Capacitors – Elenco Electronic Component Kit User Manual
Page 11
-10-
CAPACITORS
Voltage
1
Code
2
Cap. Value
3
Typical Markings
4 5
Tolerance (%)
6
Markings
7
4
0G
100pF
100pF
101
+5%
J
5.5
0L
.001
μF
.001
102
+10%
K
6.3
0J
.015
μF
.015
152
+20%
M
10
1A
.002
μF
.002
202
–10% +30%
Q
16
1C
.0022
μF
.0022
222
–10% +50%
T
25
1E
.003
μF
.003
302
–20% +80%
Z
35
1V
.033
μF
.033
333
SPECIAL
A
50
1H
.047
μF
.047
473
63
1J
.05
μF
.05
R05
Temperature
Markings
80
1K
.068
μF
.068
R068
100
2A
.1
μF
.1
104
NP0 {<10ppm /
O
C}
110
2Q
.15
μF
.15
154
N100 {<100ppm /
O
C}
125
2B
.2
μF
.2
204
N220 {<220ppm /
O
C}
160
2C
2.2
μF
2.2
2R2
N820 {<820ppm /
O
C}
180
2Z
22
μF
22
22
Y5F
200
2D
100
μF
100
100
Y5T
220
2P
220
μF
220
220
Y5V
250
2E
470
μF
470
470
X5F
315
2F
1000
μF
1000
1000
Z5U
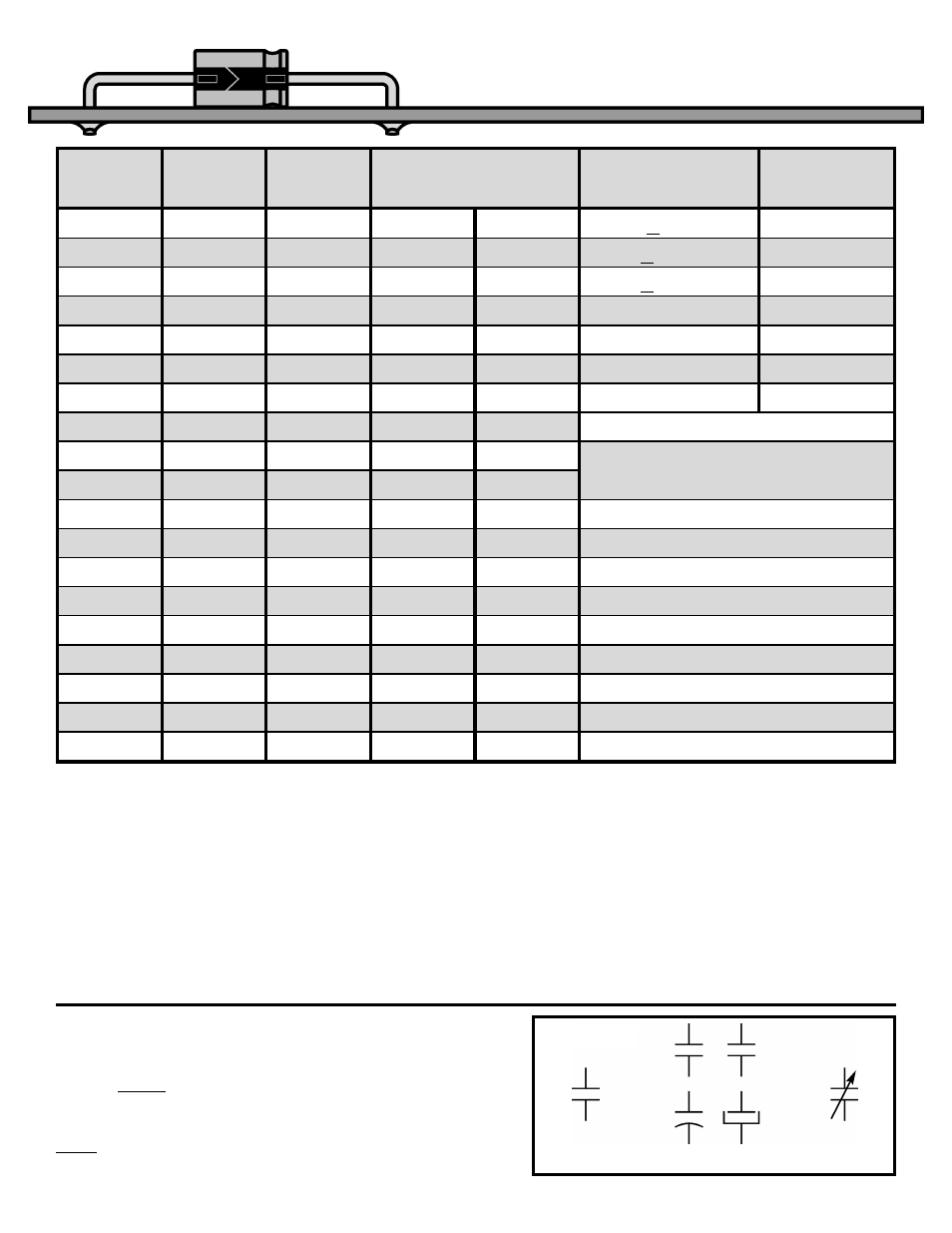
Capacitor markings vary greatly from one
manufacturer to another as the above table shows.
Voltages may be marked directly (200V) or coded
(2D). The value of capacitance may be marked
directly on the part as shown in columns 4 and 5
(note that .001
μF and 1000μF have the same
marking, but the difference in size makes the value
obvious). The number 102 may also be used to
represent 1000 (10+2 zeros). In some instances the
manufacturer may use an R to represent the
decimal point. The tolerance is usually printed
directly on the capacitors. When it is omitted, the
standard tolerance is assumed to be +80% to –20%
for electrolytics. Capacitance change with
temperature is coded in parts per million per degree
C, {N220 = 220/1,000,000 or .022%}, or by a
temperature graph. See manufacturers
specifications for complete details.
CAPACITOR SYMBOLS
Figure 16 shows the schematic symbols used to represent
capacitors. The + symbol indicates that the capacitor is
polarized and the lead marked with the + sign must always
have a
higher voltage than the other lead. The curved
plate, plate with sides, and minus sign also indicate the
capacitor is polarized and these leads must always be at a
lower voltage than the other lead. The arrow crossing
through the capacitor indicates of capacitance is variable.
Figure 16
+
–
Standard
Variable
Polarized
