Compaq Wireless LAN 300 User Manual
Page 71
Operation (Compaq Tru64 UNIX)
PowerStorm 300 AGP and 300/350 PCI Graphics Controllers 7–9
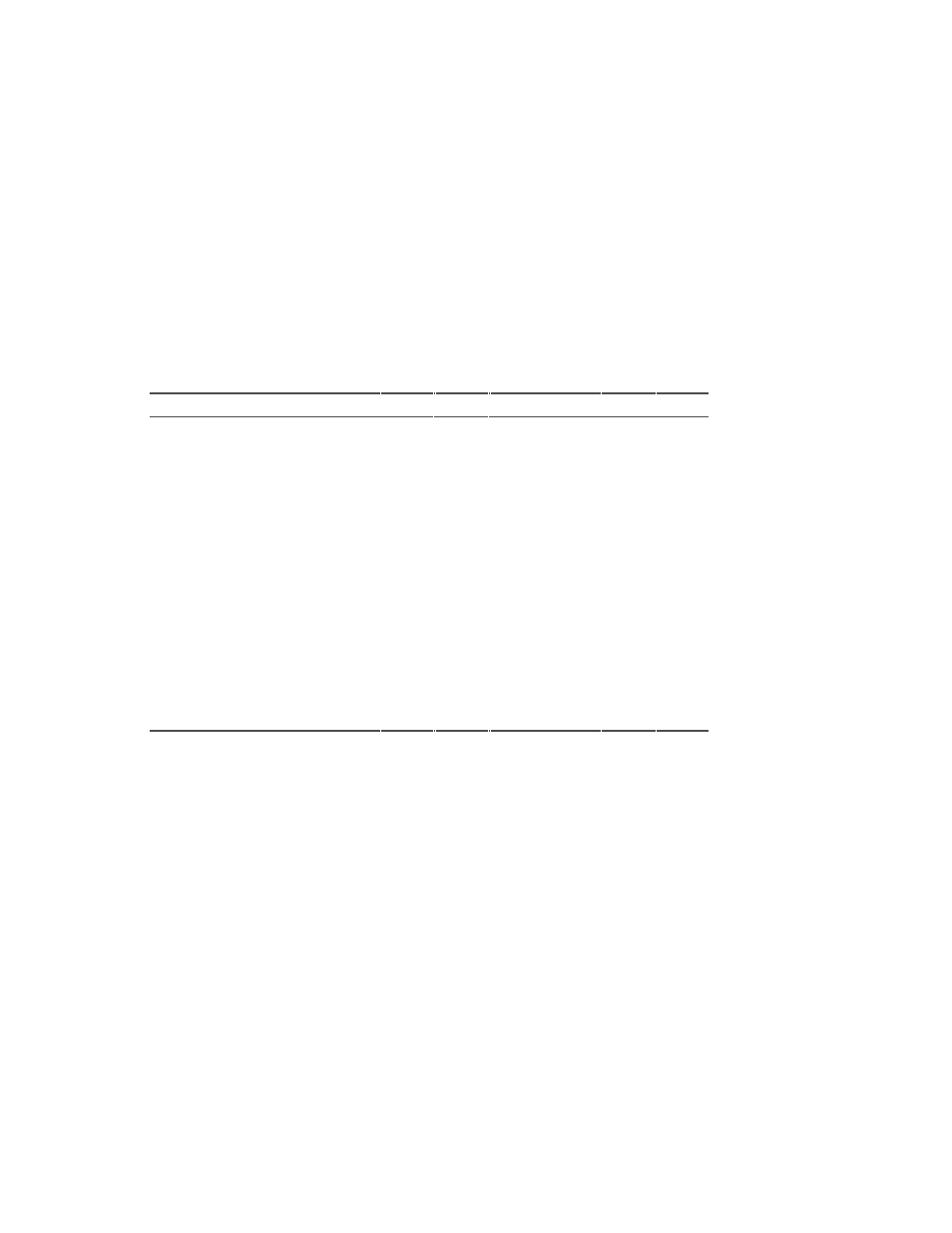
Table 7-2 Supported GLX Visuals on PowerStorm 350 PCI Graphics
Controller (continued)
Visual ID *
0x26
0x27
0x28
0x29
0x2c
0x2d
0x2e
0x2f
Color buffer
format
CI
CI
CI
CI
CI
CI
CI
CI
Color buffer size
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
Overlay planes
X
X
X
X
Double-buffered
X
X
X
X
Quad-buffered
X
X
X
X
Z-buffer size
24
24
24
24
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Stencil planes
1
1
1
1
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Accum buffer size
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
X class
Pseudo
Color
Pseudo
Color
Pseudo
Color
Pseudo
Color
Pseudo
Color
Pseudo
Color
Pseudo
Color
Pseudo
Color
X depth
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
X colormap size
256
256
256
256
256
256
256
256
X RGB masks
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
X significant bits
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
* Visual IDs listed are for the first screen. Equivalent visuals on the second head of a
dual-head configuration will have different visual IDs.
7.3.2.1 Performance and Functionality Considerations
The PowerStorm 300/350 PCI graphics controllers and drivers for the Tru64 UNIX
platform accelerate virtually all OpenGL Version 1.1 operations. However, some aspects
of OpenGL usage can adversely affect performance. Also, the functionality of
PowerStorm 300/350 graphics controllers varies among platforms. This section describes
these performance and functionality considerations.
7.3.2.1.1 Texture Mapping
Several aspects of texture mapping can affect application performance. Some of these are
under the control of the application user. Others are under the control of the application
developer.
•
When an application defines textures to OpenGL it can explicitly specify the
resolution (for example 16 or 32 bits per texel) with which textures are to be stored.
Alternatively, the application can leave this decision to the OpenGL implementation.
In this latter case, the PowerStorm 300/350 OpenGL driver will, by default, use 16
bits per texel for RGB and RGBA textures. The application user can override this
default behavior by following the steps in Section 7.2.3.
