See igbt operation and, Theory of operation, Insulated gate bipolar transistor (igbt) operation – Lincoln Electric V155-S User Manual
Page 30
THEORY OF OPERATION
E-6
E-6
INVERTEC® V155-S
INSULATED GATE BIPOLAR
TRANSISTOR (IGBT) OPERATION
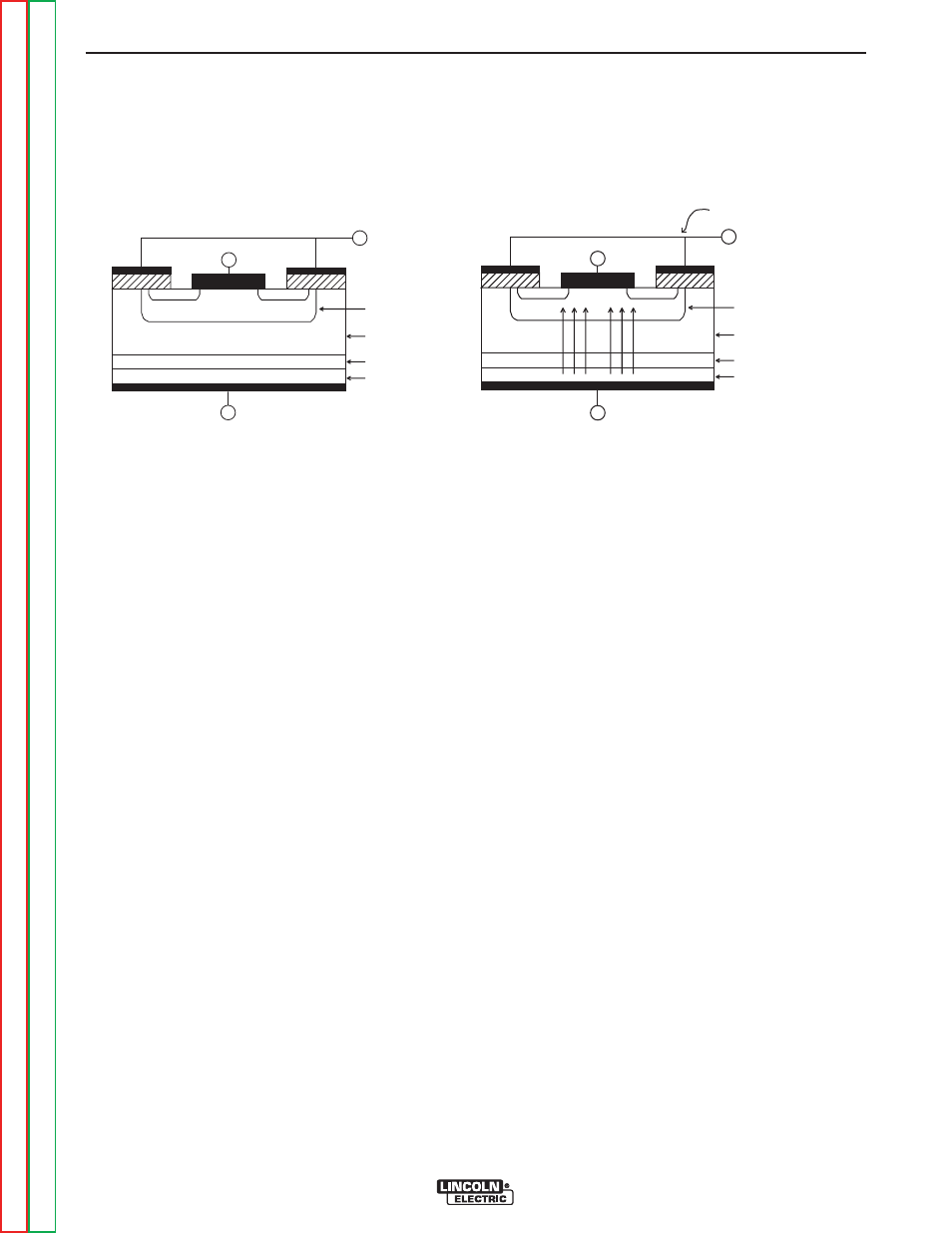
An IGBT is a type of transistor. IGBTs are semicon-
ductors well suited for high frequency switching and
high current applications.
Drawing A shows an IGBT in a passive mode. There is
no gate signal, zero volts relative to the source, and
therefore, no current flow. The drain terminal of the
IGBT may be connected to a voltage supply; but since
there is no conduction the circuit will not supply current
to components connected to the source. The circuit is
turned off like a light switch in the OFF position.
Drawing B shows the IGBT in an active mode. When
the gate signal, a positive DC voltage relative to the
source, is applied to the gate terminal of the IGBT, it is
capable of conducting current. A voltage supply con-
nected to the drain terminal will allow the IGBT to con-
duct and supply current to circuit components coupled
to the source. Current will flow through the conducting
IGBT to downstream components as long as the posi-
tive gate signal is present. This is similar to turning ON
a light switch.
FIGURE E.6 – IGBT OPERATION
DRAIN
SOURCE
GATE
INJECTING LAYER
BUFFER LAYER
DRAIN DRIFT REGION
BODY REGION
p +
n +
n -
p
n +
n +
DRAIN
SOURCE
GATE
INJECTING LAYER
BUFFER LAYER
DRAIN DRIFT REGION
BODY REGION
p +
n +
n -
p
n +
n +
POSITIVE
VOLTAGE
APPLIED
B. ACTIVE
A. PASSIVE
