2 functional principle, 1 nebulization – BUCHI ELS Detector C-650 User Manual
Page 14
C-650
Operation Manual, Version B
4 Description of function
14
4.2
Functional principle
There are three discrete steps in the operation of the detector; nebulization of the eluent, evapo-
ration of the solvent and detection of the compound(s) of interest.
Nebulization --> Evaporation --> Detection
Nebulization involves the conversion of the eluent into a fine aerosol. This aerosol is directed to
an evaporator to vaporize the solvent, then the mist is irradiated by a light source and the scat-
tered light is measured by a photomultiplier; which is related to the concentration of the com-
pound of interest in the sample.
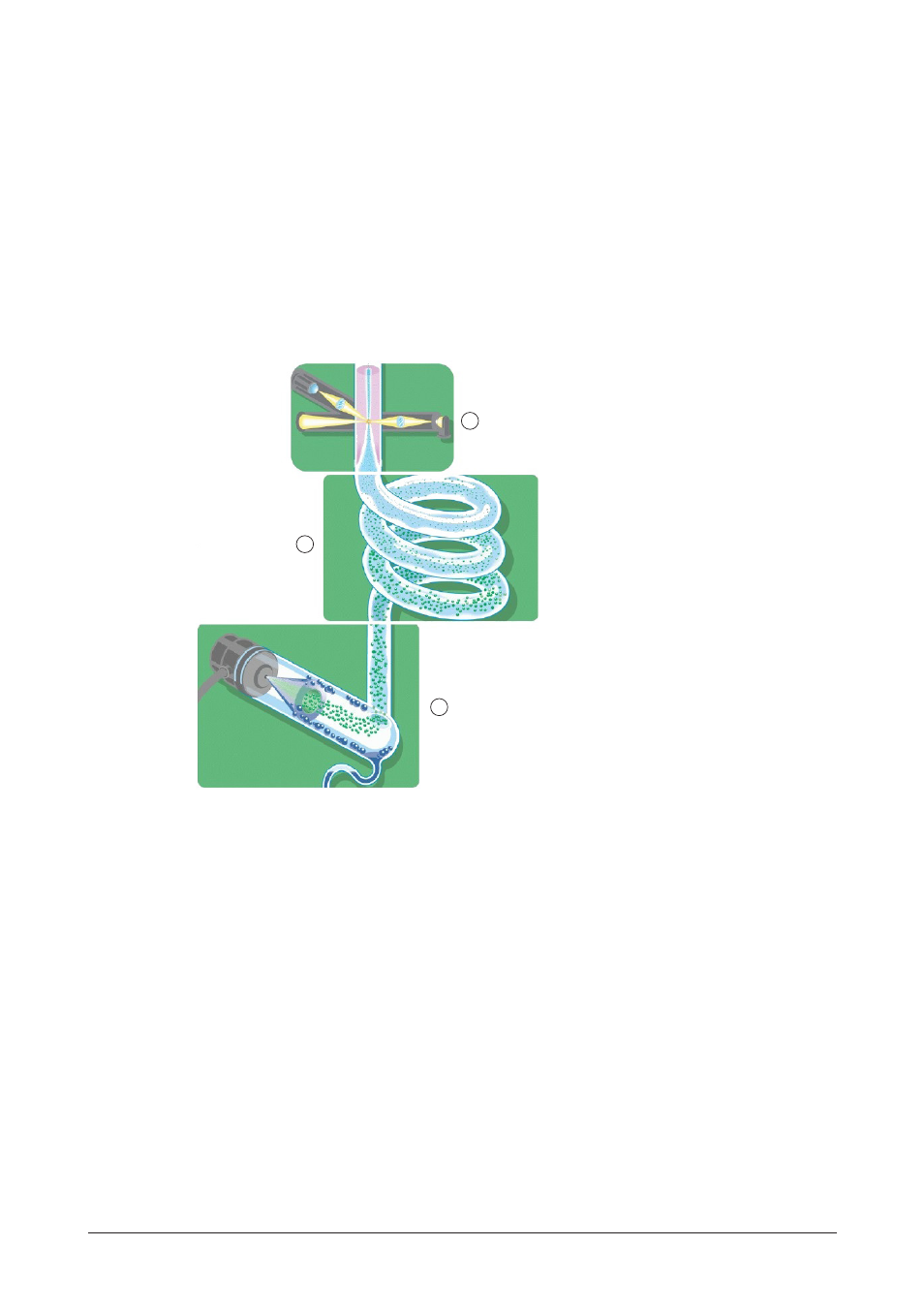
A cross sectional view of the device is presented below.
1
2
3
a Nebulization
b Evaporation
c Detection
Fig 4.2: Cross-sectional view of the detector
4.2.1
Nebulization
The eluent from the chromatograph is nebulized by the inlet gas (typically air or nitrogen). At the
outlet of the nebulizer, the aerosol travels through a chamber. Large droplets in the aerosol are
drawn to a siphon while the fine mist travels to the evaporation tube. The overall design of the
nebulizer is shown in Fig 4.3 and the nebulization chamber is shown in Fig 4.4.
The Flash Chromatography Nebulizer has a flow rate of 0.1 mL/min –5 mL/min and a back pres-
sure of 4 bar (1 mL/min) by the use of water.
