Fan rpm, Vibration, Hot gas bypass valve (standard scroll) – Greenheck ERCH (476054) User Manual
Page 34: Belt drive installation, Direction of fan wheel rotation, Warning
General Description - NOT model specific
Model ERCH Energy Recovery Ventilator
®
34
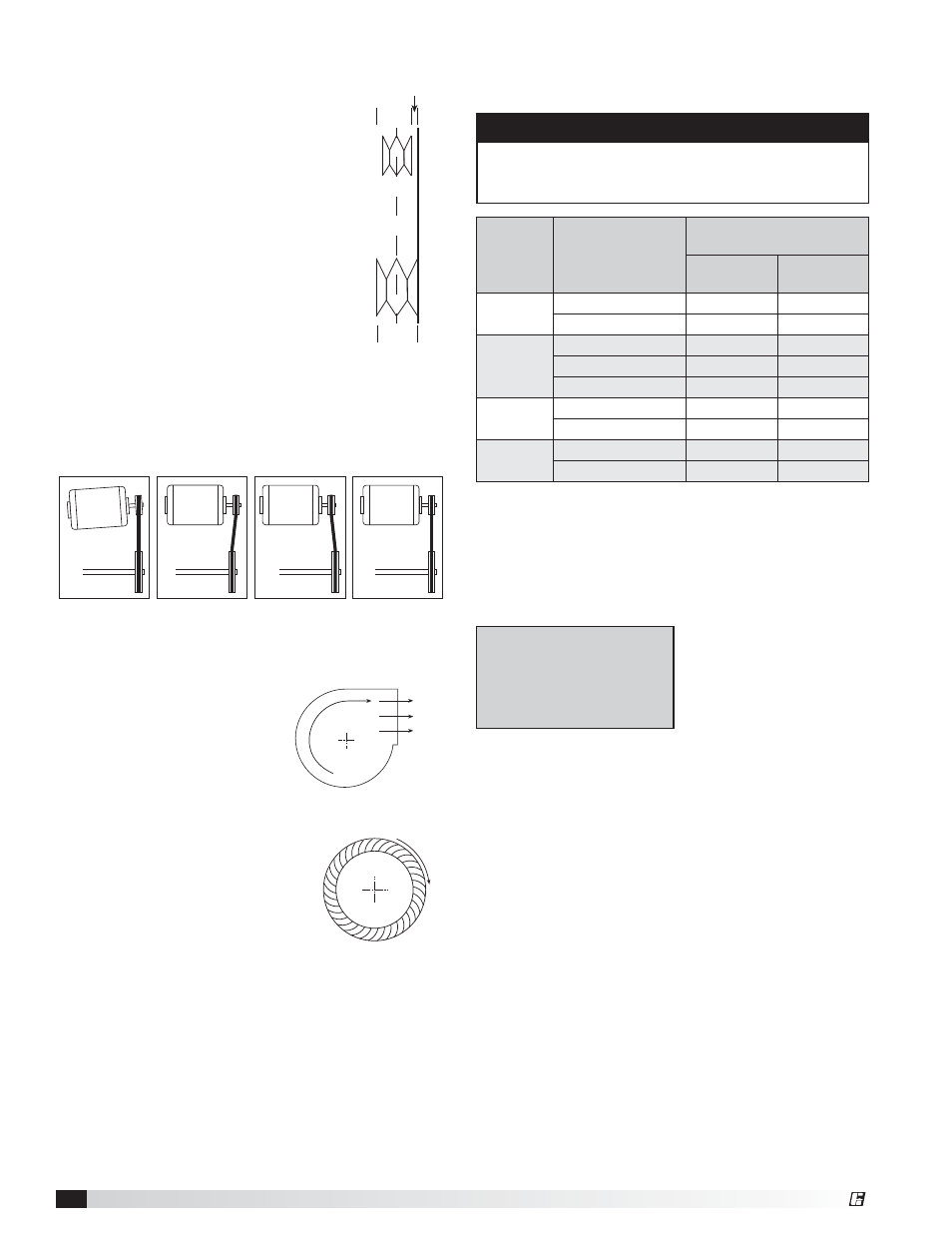
Belt Drive Installation
1. Remove the protective coating from the
end of the fan shaft and assure that it is
free of nicks and burrs.
