Test your knowledge #1, Introduction to diodes – Elenco Electronic Playground 50-in-1 Experiments User Manual
Page 23
1. __________ are the particles that flow between atoms
as part of an electric current.
2. A __________ circuit occurs when wires or
components from different parts of the circuit
accidentally connect.
3. A __________ produces electricity using a chemical
reaction.
4. To decrease the current in a circuit you may decrease
the voltage or __________ the resistance.
5. Materials which have very high resistance are called
__________ and materials which have very low
resistance are called __________.
6. Adding resistors in parallel __________ the
resistance while adding resistors in series _________
the resistance.
7. The electrical resistance of water __________ when
salt is dissolved in it.
8. Capacitors are components that can store
__________ for periods of time.
9. Capacitors have low resistance to __________
current and high resistance to __________ current.
10. Adding capacitors in parallel __________ the
capacitance while adding capacitors in series
__________ the capacitance.
(Answers are on page 5).
TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE #1
-23-
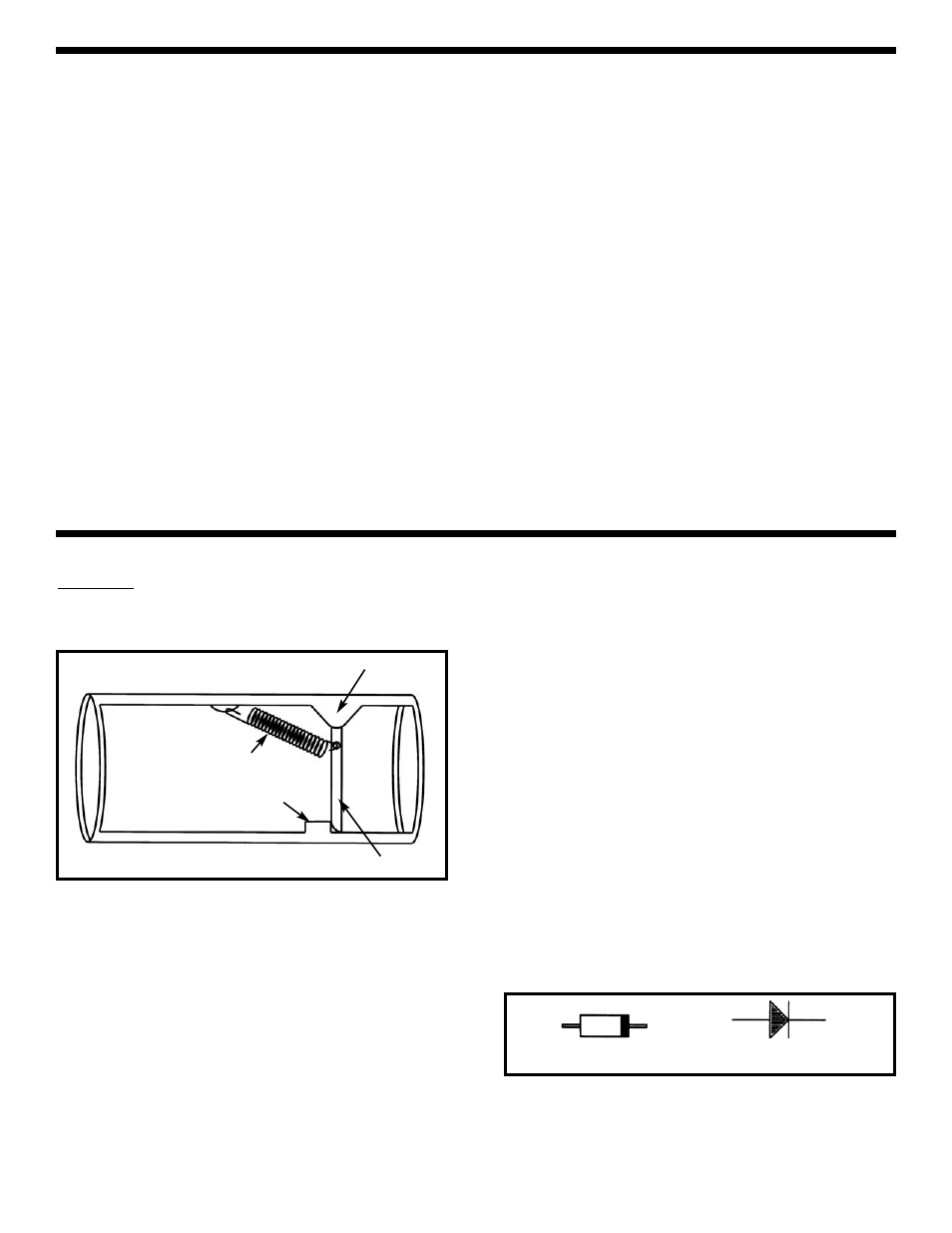
The Diode: The diode is an electronic device that allows
current to flow in only one direction. In our water pipe
analogy it may be thought of as the check valve shown
here:
The check valve only allows water to flow in one direction,
to the right in this drawing. There is a small spring and if
the water pressure exceeds a certain level then the
spring will be stretched and the valve opened. If the
pressure is to flow to the left then the plate will be
pressed against the solid stop and no water will flow.
Electronic diodes are made from materials called
semiconductors, so-called because they have more
resistance than metal conductors but less than
insulators. Most semiconductors are made of Silicon but
Gallium Arsenide and Germanium are also used. Their
key advantage is that by using special manufacturing
processes their resistance is decreased under certain
operating conditions. The manufacturing processes
create two regions of permanent electrical charge, quite
different from charging a capacitor. While the physics of
how this works is quite complicated, the effect is that
once the voltage across the diode exceeds a small turn-
on level (0.7V for Silicon) the resistance of the diode
becomes very low in one direction (so low in fact that the
current flow must be limited by other resistances in the
circuit to prevent damage to the diode). When the diode
is turned on like this we refer to it as being forward-
biased. In the other direction the diode is always a very
high resistance, we call this reverse-biased. The
schematic symbol, shown below, indicates that the diode
will allow current to flow from left to right but block current
flow from right to left.
INTRODUCTION TO DIODES
Spring
Solid Stop
Movable Plate
Water-tight Pivot
Diode
Symbol for Diode
