AML MT7570 Vehicle Mount Computer User Manual
Page 69
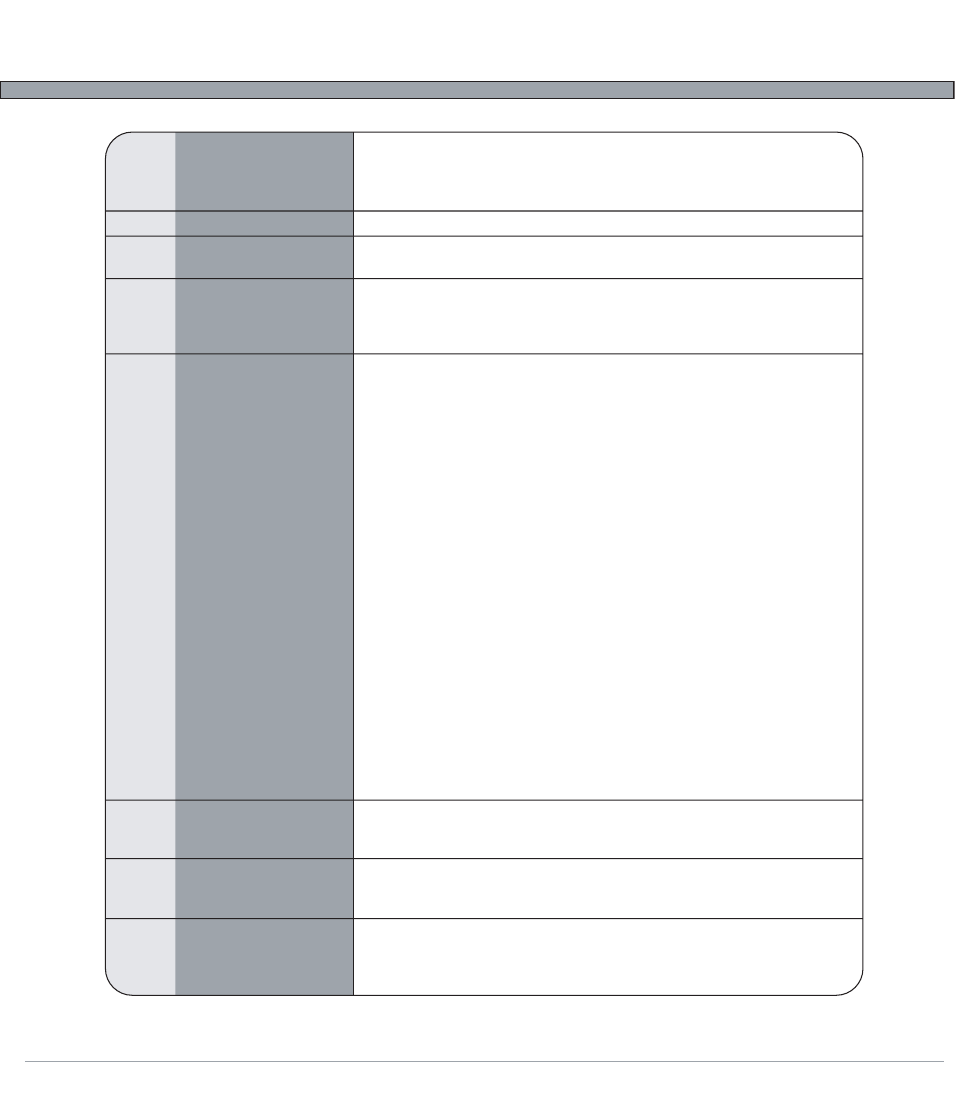
Encryption & Algorithm Overview
USER’S GUIDE
MT7570 Vehicle Mount Terminal
WPA2
(cont’d)
802.11i
TKIP
CCMP
(AES)
EAP
PSK
802.1x
RADIUS
Wifi Protected Access
Version 2 (cont’d)
IEEE 802.11i Standard
Temporal Key Integrity
Protocol
Counter Mode with
Cipher Block Chaining
Message Authentica-
tion Code Protocol
Extensible
Authentication Protocol
Pre-shared Key
IEEE 802.1x
Remote Authentication
Dial In User Service
The CCMP algorithm is the heart of WPA2 and is what sets it apart from WPA.
CCMP was designed to replace both TKIP and WEP, and handles message integ-
rity, encryption, and authentication. Most, if not all of the capabilities of WPA can
be implemented in WPA2 with CCMP, which is considered state of the art.
The IEEE standard. Commonly called WPA2.
Dynamic key rotation algorithm often used in WPA environments.
Encipherment algorithm designed to replace TKIP and WEP in WPA2/802.11i.
CCMP is considered state of the art.
EAP is a general authentication method that can be used in many technologies, but
it is most commonly found in wireless LANs. A large amount of documentation
refers to WPA-EAP as “WPA Enterprise” even though it is an ambiguous term.
There are many subtypes of EAP, but only five have been described as standard.
The MT7570 supports the following EAP types for authentication.EAP-TLS – EAP
Transport Layer Security is the original standard wireless LAN EAP authentication
protocol. Although it is rarely deployed, it is still considered one of the most secure
EAP standards available and is universally supported by all manufacturers of
wireless LAN hardware and software. The requirement for a client-side certificate,
however unpopular it may be, is what gives EAP-TLS its authentication strength
and illustrates the classic convenience vs. security trade-off. EAP-TTLS - Tunneled
Transport Layer Security was co-developed by Funk Software and Certicom and is
widely supported across platforms. It was never fully ratified, only drafted (the draft
which has since expired), but is still common due to its decent level of security and
easy setup.
EAP-PEAP - Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol is widely available in
products, and provides very decent authentication security. Its method is similar in
design to EAP-TTLS but requires only a server-side certificate to create a secure
tunnel to protect user authentication. PEAPv0/EAP-MSCHAPv2 is what most are
referring to when the term “PEAP” is used. Behind EAP-TLS, PEAPv0/EAP-
MSCHAPv2 is the second most widely supported EAP standard in the world.
EAP-LEAP - The Lightweight Extensible Authentication Protocol (LEAP) is a propri-
etary EAP method developed by Cisco Systems, Inc. It is considered less secure
than other EAP types, even by Cisco, and is not recommended in new installations.
Often called “WPA/WPA2 Personal”, PSK allows the use of common passphrases
for authentication. PSK is often used in smaller networks that wish to use the high
security of WPA/WPA2 but do not wish to employ an 802.1x authentication server.
IEEE Standard for authentication. Often in wireless documentation, references to
“802.1x” are really meaning 802.1x Authentication server or RADIUS server that
provides authentication and encryption keys to the clients.
Often, administrators will call the 802.1x server the “RADIUS” server. RADIUS is an
authentication, authorization, and accounting protocol for applications such as
network access or IP mobility. In the wireless LAN environment, RADIUS is com-
monly used to implement the 802.1x standard.