2. Check fan and motor shafts for parallel
and angular alignment.
3. Slide sheaves on shafts. Do not drive
sheaves on as this may result in bearing
damage.
4. Align fan and motor sheaves with a
straightedge to centerline.
5. Place belts over sheaves. Do not pry
or force belts, as this could result in
damage to the cords in the belts.
6. With the fan off, adjust the belt tension
by moving the motor base. (See belt
tensioning procedures in the Routine
Maintenance section of this manual).
When in operation, the tight side of the belts should
be in a straight line from sheave to sheave with a
slight bow on the slack side.
WRONG
WRONG
WRONG
CORRECT
Proper alignment of motor and drive shaft.
Direction of Fan Wheel Rotation
Blower access is labeled on unit.
Check for proper wheel rotation
by momentarily energizing the
fan. Rotation is determined
by viewing the wheel from the
drive side and should match the
rotation decal affixed to the fan
housing.
If the wheel is rotating the wrong
way, direction can be reversed
by interchanging any two of the
three electrical leads.
Check
for unusual noise, vibration, or
overheating of bearings. Refer to
the Troubleshooting section of this
manual if a problem develops.
Fan RPM
Supply fan and exhaust fan will have an adjustable
motor pulley (on 15 HP and below) preset at the factory
to the customer-specified RPM. Fan speed can be
increased or decreased by adjusting the pitch diameter
of the motor pulley. Multi-groove variable pitch pulleys
must be adjusted an equal number of turns open
or closed. Any increase in fan speed represents a
substantial increase in load on the motor. Always check
the motor amperage reading and compare it to the
amperage rating shown on the motor nameplate when
changing fan RPM. All access doors must be installed
except the control center door.
WARNING
Do not operate units with access doors open or
without proper ductwork in place as the fan motors
will overload.
Model
Blower Diameter
x Width
(inches)
Maximum RPM for
Forward-Curved Blowers
Class I
Max RPM
Class II
Max RPM
ERCH-20
10 x 6
1700
--
9 x 9
1750
2800
ERCH-45
9 x 9
1750
2800
12 x 8
1400
2000
12 x 12
1500
2000
ERCH-55
12 x 12
1500
2000
15 x 15
1250
1725
ERCH-90
15 x 15
1250
1725
18 x 18
1000
1450
Vibration
Excessive vibration may be experienced during initial
start-up and can cause a multitude of problems,
including structural and/or component failure.
Many of these conditions can be discovered by careful
observation. Refer to the Troubleshooting section of
this manual for corrective
actions. If observation
cannot locate the source
of vibration, a qualified
technician using vibration
analysis equipment
should be consulted. If the problem is wheel unbalance,
in-place balancing can be done.
Generally, fan vibration and noise is transmitted to other
parts of the building by the ductwork. To eliminate this
undesirable effect, the use of heavy canvas connectors
is recommended.
Hot Gas Bypass Valve (standard scroll)
To adjust, connect a pressure gauge to the suction line
and block the entering air to the evaporator coil. The
valve should begin to open when the suction pressure
drops to approximately 115 PSIG for R-410A (the valve
will feel warm to the touch). Adjustments are made by
first removing the cap on the bottom of the valve and
then turning the adjusting stem clockwise to increase
the setting pressure (counterclockwise to decrease).
Allow several minutes between adjustments for the
system to stabilize. When adjustment is complete,
replace the cap on the valve.
2 in.
1.5 in.
0.25 in.
centerline
straightedge
Pulley
alignment
example
Vibration Causes
Off axis or loose components
Drive component unbalance
Poor inlet / outlet conditions
Foundation stiffness
Airflow
R
o
ta
ti
o
n
Forward Curved
Rotation
