Inductors – Elenco Electronic Component Kit User Manual
Page 13
-12-
INDUCTORS
INDUCTORS,
What do they do?
The electronic component known as the inductor is
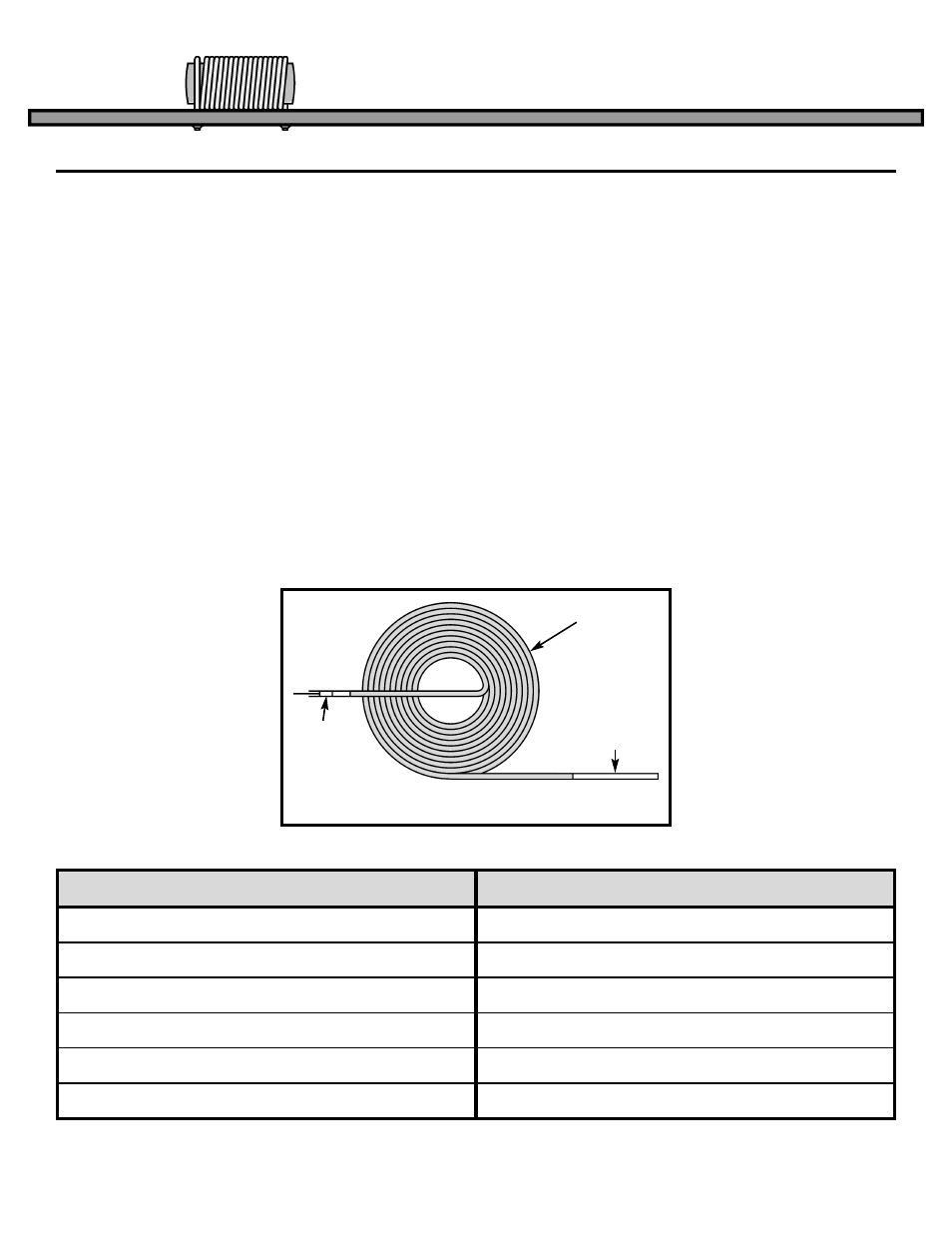
best described as electrical momentum. In our
water pipe analogy the inductor would be equivalent
to a very long hose that is wrapped around itself
many times (see Figure 18). If the hose is very long
it will contain many gallons of water. When pressure
is applied to one end of the hose, the thousands of
gallons of water would not start to move instantly. It
would take time to get the water moving due to
inertia (a body at rest wants to stay at rest). After a
while the water would start to move and pick up
speed. The speed would increase until the friction of
the hose applied to the amount of pressure being
applied to the water. If you try to instantly stop the
water from moving by holding the plunger, the
momentum (a body in motion wants to stay in
motion) of the water would cause a large negative
pressure (Suction) that would pull the plunger from
your hands.
Since Inductors are made by coiling a wire, they are
often called Coils. In practice the names Inductor
and Coil are used interchangeably. From the above
analogy, it is obvious that a coiled hose will pass
Direct Current (DC), since the water flow increases
to equal the resistance in the coiled hose after an
elapsed period of time. If the pressure on the
plunger is alternated (pushed, then pulled) fast
enough, the water in the coil will never start moving
and the Alternating Current (AC) will be blocked.
The nature of a Coil in electronics follows the same
principles as the coiled hose analogy. A coil of wire
will pass DC and block AC. Recall that the nature of
a Capacitor blocked DC and passed AC, the exact
opposite of a coil. Because of this, the Capacitor
and Inductor are often called Dual Components.
Table 5 compares the properties of capacitors and
inductors.
Plunger
Water Pipe
Large Hose Filled
with Water
Figure 18
Capacitor
Inductor
Blocks Direct Current
Blocks Alternating Current
Passes Alternating Current
Passes Direct Current
Voltage in Capacitor cannot change instantly
Current in an Inductor cannot change instantly
Quick Voltage change produces large Current
Quick Current change produces large Voltage
Stores Energy in Electric Field
Stores Energy in Magnetic Field
Current leads Voltage
Voltage leads Current
Table 5
