Experiment #17: very slow light bulb – Elenco Electronic Playground 50-in-1 Experiments User Manual
Page 31
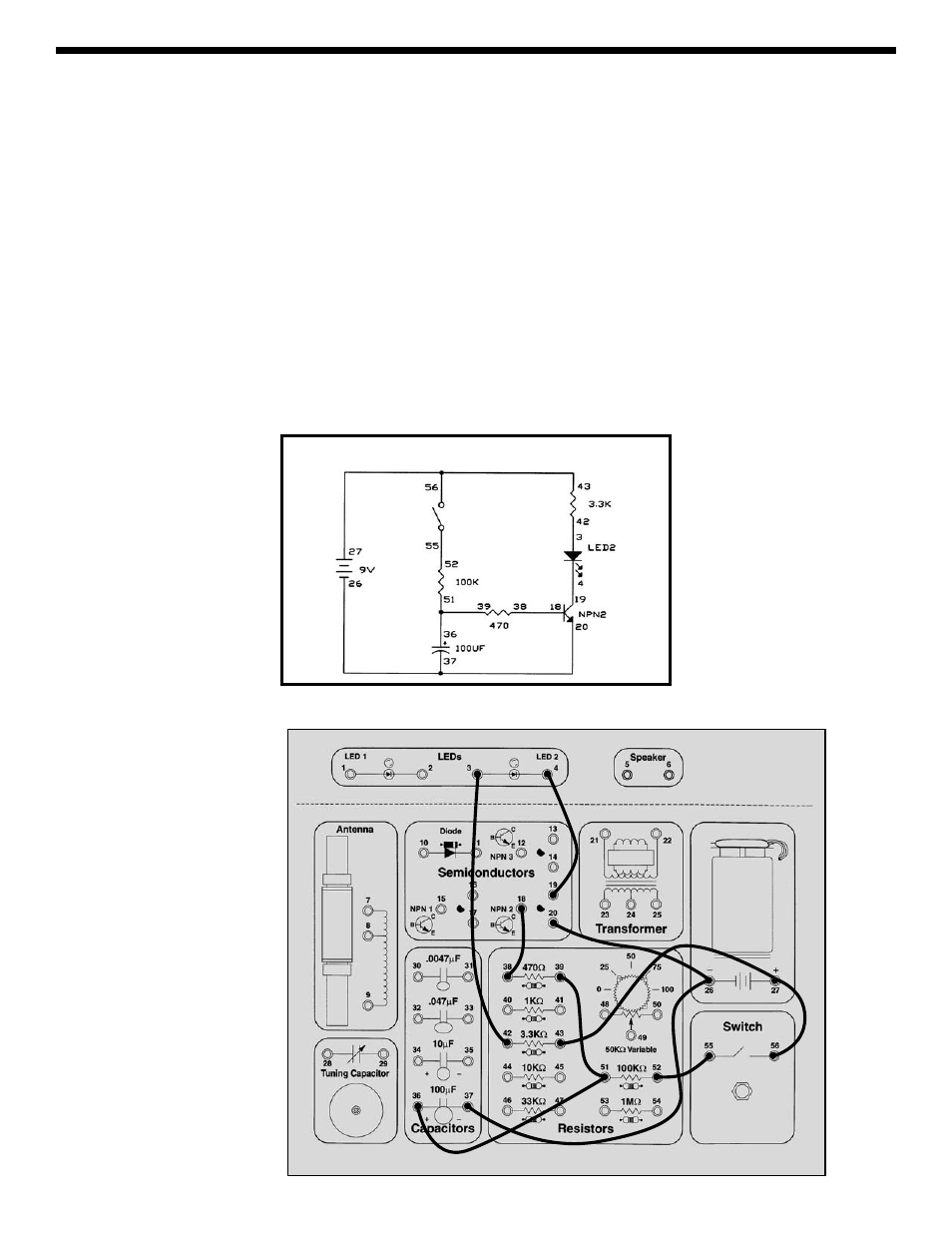
-31-
Connect the wires according to the Wiring Checklist and
press the switch, hold it down for several seconds. The
LED will slowly light up. Release the switch and the LED
will slowly go dark.
When you first press the switch all of the current flowing
through the 100K
Ω resistor goes to charge up the
capacitor, the transistor and LED will be off. When the
capacitor voltage rises to 0.7V the transistor will first turn
on and the LED will turn on. As the capacitor voltage
continues to rise the current flow through the 470
Ω
resistor and into the transistor base will increase. The
current through the LED will then rise rapidly due to the
transistor’s current gain.
When the switch is released the capacitor will discharge
through the 470
Ω resistor and the transistor base, the
LED will dim as this discharge current decreases. When
the capacitor voltage drops below 0.7V the transistor will
turn off. If you get impatient you may touch a wire
between the two capacitor springs to discharge it
instantly.
Do you know how to change the capacitor charge and
discharge times? The 100K
Ω resistor controls the
charge time, the 470
Ω controls the discharge, and the
capacitor controls both the charge and discharge.
Replace these parts with some different values and
observe the effects.
Compare this circuit to the one you used in Experiment 7
when we first introduced the capacitor. By adding a
transistor you can use a large resistor for a slow charge
time and still have a bright LED!
EXPERIMENT #17: Very Slow Light Bulb
Wiring Checklist:
o 43-to-27-to-56
o 55-to-52
o 36-to-51-to-39
o 38-to-18
o 42-to-3
o 4-to-19
o 20-to-26-to-37
Schematic
