1 byte) : Start code in binary mode
2. INV-NO (2 bytes) : Inverter number (Omissible in one-to-one communications) ... 00H to 3FH ,FFH
In case the inverter number is other than FFH (broadcast communication), command is ex-
ecuted only when the inverter number coincides with the one designated with the panel. If
the inverter number is not matched, it will be judged invalid and the data is not returned.
3. CMD (1 byte)
: Command (For details, see the table below.)
52H (R) command: The size of the data following CMD is fixed to 3 bytes. (Communication
number: 2 bytes, checksum: 1 byte)
57H (W), 50H (P) and 47H (G) commands: The size of the data following CMD is fixed to 5
bytes.
(Communication number: 2 bytes, data: 2 byte, checksum: 1 byte)
Any command other than the above is rejected and no error code is returned.
4. Communication No.(2 bytes)
: Communication number (See 11, “Parameter data.”)
5. Data (2 bytes)
: 0000H to FFFFH
57H (W) and 50H (P) commands: Write data (An area check is performed.)
47H (G) command: Dummy data (e.g., 0000) is needed.
52H (R) command: Any data is judged invalid. (No data should be added.)
6. Sum (2 bytes)
: Checksum (not omissible) 00H to FFH
Value of the last two digits (1 byte) of the sum of a series of bits (codes) from the start code
of the data returned to the data (or to the communication number for the 52H (R) command)
Ex.: 2F 52 00 ?? ... 2FH+52H+00H+00H=81H
The last two digits (??) represent the checksum. = 81
■ Details of commands and data
CMD (1 byte)
Write data (2 bytes) Hexadecimal number
52H (R): RAM read command
57H (W): RAM/EEPROM write command
50H (P): RAM write command
47H (G): RAM read command (for two-wire networks)
No data
Write data (0000H to FFFFH)
Write data (0000H to FFFFH)
Dummy data (0000H to FFFFH)
