9, power circuit description 1. block diagram, A. +5v and +12v supplies, Functions – Sharp MZ-3500 User Manual
Page 80: Description of each block, M z 3500
Attention! The text in this document has been recognized automatically. To view the original document, you can use the "Original mode".
M Z 3500
9,
POWER CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
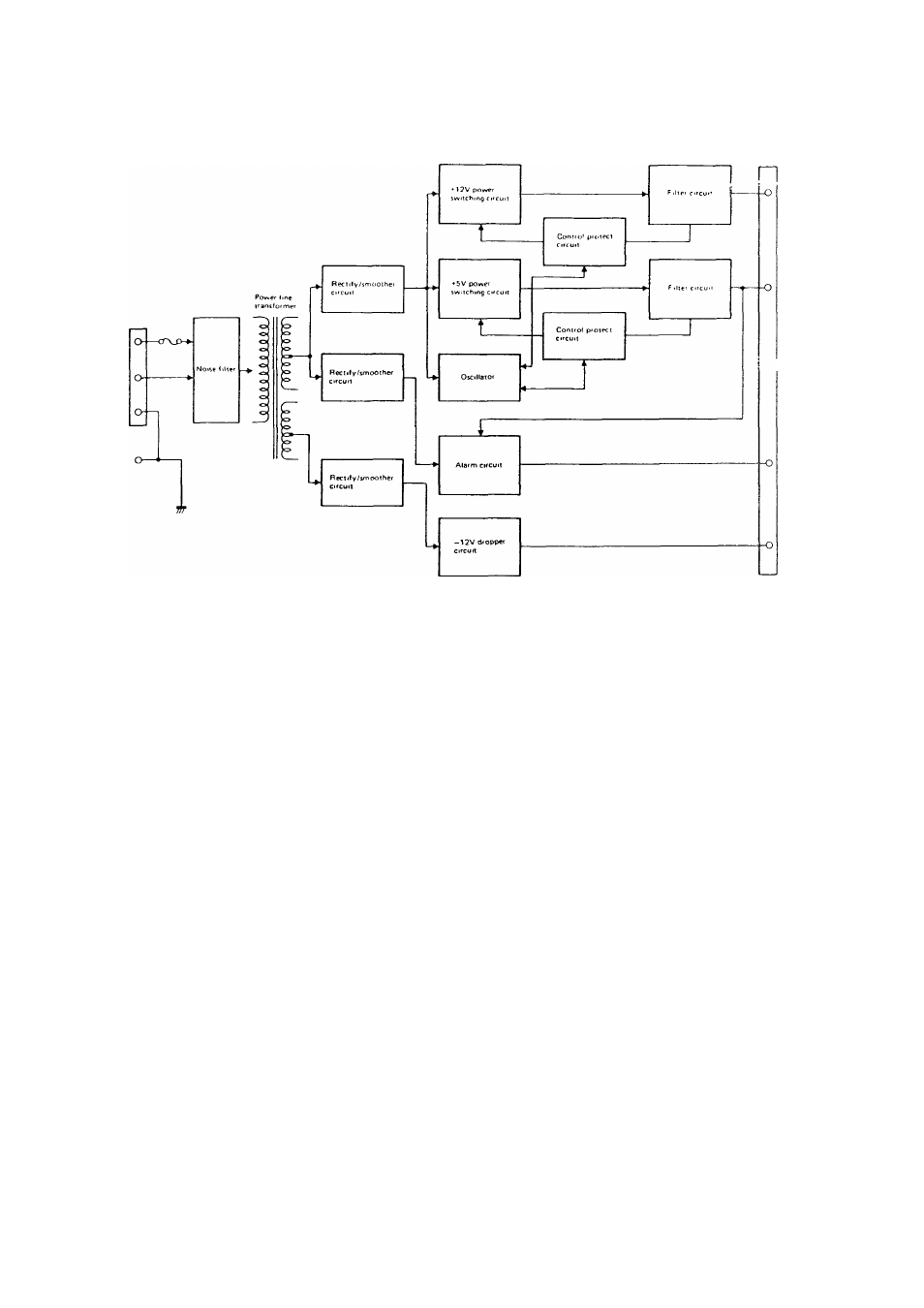
1. BLOCK DIAGRAM
- 1 2 V
O
utput
(Block diagram)
A. +5V and +12V supplies
1. Functions
a.
Supply voltage is first rectified in the rectifier circuit
and sent out to the switching regulator via the over
current
detector
provided
in
the
overcurrent
protect
circuit.
b. Next, the voltage is converted to the +5/-H2V output
in the switching regulator and sent out to the noise
' Nfilter.
c.
Change in the switching regulator output voltage is
sensed by the control circuit and is fed back to the
switching regulator after being amplified in the amplifier
located In the control circuit, for maintaining the output
voltage to a constant level.
d. The signal from the oscillator is supplied to the switch
ing regulator through the control circuit for driving the
switching regulator.
e.
For prevention of overcurrent, the protect circuit is used
for stopping the oscillator when an overcurrent is met,
and it makes the switching regulator to halt in order to
shut off +12V/-r5V supply.
2. Description of each block
a. Overcuirent protect (control/protect) circuit
When an overcurrent is met in the -r5V/-rl2V circuit, it
causes to increase the voltage at both ends of the over
current detector resistor R1, which in turn causes to
increase the Q3 collector current, for, there arises larger
voltage difference between the emitter and base of the
transistor Q3. This makes the gate voltage of the thyris
tor increased owing to activation of SR. Witf. activation
of SR it makes the oscillator voltage dropped to the
GND level at the point "a" to stop oscillation, which
also makes the switching regulator stopped by the de
activation of the transistor Q5 oscillation. This causes
the transistor Q5 inactive, and it shuts off the
-r5V/
+12V
supply,
b. Oscillation circuit
As the Q1 emitter voltage is at almost GND level whe-
the transistor Q1 is active, the Q2 base voltage tem
porarily drops close to the GND level by means of C
6
,
which in turn makes Q2 inactive and the Q2 emittei
voltage increases.
Then, the Q2 base voltage comes to rise as C
6
begins to
be charged through R
6
, and the transistor Q2 starts to
activate again. With activation of the transistor Q2, the
Q2 emitter voltage starts to drop and the Q1 base
voltage is temporarily dropped by means of C5, to shut
off the transistor Ql, which causes to increase the
transistor Ql emitter voltage.
Next, as C5 is charged by R5, it makes the Ql base
voltage
increased
which
puts
the
transistor
Ql
into
activation. In this manner, transistors Ql and Q2 are
alternately turned on and off to keep oscillating.
C5 and C
6
are charged through R5 and R
6
by on/off
action of the Ql and Q2, and discharged through Ql and
Q2.
- 87 -
