Common hopper scale arrangements, Common hopper scale arrangements -3, System design – Rice Lake Weigh Modules/Mount Assemblies User Manual
Page 5
1-3
SYSTEM DESIGN
Bulk Material Weighing Systems
Common Hopper Scale Arrangements
C. A conveyor-fed system can be improved by adding an upper
surge hopper as shown in Figure 1-7. The surge hopper allows
the conveyor to be run continuously and isolates the weigh
hopper from the sometimes erratic flow of material from the
conveyor.
Advantages of this system are:
•
Weigh hopper isolated from the feed conveyor.
•
The input conveyor can run continuously.
•
Surge hopper serves as a buffer to smooth out demand.
•
2-speed fill is possible.
•
Faster fill and higher throughput possible.
Disadvantages of this system are:
•
Higher overall height.
•
Higher cost.
•
More complex controls and mechanical arrangement.
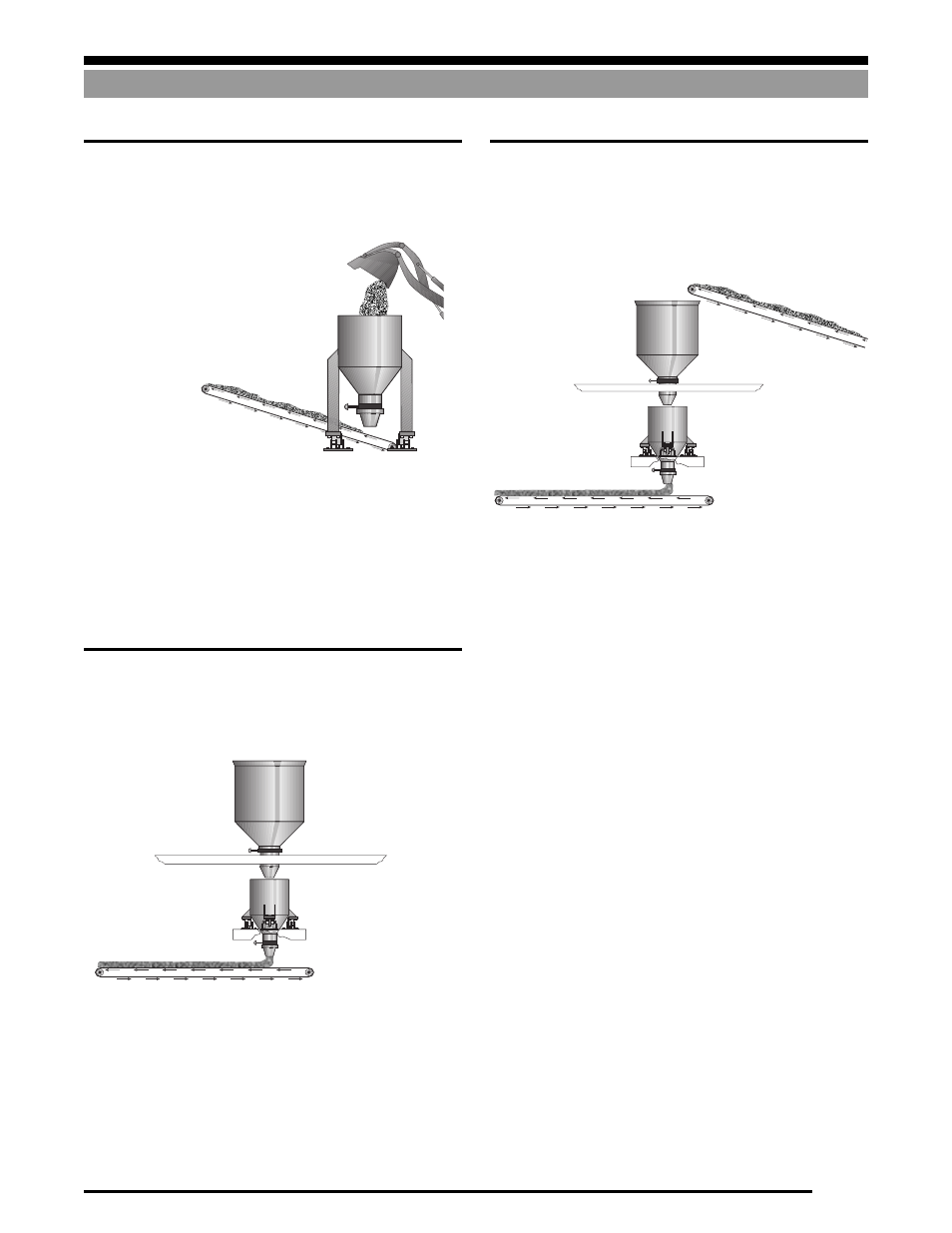
A.
One of the simplest hopper weighing systems is illustrated
below in Figure 1-5. The weigh hopper may be filled using a
feed conveyor, front-end loader, auger, etc., and the material
may be removed from the hopper using a discharge conveyor.
Advantages of this system are:
•
Low cost compared to other systems.
•
Low overall height.
Disadvantages of this system are:
•
Slow fill and discharge (low throughput).
•
Difficult to achieve an accurate prescribed weight because
of inconsistency in input material flow.
B. Figure 1-6 below illustrates a weigh hopper positioned
directly under the storage silo.
Advantages of this system are:
•
The weigh hopper is gravity-fed, simplifying the feed process
and providing a more uniform flow.
•
Faster fill cycle and hence greater throughput.
•
2-speed fill may be used for greater target accuracy.
Disadvantages of this system are:
•
Higher overall height.
•
Material must be conveyed higher to storage silo.
Figure 1-5
Figure 1-6
Figure 1-7
