C&D Technologies RS-1476 Standby Battery Vented Cell User Manual
Page 18
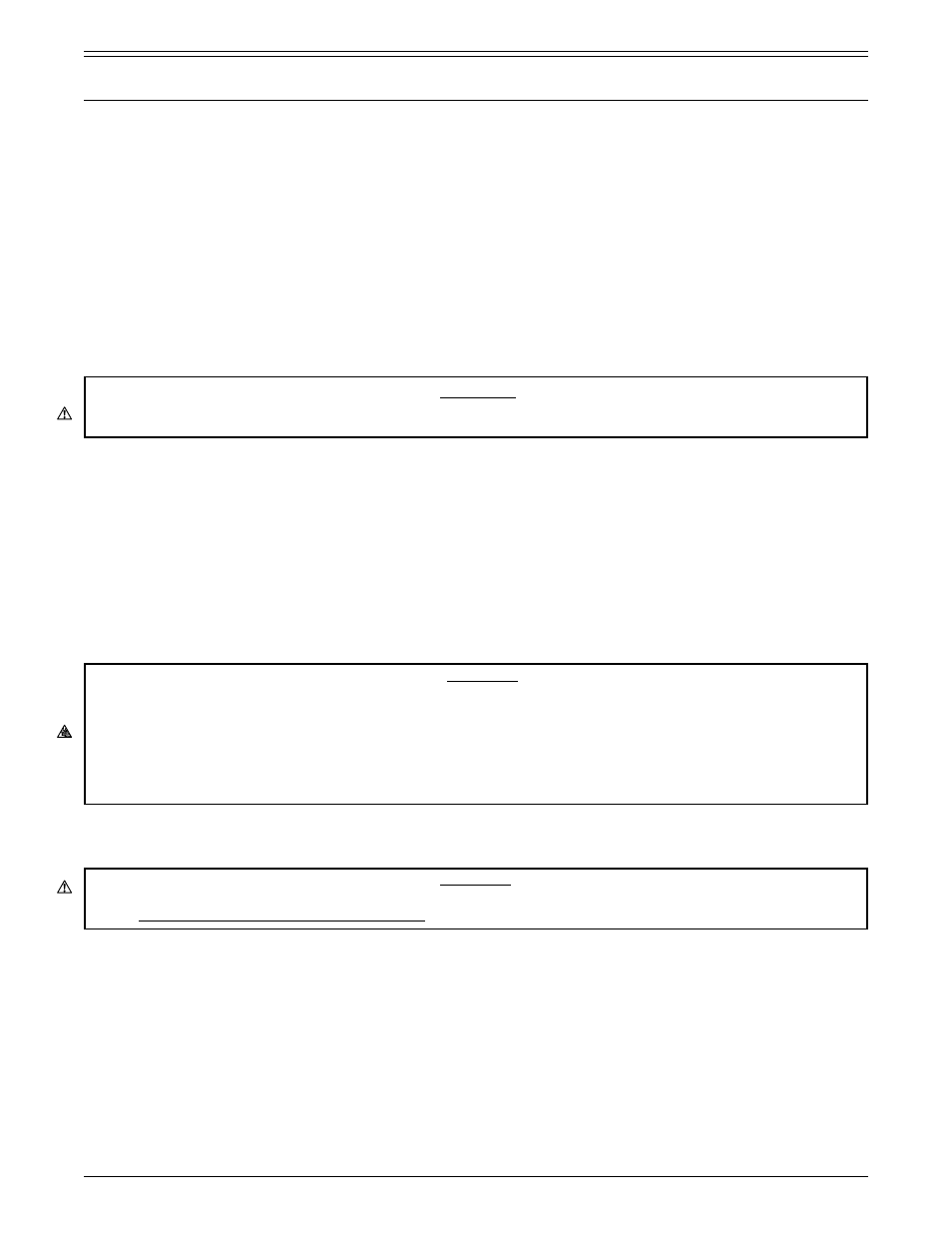
(1) Setpoint: Recommended float voltage setpoint range for the system when read at the battery terminals.
Charger settings can be calculated by multiplying the recommended target voltage times the number of series
cells in the battery system. Charger set points can be made anywhere within the range to commensurate with
the battery operating temperature, however, the best results for battery life and recharge time will be obtained
by setting the charger in the middle of the range.
(2) Individual Cell Voltage: Allowable cell voltage range. Individual cells will vary around the float voltage set
point. Cells will tend to converge around the set point over time. The individual cell voltage range is provided
to identify cells with unusually high or low voltages. These cells should be identified for further action such as
charging at a higher voltage (equalizing).
For information on constant current charging consult Part 4, Section 1.2 of this manual. See Part 4
Section 1.3 for operation at temperatures other than 77°F (25°C).
SECTION 2 - WATERING CELLS AND ADJUSTING ELECTROLYTE LEVEL
CAUTION
Do not adjust electrolyte levels before initial charging. Adjust electrolyte levels only when cells are
fully charged and stabilized at float voltage.
Before adding water to a battery, you must consider its condition and state of charge. For example, a new
battery which has recently experienced vibration during shipment will appear to have a low electrolyte level. Do
not add water to cells unless the plates are uncovered. If the plates are covered by electrolyte, the battery should
be placed on charge. The gases produced by charging will displace the electrolyte and raise it to an acceptable
level between the high and low level lines on the container. Had the level been adjusted to the high mark
before
charging, charging could have caused the electrolyte to rise to a point where it could overflow through the vent or
be forced up into the flame arrestor, requiring needless maintenance.
NOTE: Adding water to a battery to bring the initial electrolyte levels up will reduce the specific gravity, and will
introduce a high level of variation to specific gravity measurements.
If, after charging, the electrolyte levels have not risen to between the high and low level lines, sulfuric acid of the
same specific gravity
may be added to bring levels to the high mark. Adding acid is a procedure that should
be done only after consultation with C&D or performed by a C&D representative.
CAUTION
POTENTIALLY EXPLOSIVE GASES
VLA (flooded) lead acid cells release hydrogen gas during charge, which is potentially explosive. Flame
arrestors reduce the likelihood of ignition within a cell; however, caution must still be exercised not to
bring an open flame or sparks near the battery. Hydrogen can be evolved at the rate of 0.000269 cubic
feet per minute per charging ampere per cell at 77°F (25°C). The maximum level of hydrogen gas in the
battery room should not exceed concentrations specified by local codes, typically 1 to 2 percent by
volume. Do not install batteries in unventilated areas or enclosures.
SECTION 3 - CLEANING CELLS AND BATTERY RACK(S)
CAUTION
CLEANING THERMOPLASTIC CELL CONTAINERS – clean or wash the containers with clean water
only. Do not use solvents or glass cleaners.
Neutralize acid spills with a solution of sodium bicarbonate – one pound of sodium bicarbonate mixed with one
gallon of clean water. Never use ammonia, soda ash, sodium hydroxide, or any strong alkalis. If alkalis are
inadvertently spilled on the containers, they should be immediately washed off with clean water.
SECTION 4 - BATTERY OPERATION
4.1 Float service
In ideal float service, a battery is always maintained in a fully charged condition. However, in the event of a
power failure or system test in which the chargers are shut down, the battery must support the load resulting in
a battery discharge. Typically, a standby battery will not be subjected to more than one test discharge each year
and a transfer test monthly.
PART 2
CHARGING AND OPERATION OF BATTERY (CONTINUED)
RS1476/0215/CD
16
www.cdtechno.com
