Airflow, Airflow –26 – Altera PowerPlay Early Power Estimator User Manual
Page 38
3–26
Chapter 3: Using Cyclone III PowerPlay Early Power Estimator
Factors Affecting PowerPlay Early Power Estimator Accuracy
PowerPlay Early Power Estimator User Guide for Cyclone III FPGAs
© June 2009 Altera Corporation
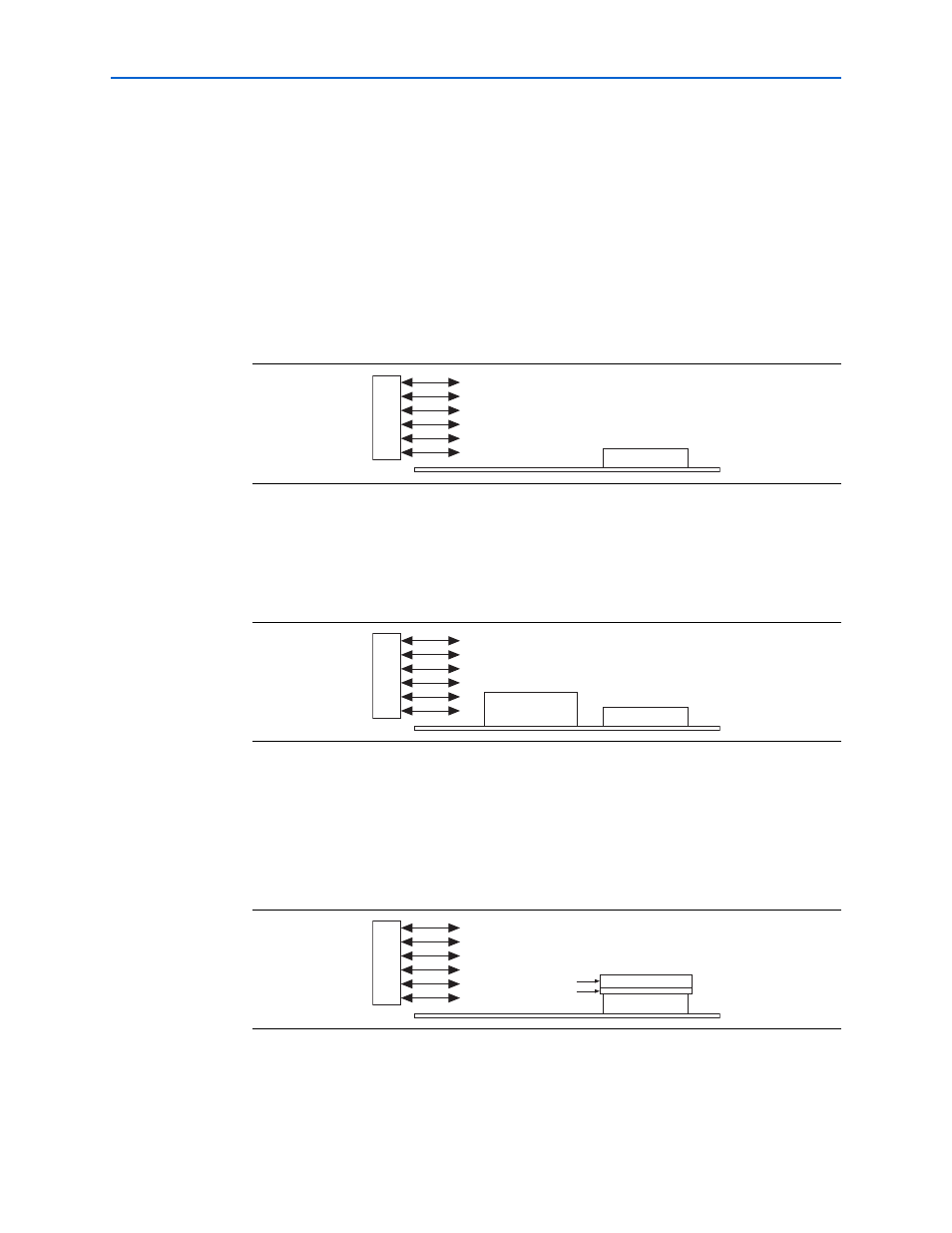
Airflow
The PowerPlay Early Power Estimator allows you to specify the airflow present at the
device. This value affects thermal analysis and bears directly on the power consumed
by the device. To obtain an accurate estimate, you must correctly determine the
airflow at the FPGA, not the output of the fan providing the airflow.
Often it is difficult to place the device adjacent to the fan providing the airflow. In that
case, the path of the airflow is likely to traverse a length on the board before reaching
the device, thus diminishing the actual airflow the device receives. In the example
shown in
Figure 3–21
, a fan is placed at the end of the board. The airflow at the FPGA
is weaker than what it is at the fan.
In many cases, you must also take into consideration blocked airflow. In the following
example (
Figure 3–22
), there is a device blocking the airflow from the FPGA,
significantly reducing the airflow seen at the FPGA. Also, the airflow from the fan
often cools board components and other devices before reaching the FPGA.
If you are using a custom heat sink, there is no need to enter the airflow directly into
the PowerPlay Early Power Estimator, but it is required to compute the
SA
for the heat
sink with the knowledge of what the airflow is at the device. Most heat sinks have fins
located above the heat sink to facilitate airflow.
Figure 3–23
shows the case of an FPGA with a heat sink.
Figure 3–21. Airflow and FPGA Position
Figure 3–22. Airflow with Component and FPGA Positions
Figure 3–23. AirFlow and Heat Sinks
F
A
N
FPGA
F
A
N
FPGA
Device
F
A
N
FPGA
Heat Sink Fins
Heat Sink
