Key concepts – Cisco 6500 User Manual
Page 3
4-3
Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide, Release 12.2SX
OL-13013-06
Chapter 4 Configuring Virtual Switching Systems
Understanding Virtual Switching Systems
Key Concepts
The VSS incorporates the following key concepts:
•
Virtual Switching System, page 4-3
•
VSS Active and VSS Standby Chassis, page 4-3
•
•
Multichassis EtherChannel, page 4-5
Virtual Switching System
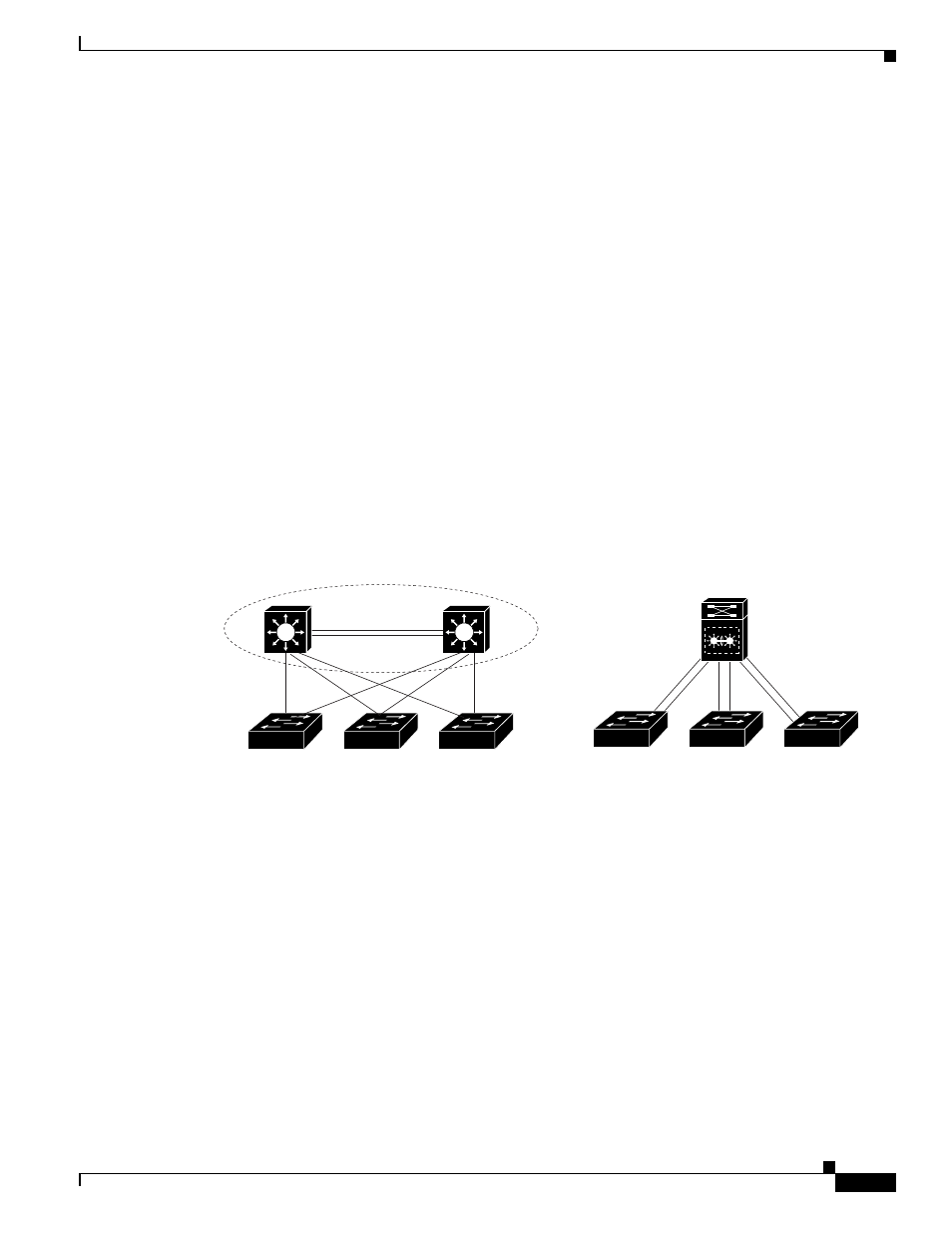
A VSS combines a pair of switches into a single network element. For example, a VSS in the distribution
layer of the network interacts with the access and core networks as if it were a single switch. See
An access switch connects to both chassis of the VSS using one logical port channel. The VSS manages
redundancy and load balancing on the port channel. This capability enables a loop-free Layer 2 network
topology. The VSS also simplifies the Layer 3 network topology because the VSS reduces the number
of routing peers in the network.
Figure 4-2
VSS in the Distribution Network
VSS Active and VSS Standby Chassis
When you create or restart a VSS, the peer chassis negotiate their roles. One chassis becomes the VSS
active chassis, and the other chassis becomes the VSS standby.
The VSS active chassis controls the VSS. It runs the Layer 2 and Layer 3 control protocols for the
switching modules on both chassis. The VSS active chassis also provides management functions for the
VSS, such as module online insertion and removal (OIR) and the console interface.
The VSS active and VSS standby chassis perform packet forwarding for ingress data traffic on their
locally hosted interfaces. However, the VSS standby chassis sends all control traffic to the VSS active
chassis for processing.
181321
Virtual Distribution Switch
Virtual Distribution Switch
Access
Access
Physical view
Logical view
