Dolby Laboratories DP564 User Manual
Page 80
DP564 Multichannel Audio Decoder
Appendix A: Metadata
A-10
It is important to consider the output signals from each piece of equipment that can
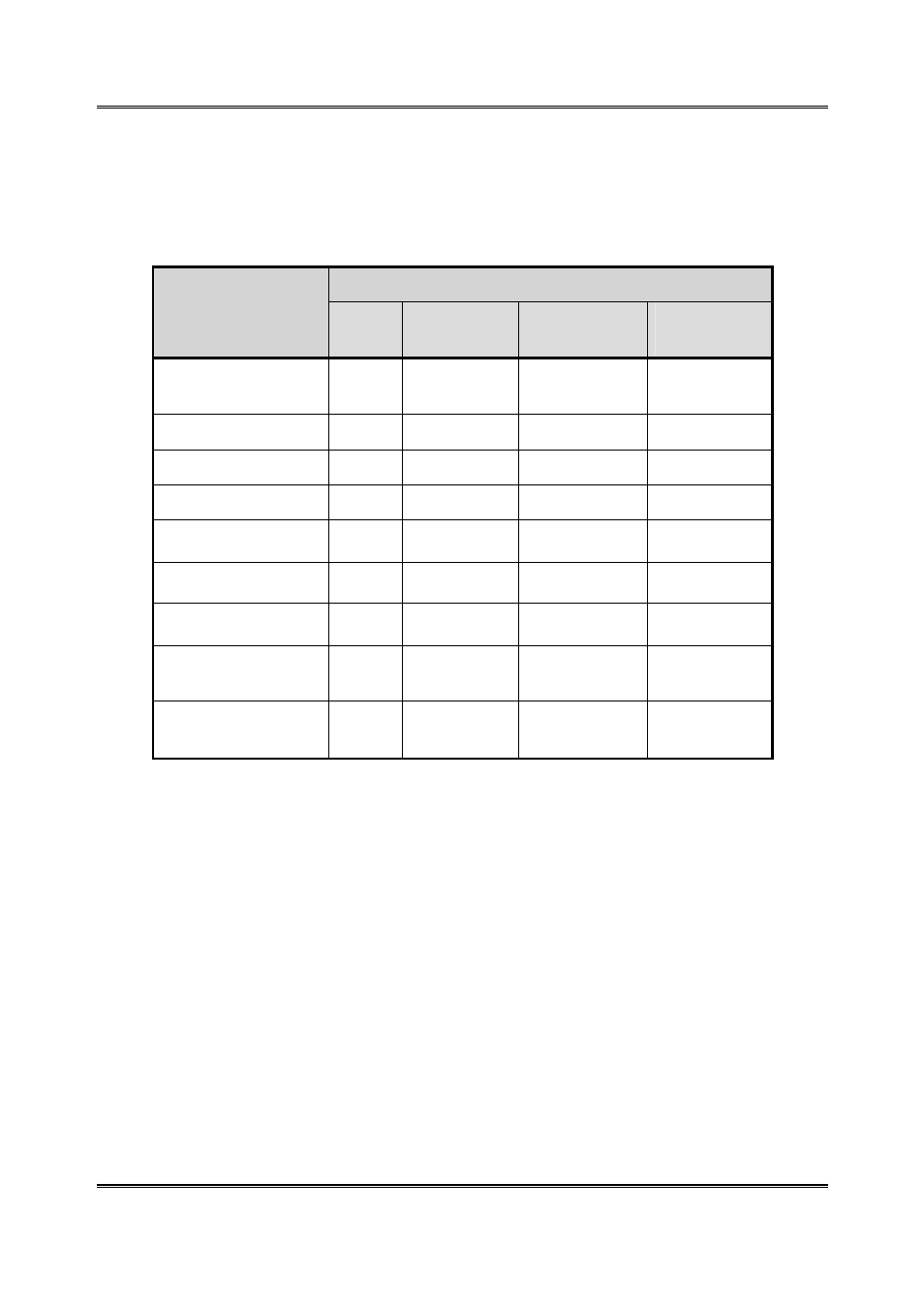
receive a Dolby Digital program in the home. Table A-2 shows the output types from
different equipment.
Table A-2 Outputs from Various Dolby Digital Signal Processing Equipment
Output
Equipment
Digital 5.1-Channel
Analog
Two-Channel
Analog
RF
Remodulated
5.1-channel amplifier
The standard home theater
A/V amp
r
r
5.1-channel decoder
r
r
Hi-end DVD player
r
r
r
DVD player
r
r
PC
Includes games consoles
r
(some units)
r
High-end set-top box
Often HDTV
r
r
r
r
Set-top box
Usually SDTV
r
r
r
IDTV
TV set with an integrated
digital TV tuner
r
r
High-end TV
Large screen TV with a
5.1-channel speaker system
r
r
Set-top boxes, used for the reception of terrestrial, cable, or satellite Digital
Television, typically offer an analog mono signal modulated on the RF/Antenna
output, a line-level analog stereo signal, and an optical or coaxial digital output. DVD
players offer an analog stereo and a digital output, and some offer a six-channel
analog output (for a 5.1-channel presentation). Portable DVD players offer analog
stereo, headphone, and digital outputs. DVD players in computers and game consoles
offer a digital output as well as analog stereo, headphone, and possibly six-channel
analog outputs. 5.1-channel amplifiers, decoders and receivers have six-channel
analog outputs and possibly six speaker-level outputs.
In all of these cases, a Dolby Digital decoder creates the analog audio output signal.
In the case of the set-top box or DVD player, the analog stereo output is a downmixed
version of the Dolby Digital data stream. The digital output delivers the Dolby Digital
data stream to either a downstream decoder or a Dolby Digital capable integrated
amplifier.
