Alarm circuit – Sharp MZ-3500 User Manual
Page 82
Attention! The text in this document has been recognized automatically. To view the original document, you can use the "Original mode".
M2 3500
c. Power switching circuit
As the signal from the oscillator is amplified through Q7
to Q
6
to change current to the transformer T2, it causes
voltage to appear on the base of Q5 (one of components
is cut by Dl), so that the transistor Q5 begins to per
form
switching
operation
in
synchronization
with
the
oscillation frequency. As Q2 is switched, current is
supplied to the emitter side of the transistor Q5, which
produces smoothed voltage through the capacitor Cl
and the coil L2. The circuit composed of D4 and VR1 is
the reference voltage for the -h5 or -H12V supply, which
is used to control the emitter current flowing to the
transistor Q9. The current supplied from Q9 is used to
create Tr3 inactive by the delayed Cl and C2 voltages
which supplied from Tr1-R2-VR1-D3. It goes high with
deactivation of Tr3.
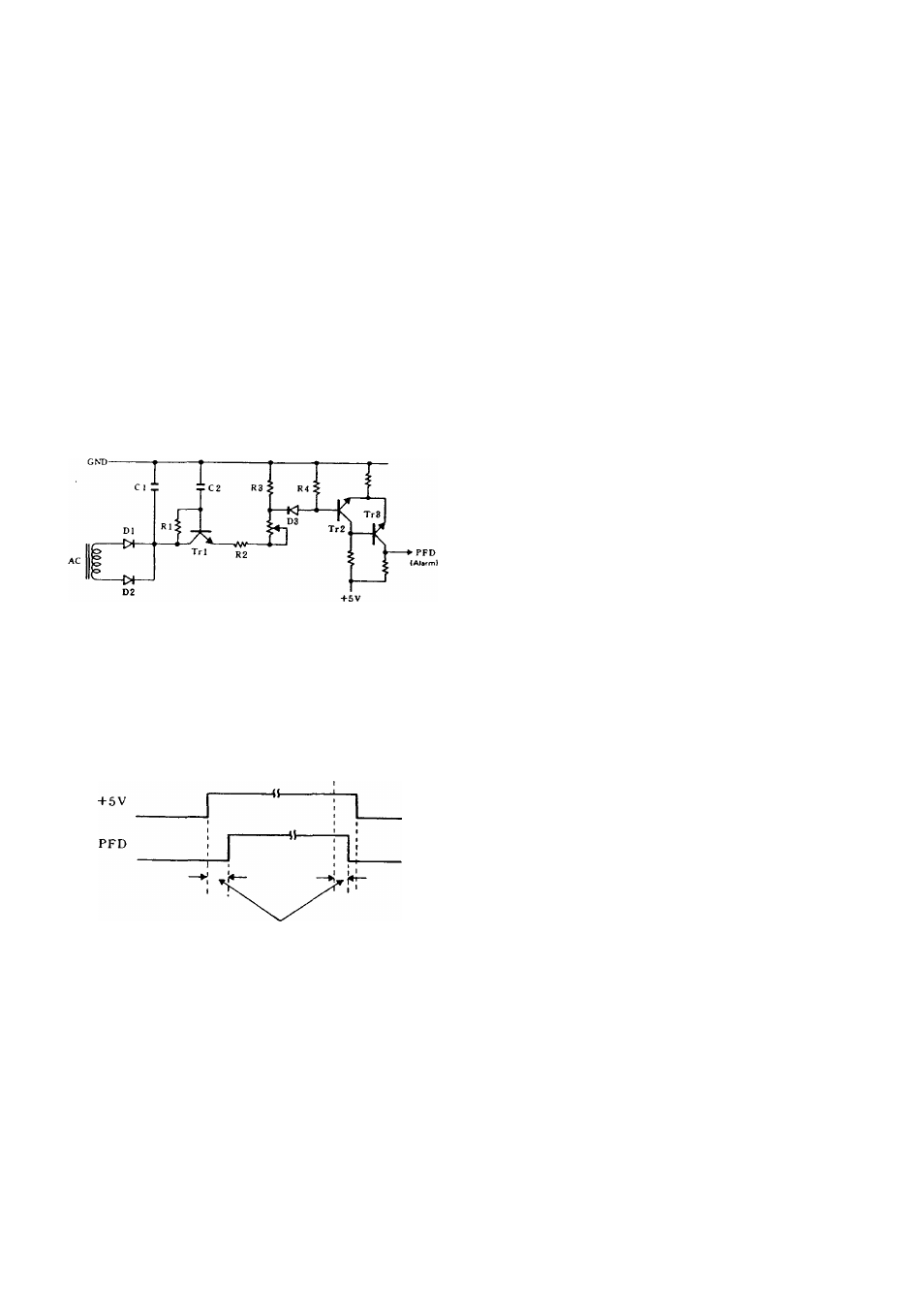
3. Alarm circuit
(Alarm generation circuit)
When power turns off, the voltage accumulated in Cl
and C2 are supplied to the base of Tr2 via Tri ... and
D3, so that Tr2 is kept active and Tr3 inactive for some
times after power off.
Timing chart
SW
ON
- 89 -
