Load sharing, Vrrp load balancing mode – H3C Technologies H3C S6800 Series Switches User Manual
Page 28
20
Load sharing
A router can join multiple VRRP groups and has different priorities in different VRRP groups, and it can act
as the master in one VRRP group and a backup in another.
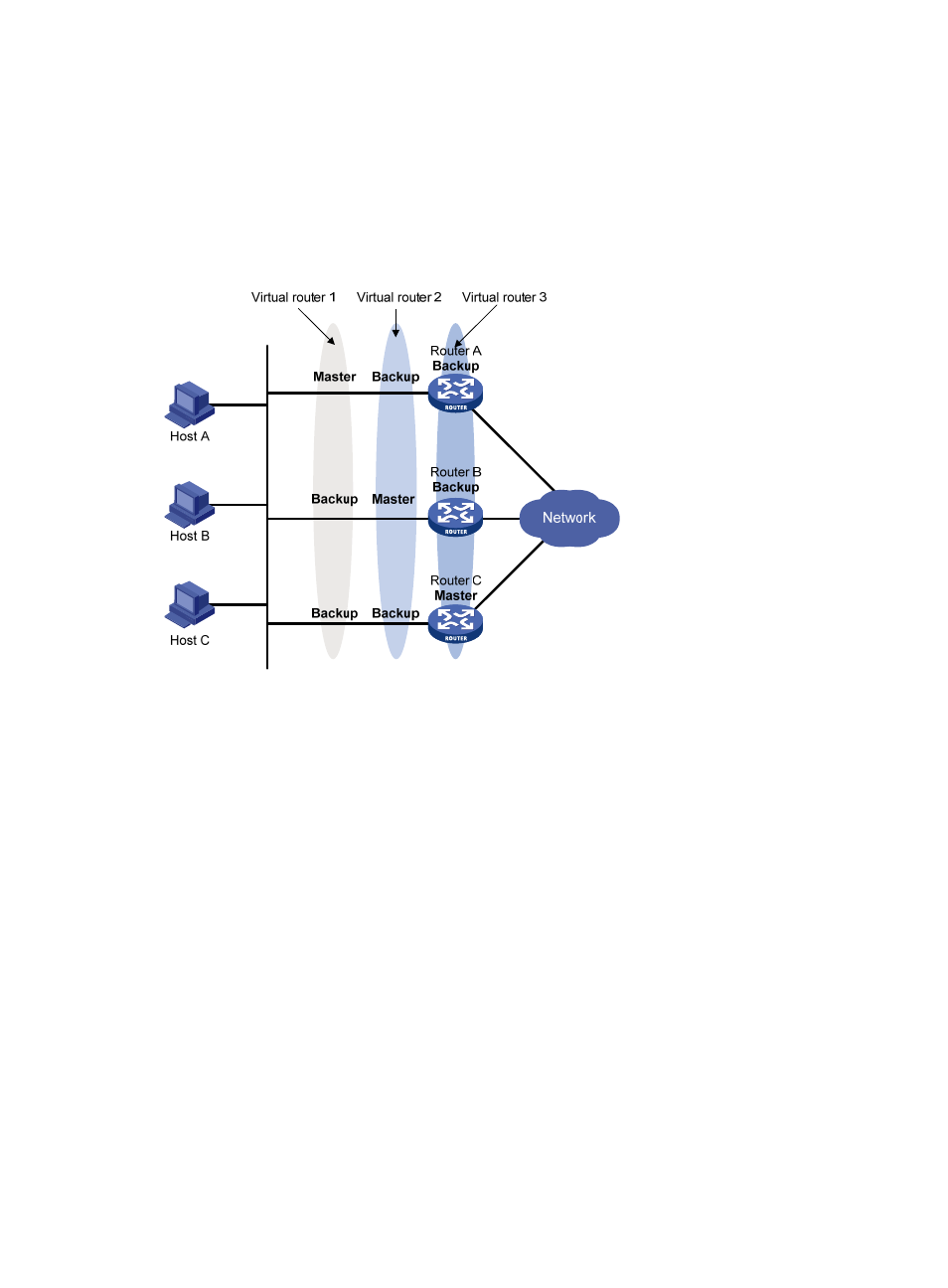
In load sharing mode, multiple VRRP groups provide gateway services. This mode requires at least two
VRRP groups, and each group has one master and multiple backups. The master roles in the VRRP groups
are assumed by different routers, as shown in
.
Figure 10 Load sharing of VRRP
A router can be in multiple VRRP groups and have a different priority in each group.
As shown in
, the following VRRP groups are present:
•
VRRP group 1—Router A is the master. Router B and Router C are the backups.
•
VRRP group 2—Router B is the master. Router A and Router C are the backups.
•
VRRP group 3—Router C is the master. Router A and Router B are the backups.
To implement load sharing among Router A, Router B, and Router C, hosts on the subnet must be
configured with the virtual IP addresses of VRRP group 1, 2, and 3 as default gateways, respectively.
When you configure them, make sure that each router is assigned an appropriate priority in each VRRP
group so that each router can take the expected role in each group.
VRRP load balancing mode
In a standard-mode VRRP group, only the master can forward packets and backups are in listening state.
You can create multiple VRRP groups to share traffic, but you must configure different gateways for hosts
on the subnet.
In load balancing mode, a VRRP group maps its virtual IP address to multiple virtual MAC addresses,
assigning one virtual MAC address to each member router. Every router in this VRRP group can forward
traffic and respond to IPv4 ARP requests or IPv6 ND requests from hosts. Because their virtual MAC
