3 tos/dscp – PLANET FGSD-1022 User Manual
Page 122
User’s Manual of FGSD-1022 Series
4.9.3 TOS/DSCP
TOS/DSCP priority is obtained through a 6-bit Type-of-Service (TOS) or Differentiated Service Code Point (DSCP) to
3-bit priority mapping.
The Type of Service (TOS) octet in the IPv4 header is divided into three parts; Precedence (3 bits), TOS (4 bits), and MBZ
(1 bit). The Precedence bits indicate the importance of a packet, whereas the TOS bits indicate how the network should
make tradeoffs between throughput, delay, reliability, and cost (as defined in RFC 1394). The MBZ bit (for “must be zero”) is
currently unused and is either set to zero or just ignored.
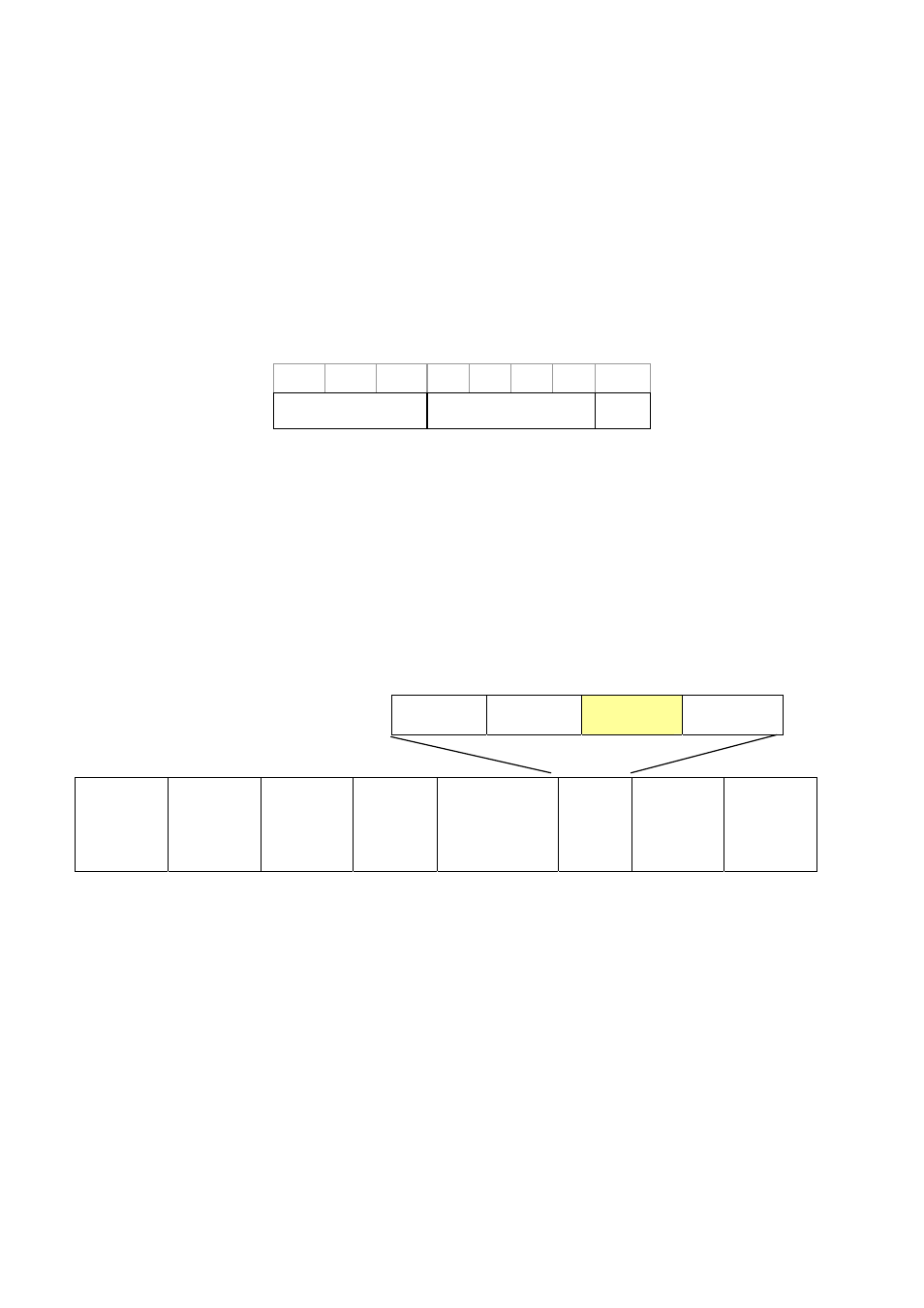
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Precedence TOS
MBZ
IPv4 Packet Header Type of Service Octet
The four TOS bits provide 15 different priority values, however only five values have a defined meaning.
DiffServ Code Point (DSCP)
- is the traffic prioritization bits within an IP header that are encoded by certain applications
and/or devices to indicate the level of service required by the packet across a network. DSCP are defined in RFC2597 for
classifying traffic into different service classes. The Managed Switch extracts the codepoint value of the DS field from IPv4
packets and identifies the priority of the incoming IP packets based on the configured priority.
4 bit
4 bit
6 bit
2 bit
122
VER=0100
Header Size
DiffServ
RES
Preamble
Destination
Address
Source
Address
VLAN
TAG
(Optional)
Ethernet Type
(0800)
Data FCS
6 bytes 6 bytes
4 bytes
2 bytes
2 bytes
46-1517 bytes
4 bytes
Figure 4-9-4:
IPv4 frame format
The DSCP is six bits wide, allowing coding for up to 64 different forwarding behaviors. The DSCP retains backward
compatibility with the three precedence bits so that non-DSCP compliant, TOS-enabled devices, will not conflict with the
DSCP mapping. Based on network policies, different kinds of traffic can be marked for different kinds of forwarding.
