How are they made, Capacitors, The metal foil capacitor – Elenco Electronic Component Kit User Manual
Page 8
-7-
CAPACITORS,
How are they made?
There are many different types of capacitors used in
electronics. Each type is made from different
materials and with different methods. Capacitors
are also made to handle different amounts of
electrical pressure or voltage. Each capacitor is
marked to show the maximum voltage that it can
withstand without breaking down. All capacitors
contain the same fundamental parts, which consist
of two or more conductive plates separated by a
nonconductive material. The insulating material
between the plates is called the dielectric. The basic
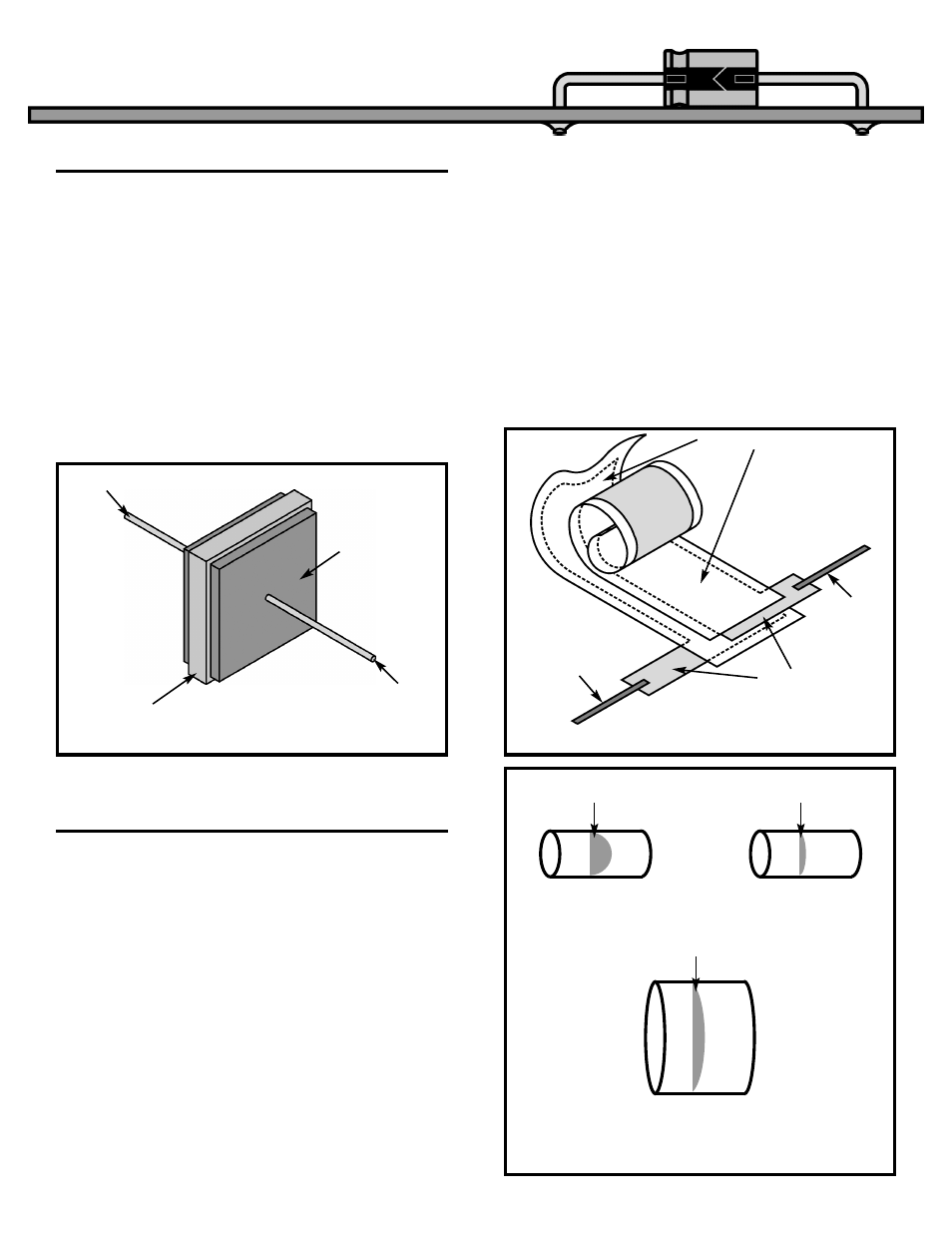
elements necessary to build a capacitor are shown
in Figure 10.
Perhaps the most common form of capacitor is
constructed by tightly winding two foil metal plates
that are separated by sheets of paper or plastic as
shown in Figure 11. By picking the correct insulating
material the value of capacitance can be increased
greatly, but the maximum working voltage is usually
lowered. For this reason, capacitors are normally
identified by the type of material used as the
insulator or dielectric. Consider the water pipe with
the rubber diaphragm in the center of the pipe. The
diaphragm is equivalent to the dielectric in a
capacitor. If the rubber is made very soft, it will
stretch out and hold a large amount of water, but it
will break easily (large capacitance, but low working
voltage). If the rubber is made very stiff, it will not
stretch far, but will be able to withstand higher
pressure (low capacitance, but high working
voltage). By making the pipe larger and keeping the
stiff rubber we can achieve a device that holds a
large amount of water and withstands a high amount
of pressure (high capacitance, high working voltage,
large size). These three types of water pipes are
illustrated in Figure 12. The pipes follow the rule that
the capacity to hold water, (Capacitance) multiplied
by the amount of pressure they can take (Voltage)
determines the size of the pipe. In electronics the
CV product determines the capacitor size.
CAPACITORS
THE METAL FOIL CAPACITOR
Soft Rubber
Figure 12
Stiff Rubber
Stiff Rubber
Larger Size
Large Capacity
Low Pressure
Low Capacity
but can withstand
High Pressure
High Capacity and can withstand High Pressure
Figure 10
Lead 1
Nonconductive Material
Conductive Plate
Lead 2
Figure 11
Lead 1
Paper or Plastic Insulator
Conductive Foil
Lead 2
