Elenco Electronic Playground 50-in-1 Experiments User Manual
Page 18
Similarly, capacitors are described by their capacity for
holding electric charge, called their Capacitance, and
their ability to withstand electric pressure (voltage)
without damage. Although there are many different types
of capacitors made using many different materials, their
basic construction is the same. The wires (leads)
connect to two or more metal plates that are separated
by high resistance materials called dielectrics.
The dielectric is the material that holds the electric
charge (pressure), just like the rubber diaphragm holds
the water pressure. Some dielectrics may be thought of
as stiff rubber, and some as soft rubber. The capacitance
and working voltage of the capacitor is controlled by
varying the number and size of metal-dielectric layers,
the thickness of the dielectric layers, and the type of
dielectric material used.
Capacitance is expressed in farads (F, named after
Michael Faraday whose work in electromagnetic
induction led to the development of today’s electric
motors and generators), or more commonly in
microfarads (
μF, millionths of a farad) or picofarads (pF,
millionths of a microfarad). Almost all capacitors used in
electronics vary from 1pF to 1000
μF.
Your Electronic Playground includes two electrolytic
(10
μF and 100μF) and two disc (.0047μF and .047μF)
capacitors. (Mylar capacitors may have been substituted
for the disc ones, their construction and performance is
similar). Electrolytic capacitors (usually referred to as
lytics) are high capacitance and are used mostly in power
supply or low frequency circuits. Their capacitance and
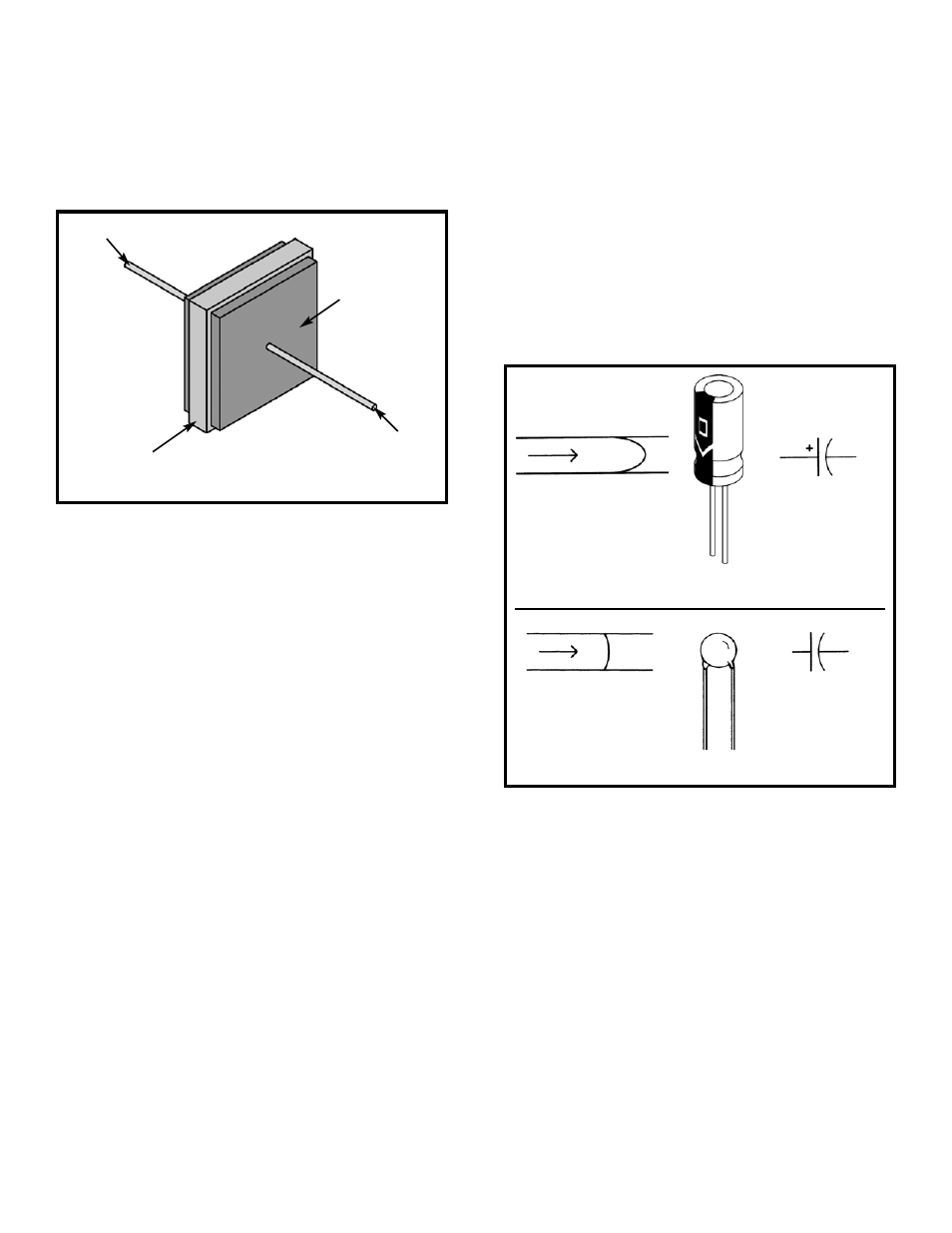
voltage are usually clearly marked on them. Note that
these parts have “+” and “–” polarity (orientation)
markings, the lead marked “+” should always be
connected to a higher voltage than the “–” lead (all of your
Wiring Checklists account for this). Disc capacitors are
low capacitance and are used mostly in radio or high
frequency applications. They don’t have voltage or
polarity markings (they can be hooked up either way).
Capacitors have symbols as follows:
-18-
Construction of a Capacitor
Lead 1
Dielectric
Metal Plate
Lead 2
Soft Diaphragm
Symbol for
Electrolytic
Capacitor
(–) (+)
Electrolytic Capacitor
Disc Capacitor
Stiff Diaphragm
Symbol for
Disc
Capacitor
